| El Vizcaíno Biosphere Reserve | |
|---|---|
IUCN category VI (protected area with sustainable use of natural resources) | |
 A pelican on the coast of the El Vizcaíno Biosphere Reserve | |
 Location in Mexico | |
| Location | Baja California Sur, Mexico |
| Nearest city | Mulegé Municipality |
| Coordinates | 27°47′32″N 114°13′40″W / 27.79222°N 114.22778°W |
| Area | 55,555 km2 (21,450 sq mi) |
| Established | 1988 |
| Official name | Whale Sanctuary of El Vizcaino |
| Type | Natural |
| Criteria | x |
| Designated | 1993 (17th session) |
| Reference no. | 554 |
| Region | Latin America and the Caribbean |
The El Vizcaíno Biosphere Reserve, created in 1988,[1] is located in Mulegé Municipality in northern Baja California Sur, at the center of the Baja California Peninsula between the Pacific Ocean and the Gulf of California. With an area of over 24,930 km2 (9,630 sq mi)),[2] it is the largest wildlife refuge in Mexico and borders the northern edge of the Valle de los Cirios Protected Area of Flora and Fauna.
History
Native groups first inhabited this region over eleven thousand years ago. They may have been nomads who came overland from the north of the American continent, or they may have been marine-oriented groups using boats to follow the coastline. At the dawn of the historic period, their successors were the Cochimi, foragers who exploited the natural resources of the coast, the inland plains, and the Sierra de San Francisco. Travelers trekking into this mountainous region can still see the natives' cave art. Spanish explorers arrived in the area in the 16th century. Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo was the first explorer to navigate the coastlines, whereas Sebastián Vizcaíno explored inland, in what is now the biosphere reserve in 1596 on behalf of Gaspar de Zúñiga, viceroy of New Spain.[3]
Fauna
Animals that have adapted to these extreme conditions include a variety of nocturnals such as coyotes, rodents, and hares; others have adapted to only ingesting water from succulents. Outstanding among the mammals is the Baja California pronghorn (Antilocapra americana peninsularis), an endemic subspecies of the Pronghorn, which is one of the swiftest mammals on Earth. The last populations of this subspecies can be found in the region. The Vizcaíno is also the habitat of the desert bighorn sheep (Ovis canadensis nelsoni), Mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus peninsulae), and dozens of resident and migratory birds. Of special importance: the ospreys, cormorants, herons, and gulls—and four species of sea turtles. On the coastline and islets there are many marine mammals, such as northern elephant seals (Mirounga angustirostris), California sea lions (Zalophus californianus), dolphins, and gray whales (Eschrichtius robustus).
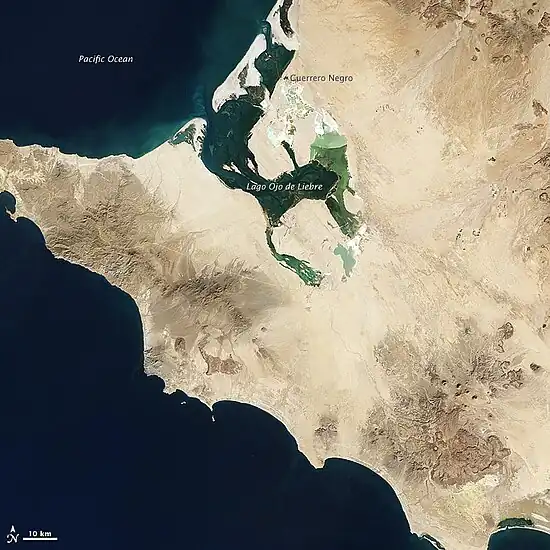
View

References
- ↑ Vizcaino Biosphere Reserve - Park Profile - General information. Retrieved 09-14-2008.
- ↑ ANP 282 - El Vizcaíno Archived March 4, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 01-03-2015.
- ↑ Jiménez González, Victor Manuel (July 2015). Baja California Sur - Los Cabos - Cabo San Lucas - Loreto - La Paz: Guía de viaje del Estado de Baja California Sur.
