卡尔尼科巴语
| 卡尔尼科巴语 | |
|---|---|
| 发音 | [puː] |
| 母语国家和地区 | 印度 |
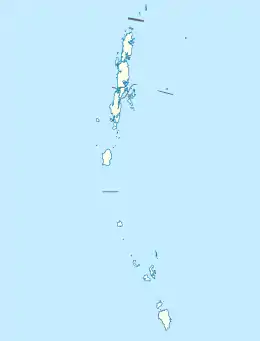
| 区域 | 尼科巴群岛 |
母语使用人数 | 3.7万 (2005)[1] |
| 語系 | 南亚语系
|
| 文字 | 拉丁字母 |
| 語言代碼 | |
| ISO 639-3 | caq |
| Glottolog | carn1240[2] |
| ELP | Car Nicobarese |
 卡尔尼科巴语  卡尔尼科巴语 | |
| 坐标:9.19°N 92.77°E | |
尽管和越南语和高棉语是远亲,其更可能和临近的南岛语系语言如尼亚斯语和亚齐语有关,它们同属一个语言联盟。[3]
卡尔尼科巴语是动宾主语序语言,一定程度上是黏着语。[4]其有相当复杂的动词后缀系统和一些中缀,如不同的属格助词和“疑问”语气的名词和代词。[5]
音系
词汇
保罗·西德维尔(2017)[7]在ICAAL 2017会议上发布了他的原始尼科巴语。
| 义 | 卡尔尼科巴语 | 原始尼科巴语 |
|---|---|---|
| 热 | taɲ | *taɲ |
| 四 | fɛːn | *foan |
| 孩子 | kuːn | *kuːn |
| 唇 | (minuh) | *manuːɲ |
| 狗 | ʔam | *ʔam |
| 夜 | hatəːm | *hatəːm |
| 雄性 | koːɲ | *koːɲ |
| 耳 | naŋ | *naŋ |
| 一 | heŋ | *hiaŋ |
| 腹 | (ʔac) | *ʔac |
| 日 | (tavuːj) | - |
| 甘 | (pacaːka) | - |
| 溢出 | tareːci | *roac |
| 鼻 | mɛh | *moah |
| 乳 | tɛh | *toah |
| 咳 | ʔɛhɛ | *ʔoah |
| 臂 | kɛl | *koal |
| 内 | ʔɛl | *ʔoal |
| 四 | feːn | *foan |
| 肘 | sikɔŋ | *keaŋ |
形态
共享形态学交替:老AA型使役动词h有两个词素变体,前缀ha-出现在单音节词根中,中缀-um-出现在双音节词干中(注释:声母*p > h发生在非重读音节)。
- ɲa - “吃” / haɲaː “喂”
- pɯɲ - “哭” / hapɯɲ-ɲɔː “使哭”
- kucik - “变得可口” / kumcik “尝”
- kale - “勇气” / kumle “勇敢”
参考
- 卡尔尼科巴语于《民族语》的链接(第18版,2015年)
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian (编). . . Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. 2016.
- Cysouw, Michael; Quantitative explorations of the world-wide distribution of rare characteristics, or: the exceptionality of north-western European languages (页面存档备份,存于); pp. 11-12
- . [2021-04-07]. (原始内容存档于2020-12-04).
- Whitehead, Rev. G.; Dictionary of the Car (Nicobarese) language; published 1925 by American Baptist Mission Press; pp. xxvi-xxxii
- Sidwell, Paul. . The Handbook of Austroasiatic Languages: Leiden: Brill. 2015: 1231–1240.
- Sidwell, Paul. 2017. "Proto-Nicobarese Phonology, Morphology, Syntax: work in progress". International Conference on Austroasiatic Linguistics 7, Kiel, Sept 29-Oct 1, 2017.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.