Yang County
洋县 | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) Yang County City God Temple | |
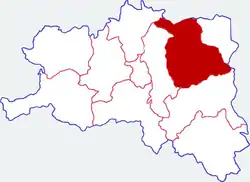 Location in Hanzhong | |
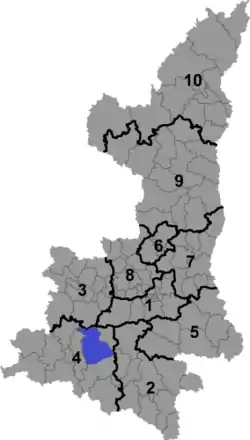 Location in Shaanxi | |
| Coordinates: 33°13′N 107°32′E / 33.217°N 107.533°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Shaanxi |
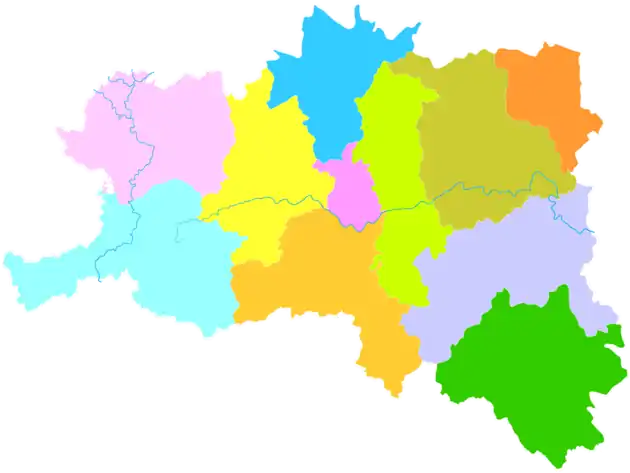
| Prefecture-level city | Hanzhong |
| Area | |
| • Total | 3,206 km2 (1,238 sq mi) |
| Population (2018) | 387,000 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China standard time) |
| Postal Code | 723300 |
| Website | http://www.yangxian.gov.cn/ |
Yang County, or Yangxian (simplified Chinese: 洋县; traditional Chinese: 洋縣; pinyin: Yáng Xiàn), is a county in Hanzhong, Shaanxi Province, China.[1] The county spans an area of 3,206 square kilometres (1,238 sq mi), and has a population of about 445,000.[1] Yang County lies within the Shaanan region, on the easternmost portion of the Hanzhong Basin, bordered by the Daba Mountains to the south, and the Qin Mountains to the north.[1]
History


.jpg.webp)
The area of present-day Yang County has been inhabited for approximately 7,000 years, since the Neolithic period.[2] The area belonged to the Liang dynasty.[2]
Prior to being annexed into the Jin dynasty, the area was organized as Chenggu County (simplified Chinese: 城固县; traditional Chinese: 城固縣).[2] During the Jin dynasty, the area was organized as Xingdao County (simplified Chinese: 兴道县; traditional Chinese: 興道縣) and Huangjin County (simplified Chinese: 黄金县; traditional Chinese: 黃金縣).[2]
Upon the establishment of the Tang dynasty in 758CE, it became the seat of Yang Prefecture (Chinese: 洋州).[2]
In 1370, under the Ming dynasty, the area was re-organized as Yang County (simplified Chinese: 洋县; traditional Chinese: 洋縣).[2]
In 1913, under Republican China, the area was placed under Hangzhong Circuit (simplified Chinese: 汉中道; traditional Chinese: 漢中道).[2] In 1928, Hanzhong Circuit was abolished and the area was governed directly by Shaanxi Province officials.[2]
Beginning in August 1931, groups loyal to the Chinese Communist Party began organizing in the area.[2] On December 4, 1949, these groups coordinated with the People's Liberation Army to take control of the area.[2] On December 14, the Yang County People's Government was established to formally govern the area.[2] Between the county's re-establishment in December 1949 and September 1961, it was re-organized eight times.[2] Since then, Yang County has not been re-organized, and has remained under the jurisdiction of Hanzhong.[2]
A number of major historical figures in Chinese history, including Du Fu, Bai Juyi, Su Shi, and Wen Tong, have visited present-day Yang County.[1]
Administrative divisions
Yang County is divided into 3 subdistricts and 15 towns.[1][3][4] These township-level divisions are then further divided into 16 residential communities and 271 administrative villages.[1]
The county's 3 subdistricts are:
- Yangzhou Subdistrict (Chinese: 洋州街道; pinyin: Yángzhōu Jiēdào)
- Zhifang Subdistrict (simplified Chinese: 纸坊街道; traditional Chinese: 紙坊街道; pinyin: Zhǐfāng Jiēdào)
- Qishi Subdistrict (Chinese: 戚氏街道; pinyin: Qīshì Jiēdào)
The county's 15 towns are:
- Longting (simplified Chinese: 龙亭镇; traditional Chinese: 龍亭鎮; pinyin: Lóngtíng Zhèn)
- Xiecun (simplified Chinese: 谢村镇; traditional Chinese: 謝村鎮; pinyin: Xiècūn Zhèn)
- Machang (simplified Chinese: 马畅镇; traditional Chinese: 馬暢鎮; pinyin: Mǎchàng Zhèn)
