| YingJi-7 (C-701) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | anti-ship missile |
| Place of origin | People's Republic of China |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | CASIC Third Academy |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 117 kg.[1] |
| Warhead | 30.5 kg semi armour-piercing high explosive[1] |
| Engine | Rocket engine[2] |
Operational range | 25 km[3] |
| Maximum speed | Subsonic |
Guidance system | Active radar or electro-optical |
Launch platform | Ground, ship, air |
The YJ-7 (Chinese: 鹰击-7; pinyin: yingji-7; lit. 'Eagle Strike 7') is a Chinese subsonic anti-ship missile. It is manufactured by the Third Academy of the China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation (CASIC).[3] The export version of the YJ-7 is the C-701.[1]
History
The radar-guided C-701 was displayed by the China Precision Machinery Import-Export Corporation (CPMIEC) at the 2004 China International Aviation & Aerospace Exhibition.[4]
In April 2006, it was reported that radar-guided C-701s were fired during Iranian military exercises.[4]
Variants
Operators
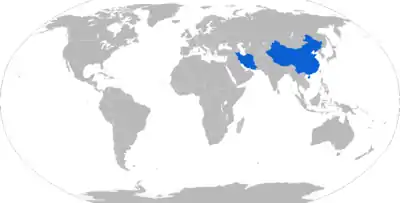
Map with C-701 operators in blue
Current operators
- Armed Forces of the Islamic Republic of Iran: C-701, Kowsar (patrol boats,[6] shore batteries.[7])
- People's Liberation Army Navy: YJ-7 (Harbin Z-8 and Z-9C helicopters)[8]
See also
References
- Bibliography
- "China Missile Chronology" (PDF). Nuclear Threat Initiative. 8 June 2012. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- Cordesman, Anthony H.; Lin, Aaron (February 2015). The Iranian Sea-Air-Missile Threat to Gulf Shipping (PDF). Center for Strategic and International Studies. ISBN 978-1-4422-4077-3.
- Gormley, Dennis M.; Erickson, Andrew S.; Yuan, Jingdong (2014). A Low-Visibility Force Multiplier: Assessing China's Cruise Missile Ambitions (PDF) (Report). Washington, D.C.: National Defense University Press.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.