
A zenith telescope is a type of telescope that is designed to point straight up at or near the zenith. They are used for precision measurement of star positions, to simplify telescope construction, or both.
A classic zenith telescope, also known as a zenith sector employs a strong altazimuth mount, fitted with levelling screws. Extremely sensitive levels are attached and the telescope has an eyepiece fitted with a micrometer.[1] They are used for the measurement of small differences of zenith distance, and used in the determination of astronomic latitude.
Other types of zenith telescopes include the Monument to the Great Fire of London, which includes a central shaft meant for use as a zenith telescope. High-precision (and fixed building) zenith telescopes were also used until the early 1980s to track Earth's north pole position e.g. Earth's rotation axis position (polar motion). Since then radio astronomical quasar measurements (VLBI) have also measured Earth's rotation axis several orders of magnitude more accurately than optical tracking.
The NASA Orbital Debris Observatory with an aperture of 3 m and the Large Zenith Telescope with an aperture of 6 m are constructed as zenith telescopes, as the use of liquid mirrors limits them to pointing straight up.[2]
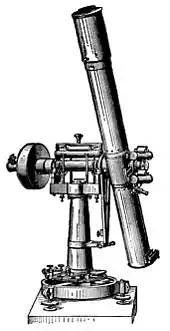 Zenith Telescope |
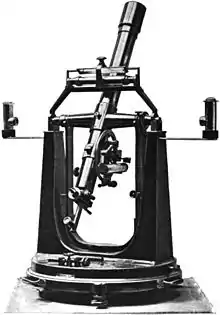 Astronomical transit and zenith telescope, 1898 |
See also
References
- ↑ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 11 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 607–615.
- ↑ Cabanac, Rémi A.; Borra, Ermanno F.; Beauchemin, Mario (1998). "A Search for Peculiar Objects with the NASA Orbital Debris Observatory 3 Meter Liquid Mirror Telescope". The Astrophysical Journal. 509 (1): 309. arXiv:astro-ph/9804267. Bibcode:1998ApJ...509..309C. doi:10.1086/306488. S2CID 119434586.