- Yishui (simplified Chinese: 溢水镇; traditional Chinese: 溢水鎮; pinyin: Yìshuǐ Zhèn)
- Moziqiao (simplified Chinese: 磨子桥镇; traditional Chinese: 磨子橋鎮; pinyin: Móziqiáo Zhèn)
- Huangjiaying (simplified Chinese: 黄家营镇; traditional Chinese: 黃家營鎮; pinyin: Huángjiāyíng Zhèn)
- Huang'an (simplified Chinese: 黄安镇; traditional Chinese: 黃安鎮; pinyin: Huáng'ān Zhèn)
- Huangjinxia (simplified Chinese: 黄金峡镇; traditional Chinese: 黃金峽鎮; pinyin: Huángjīnxiá Zhèn)
- Huaishuguan (simplified Chinese: 槐树关镇; traditional Chinese: 槐樹關鎮; pinyin: Huáishùguān Zhèn)
- Jinshui (simplified Chinese: 金水镇; traditional Chinese: 金水鎮; pinyin: Jīnshuǐ Zhèn)
- Huayang (simplified Chinese: 华阳镇; traditional Chinese: 華陽鎮; pinyin: Huáyáng Zhèn)
- Maoping (simplified Chinese: 茅坪镇; traditional Chinese: 茅坪鎮; pinyin: Máopíng Zhèn)
- Baliguan (simplified Chinese: 八里关镇; traditional Chinese: 八里關鎮; pinyin: Bālǐguān Zhèn)
- Sangxi (simplified Chinese: 桑溪镇; traditional Chinese: 桑溪鎮; pinyin: Sāngxī Zhèn)
- Guandi (simplified Chinese: 关帝镇; traditional Chinese: 關帝鎮; pinyin: Guāndì Zhèn)
Geography




Yang County is located in southwestern Shaanxi Province,[1] near Chenggu County and Xixiang County, and is part of the Shannan region.[1] It sits in the eastern Hanzhong Basin, on the Han River.[1] The Daba Mountains are to the south of the county; to the north are the Qin Mountains.[1][5] The administrative area (prefecture) ranges in latitude from 33°02′ to 33°43′N and in longitude from 107°11′ to 108°33′E, and is 3,206 square kilometres (1,238 sq mi).[6] The northern part of the county generally has a higher elevation, while the southern part is generally lower in elevation.[5] Yang County's lowest point, in the town of Huangjinxia lies at 389.7 metres (1,279 ft) above sea level.[5] The county's highest point is a mountain called Hurenpingliang (Chinese: 昏人坪梁), in the Qin Mountains, which reaches 3,071 metres (10,075 ft) above sea level in elevation.[5]
Climate
Yang County has a humid subtropical climate, with an average annual temperature of 14.5 °C (58.1 °F).[7] The highest recorded temperature in the county is 38.7 °C (101.7 °F), and the lowest temperature recorded in the county is −10.1 °C (13.8 °F).[7] Yang County experiences an average annual precipitation of 839.7 millimetres (33.06 in), with the highest recorded annual precipitation being 1,376.1 millimetres (54.18 in), and the lowest recorded annual precipitation being 533.2 millimetres (20.99 in).[7] The average wind speed in the county is 1.2 metres per second (2.7 mph), with the highest recorded sustained wind speed being 18 metres per second (40 mph), and the highest recorded wind measurement being 25 metres per second (56 mph).[7] The county experiences an average of 1752.2 hours of sunshine, and 239 frost-free days annually.[7]
| Climate data for Yangxian (1991–2020 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 8.3 (46.9) |
11.5 (52.7) |
17.0 (62.6) |
22.9 (73.2) |
26.6 (79.9) |
29.7 (85.5) |
31.7 (89.1) |
31.4 (88.5) |
25.8 (78.4) |
20.0 (68.0) |
13.9 (57.0) |
8.8 (47.8) |
20.6 (69.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.6 (36.7) |
5.6 (42.1) |
10.3 (50.5) |
15.9 (60.6) |
20.2 (68.4) |
23.9 (75.0) |
26.2 (79.2) |
25.7 (78.3) |
20.8 (69.4) |
15.1 (59.2) |
8.9 (48.0) |
3.6 (38.5) |
14.9 (58.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −1.1 (30.0) |
1.5 (34.7) |
5.4 (41.7) |
10.6 (51.1) |
15.1 (59.2) |
19.4 (66.9) |
22.1 (71.8) |
21.6 (70.9) |
