The Golden Woman, Golden Hag, Golden Lady (Russian: Золотая баба, zolotaya baba, archaic name: Злата баба, zlata baba, Latin: aurea anus)[1] is a legendary idol, an alleged item of worship of the indigenous peoples of Northeastern Europe/Northwestern Siberia. Early references about it are contradictory, both in its geographical location and in description.
Maciej Miechowita in his Tractatus de duabus Sarmatis Europiana et Asiana et de contentis in eis (1517) described it as follows:
Accipiat quinto, quod post terram Viatka nuncupatam in Scythiam penetrando iacet magnum idolum Zlota baba, quod interpretatum sonat aurea anus seu vetula, quod gentes vicinae colunt et venerantur, nec aliquis in proximo gradiens aut feras agitando et in venatione sectando vacuus et sine oblatione pertransit, quinimo si munus nobile deest, pellem aut saltem de veste extractum pilum in offertorium idolo proicit et inclinando se cum reverentia pertransit.
Giles Fletcher in his Of the Russe Common Wealth (1591) writes that some maps and descriptions of countries, e.g., one by Herberstein, mention a "Slata Baba, or the golden hagge", an idol in the shape of an old woman who serves as an oracle for indigenous priests. However Fletcher sees this as a myth. He further writes that in Obdoria, near the mouth of Ob River there is a rock of shape resembling a ragged woman bearing a child in her hands, and Obdorian Samoyeds use it in their pagan sorcery.[2]
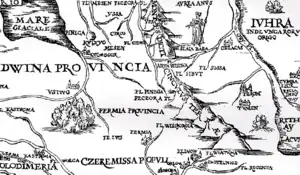
The Golden Woman appears as Zolotaia baba on the 1569 map of the world by Gerardus Mercator.
See also
References
- ↑ Roman Krzywy, "Złota Baba – pogańskie sanktuarium na krańcach państwa carów" (The Golden Woman – a Pagan Sanctuary at the Confines of the Tsarist State) Religie i kościoły, Museum of King Jan III's Palace at Wilanów. Retrieved 12 January 2014.
- ↑ Russia at the Close of the Sixteenth Century, Comprising the Treatise "Of the Russe Common Wealth" (Google eBook) p.99
Further reading
- Алексеев М. П. Сибирь в известиях западно-европейских путешественников и писателей. XIII—XVIII вв. — 2-е изд. — Иркутск, 1941.
- Соколова З. П. Ардви Сура Анахита иранцев и «Злата Баба» финно-угров // Советская археология. — 1990. — № 3.
- Золотая баба // Северная энциклопедия. — М.: Европейские издания, 2004. — С. 303—304.
- Мароши В. В. Использование мифопоэтического ресурса в современной региональной прозе: охота за Сорни-Най // Литература Урала: история и современность: Сборник статей. — Вып. 3. — Т. 2. — Екатеринбург: Издательский дом «Союз писателей», 2007. — С. 266—278.
- Бурыкин А. А. Золотая баба — идол или топоним? // Культура как система в историческом контексте: опыт Западно-Сибирских археолого-этнографических совещаний… — Материалы Международной Западно-Сибирской археолого-этнографической конференции. Томск, 19–21 мая 2010 г. — Томск: Аграф-Пресс, 2010. — 506 с. — С. 54–56.