 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Visipaque |
| Other names | 5-[acetyl-[3-[acetyl-[3,5-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropylcarbamoyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-phenyl]amino]-2-hydroxy-propyl]amino]-N,N'-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodo-benzene-1,3-dicarboxamide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Multum Consumer Information |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | Negligible |
| Metabolism | Excreted unchanged |
| Elimination half-life | 2.1 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.124.306 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
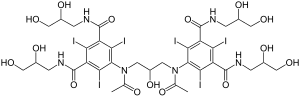
| Formula | C35H44I6N6O15 |
| Molar mass | 1550.191 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Iodixanol, sold under the brand name Visipaque, is an iodine-containing non-ionic radiocontrast agent.[2]
It is available as a generic medication.[3][4]
Medical uses
The radiocontrast agent is given intravenously for computed tomography (CT) imaging of the head, body, excretory urography and venography. The radiocontrast agent is also given intra-arterially for angiography imaging.[5]
Adverse effects
About 30% of those received intravenous iodixanol injection has warmth, pain, or discomfort at the site of the injection. Other adverse effects include: taste perversion (3.5%), nausea (2.8%), and headache (2.5%).[5]
Society and culture
Available forms
The contrast can either be given intra-arterialy or intravenously.[5]
Veterinary uses
Iodixanol is also the active ingredient in a number of 'cushion' products used during the centrifugation of stallion semen. It is layered underneath the extended stallion semen allowing for a higher g force to be used with less sperm damage and better recovery rates. Post centrifugation the supernatant above and the cushion below is removed, leaving a concentrated sperm pellet in the conical tube.[6]
References
- ↑ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ↑ Spencer CM, Goa KL (December 1996). "Iodixanol. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and diagnostic use as an x-ray contrast medium". Drugs. 52 (6): 899–927. doi:10.2165/00003495-199652060-00013. PMID 8957160. S2CID 195690679.
- ↑ "2022 First Generic Drug Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 3 March 2023. Archived from the original on 30 June 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- ↑ "Competitive Generic Therapy Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 29 June 2023. Archived from the original on 29 June 2023. Retrieved 29 June 2023.
- 1 2 3 "Visipaque (iodixanol injection)" (PDF). US Food and Drug Administration. 1 September 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 April 2022.
- ↑ Waite JA, Love CC, Brinsko SP, Teague SR, Salazar JL, Mancill SS, Varner DD (September 2008). "Factors impacting equine sperm recovery rate and quality following cushioned centrifugation". Theriogenology. 70 (4): 704–14. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2008.04.047. PMID 18573520.
External links
- https://web.archive.org/web/20160825063320/http://www.cosmobiousa.com/axis-shield-density-gradient-optiprep.html
- http://www3.gehealthcare.com/en/products/categories/contrast_media/visipaque
- https://web.archive.org/web/20110927141156/http://www.gehealthcare.com/caen/md/docs/visipaquepieng.pdf
- Iodixanol drug label/data at DailyMed from U.S. National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.