17.4 (63.3) |
12.0 (53.6) |
5.7 (42.3) |
0.2 (32.4) |
10.8 (51.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 4.4 (0.17) |
9.2 (0.36) |
22.5 (0.89) |
54.4 (2.14) |
83.8 (3.30) |
93.6 (3.69) |
138.9 (5.47) |
105.9 (4.17) |
127.7 (5.03) |
75.0 (2.95) |
33.0 (1.30) |
6.0 (0.24) |
754.4 (29.71) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 3.6 | 4.3 | 7.8 | 9.8 | 12.0 | 11.7 | 12.8 | 10.6 | 13.4 | 13.5 | 8.7 | 5.0 | 113.2 |
| Average snowy days | 2.9 | 1.8 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | 1.2 | 6.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 76 | 73 | 71 | 74 | 75 | 77 | 80 | 78 | 83 | 86 | 86 | 82 | 78 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 100.4 | 93.2 | 136.5 | 164.9 | 175.6 | 178.3 | 202.8 | 196.8 | 120.1 | 104.0 | 86.1 | 89.0 | 1,647.7 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 32 | 30 | 37 | 42 | 41 | 42 | 47 | 48 | 33 | 30 | 28 | 29 | 37 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[8][9] | |||||||||||||
Economy

Yang County has a sizable agricultural sector, which grows 469 different types of ingredients for traditional Chinese medicine, such as Magnolia officinalis, jujube, and Scutellaria baicalensis.[1] Other distinct agricultural products to the county include its distinct black rice, and its distinct red rice.[1]
The county also has a number of mineral deposits.[1]
Yang County has a number of tourist sites, including the AAAA-rated Huayang Scenic Area (Chinese: 华阳景区), and the AAA-rated Tomb of Cai Lun.[1]
Transport

Yang County is served by Hanzhong Airport and the Yangpingguan–Ankang Railway. Its major roads are the G5 Beijing–Kunming Expressway, part of the National Expressway System; China National Highway 108; and Provincial Road 230.
The Xi'an–Chengdu High-Speed Railway, currently under construction, is scheduled to begin operations in December 2017.[10][11]
Education
Notes and references
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 概况 [Overview] (in Chinese). Yang County People's Government. 2020-06-23. Archived from the original on 2021-01-04. Retrieved 2021-01-04.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 历史沿革 [Historical Development] (in Chinese). Yang County People's Government. 2020-10-19.
- ↑ 2020年统计用区划代码(洋县) (in Chinese). National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2020. Archived from the original on 2021-01-04. Retrieved 2020-01-04.
- ↑ (in Chinese) Profile of Yang County , Accessed 2016-04-15.
- 1 2 3 4 地形特征 [Topographic Features] (in Chinese). Yang County People's Government. 2020-10-08. Archived from the original on 2021-01-04. Retrieved 2021-01-04.
- ↑ (in Chinese) Profile of Yang County , Accessed 2016-04-15. Archived 2016-04-24 at the Wayback Machine
- 1 2 3 4 5 洋县气候 [Yang County Climate] (in Chinese). Yang County People's Government. 2020-10-08. Archived from the original on 2021-01-04. Retrieved 2021-01-04.
- ↑ 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 24 September 2023.
- ↑ 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 24 September 2023.
- ↑ "China plans high speed rail link for Chengdu-Xi'an" A.P. 2010-11-02
- ↑ 中国首条穿越秦岭高铁年底开工 绕避生态敏感区 [First high-speed rail line to cross the Qin Ling to begin construction late this year, and is expected to avoid environmentally sensitive areas] (in Simplified Chinese). China News. 2010-11-03.
Relative location
| Map (Location of Yang County Prefecture within Hanzhong.) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|