兼性厭氧菌
兼性厌氧菌是一類既可以進行有氧呼吸,也能夠進行無氧呼吸或發酵的微生物。在氧氣充足時,它們會通過有氧呼吸來產生ATP(三磷酸腺苷),但當氧氣缺乏時,它們的呼吸方式就會變為無氧呼吸[1] 。與其不同,專性需氧微生物在無氧環境下無法產生ATP;專性厭氧微生物則因為無過氧化氫酶等物質而會在有氧環境下死亡[2]。
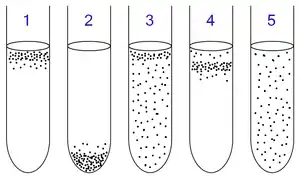
圖為5支培養有不同種類微生物的試管。試管內的培養基為巰基乙酸肉湯。
1中培養的是專性需氧微生物。因為它們不能進行發酵及無氧呼吸,所以它們浮在了氧含量最高的上層。
2中培養的是專性厭氧微生物。因為它們體內因無過氧化氫酶等物質無法在有氧條件下存活,故浮在氧含量最低的下層。
3中培養的是兼性厭氧菌。它們既可以在有氧條件下也能夠在無氧條件下生存,所以它們分佈在試管培養基上的各處。但因為有氧呼吸較無氧呼吸能產生更多的ATP(三磷酸腺苷),故更多的菌體分佈在上層。
4中培養的是微需氧微生物。它們不能進行發酵及無氧呼吸,也不能在高氧濃度環境中存活,故它們浮在試管中上層。
5中培養的是耐氧厭氧生物。這種細菌不能進行有氧呼吸,但卻可以在高氧濃度環境下存活,所以它們均勻地分佈在試管培養基上各處。
1中培養的是專性需氧微生物。因為它們不能進行發酵及無氧呼吸,所以它們浮在了氧含量最高的上層。
2中培養的是專性厭氧微生物。因為它們體內因無過氧化氫酶等物質無法在有氧條件下存活,故浮在氧含量最低的下層。
3中培養的是兼性厭氧菌。它們既可以在有氧條件下也能夠在無氧條件下生存,所以它們分佈在試管培養基上的各處。但因為有氧呼吸較無氧呼吸能產生更多的ATP(三磷酸腺苷),故更多的菌體分佈在上層。
4中培養的是微需氧微生物。它們不能進行發酵及無氧呼吸,也不能在高氧濃度環境中存活,故它們浮在試管中上層。
5中培養的是耐氧厭氧生物。這種細菌不能進行有氧呼吸,但卻可以在高氧濃度環境下存活,所以它們均勻地分佈在試管培養基上各處。
常見的兼性厭氧菌包括葡萄球菌屬、鏈球菌屬[3]、大腸桿菌、 李斯特菌[4]奧奈達湖希瓦氏菌、弧菌屬等。一些真核生物,比如像酵母菌這樣的真菌[5]亦屬兼性厭氧菌之列。此外,沙蠶等部分水生無脊椎動物的呼吸方式亦與兼性厭氧菌相同[6]。
參考
- Hogg, S. 1st. Wiley. 2005: 99-100. ISBN 0-471-49754-1.
- Prescott LM, Harley JP, Klein DA. 3rd. Wm. C. Brown Publishers. 1996: 130-131. ISBN 0-697-29390-4.
- Ryan KJ; Ray CG (editors). 4th. McGraw Hill. 2004: 261-271, 273-296. ISBN 0-8385-8529-9.
- Singleton P. 5th. Wiley. 1999: 444–454. ISBN 0-471-98880-4.
- Carlile MJ, Watkinson SC, Gooday GW. 2nd. Academic Press. 2001: 85-105. ISBN 0-12-738446-4.
- Schöttler, U. (PDF). Marine Ecology Progress Series. November 30, 1979, 1: 249–54 [February 14, 2010]. ISSN 1616-1599. doi:10.3354/meps001249. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2020-12-12).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
