奇偶排序
奇偶排序(英語:),或奇偶换位排序、砖排序[1],是一种相对简单的排序算法,最初发明用于有本地互连的并行计算。这是与冒泡排序特点类似的一种比较排序。
| 奇偶排序 | |
|---|---|
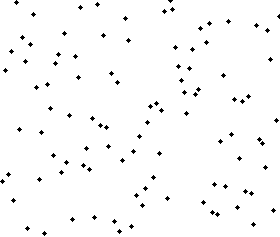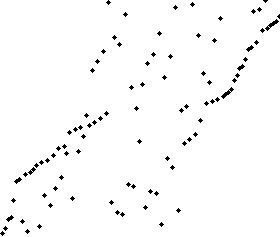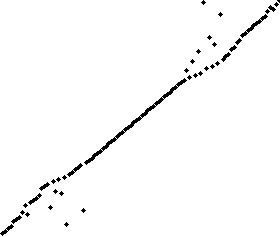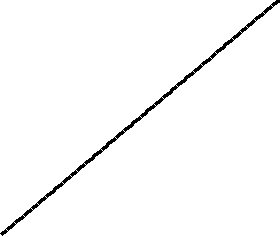 使用奇偶排序法对一列随机数字进行排序的过程 | |
| 概况 | |
| 類別 | 排序算法 |
| 資料結構 | 数组 |
| 复杂度 | |
| 最坏时间复杂度 | |
| 最优时间复杂度 | |
| 最佳解 | 不 |
| 相关变量的定义 | |
该算法中,通过比较数组中相邻的(奇-偶)位置数字对,如果该奇偶对是错误的顺序(第一个大于第二个),则交换。下一步重复该操作,但针对所有的(偶-奇)位置数字对。如此交替进行下去。
处理器数组的排序
在并行计算排序中,每个处理器对应处理一个值,并仅有与左右邻居的本地互连。所有处理器可同时与邻居进行比较、交换操作,交替以奇-偶、偶-奇的顺序。该算法由Habermann在1972年最初发表并展现了在并行处理上的效率。[2]
该算法可以有效地延伸到每个处理器拥有多个值的情况。在Baudet–Stevenson奇偶合并分割算法中,每个处理器在每一步对自己所拥有的子数组进行排序,然后与邻居执行合并分割或换位合并。[3]
程式代碼
C语言
void odd_even_sort(int arr[], int len) {
int odd_even, i;
int temp;
int sorted = 0;
while (!sorted) {
sorted = 1;
for (odd_even = 0; odd_even < 2; odd_even++)
for (i = odd_even; i < len - 1; i += 2)
if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]) {
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
arr[i + 1] = temp;
sorted = 0;
}
}
}
C++
template<typename T> //整數或浮點數皆可使用,若要使用物件(class)時必須設定大於(>)的運算子功能
void odd_even_sort(T arr[], int len) {
int odd_even, i;
bool sorted = false;
while (!sorted) {
sorted = true;
for (odd_even = 0; odd_even < 2; odd_even++)
for (i = odd_even; i < len - 1; i += 2)
if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1]) {
swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1]);
sorted = false;
}
}
}
Python
# 假设已有列表a等待排序
while True:
sorted = True
# 处理奇-偶对
for i in xrange(1, len(a)-1, 2):
if a[i] > a[i+1]:
a[i], a[i+1] = a[i+1], a[i] # 交换
sorted = False
# 处理偶-奇对
for i in xrange(0, len(a)-1, 2):
if a[i] > a[i+1]:
a[i], a[i+1] = a[i+1], a[i] # 交换
sorted = False
if sorted:
break
JavaScript
Array.prototype.odd_even_sort = function() {
var odd_even, i;
var temp;
var sorted = 0;
while (!sorted) {
sorted = 1;
for ( odd_even = 0; odd_even < 2; odd_even++)
for ( i = odd_even; i < this.length - 1; i += 2)
if (this[i] > this[i + 1]) {
temp = this[i];
this[i] = this[i + 1];
this[i + 1] = temp;
sorted = 0;
}
}
return this;
};
PHP
function swap(&$x, &$y) {
$t = $x;
$x = $y;
$y = $t;
}
function odd_even_sort(&$arr) {//php的陣列視為基本型別,所以必須用傳參考才能修改原陣列
$sorted = 0;
while (!$sorted) {
$sorted = 1;
for ($odd_even = 0; $odd_even < 2; $odd_even++)
for ($i = $odd_even; $i < count($arr) - 1; $i += 2)
if ($arr[$i] > $arr[$i + 1]) {
swap($arr[$i], $arr[$i + 1]);
$sorted = 0;
}
}
}
参考文献
- Phillips, Malcolm. . [3 August 2011]. (Sort Techniques 原始内容 请检查
|url=值 (帮助)存档于2011年10月28日). - N. Haberman (1972) "Parallel Neighbor Sort (or the Glory of the Induction Principle)," CMU Computer Science Report (available as Technical report AD-759 248, National Technical Information Service, US Department of Commerce, 5285 Port Royal Rd Sprigfield VA 22151).
- S. Lakshmivarahan, S. K. Dhall, and L. L. Miller, Franz L. Alt and Marshall C. Yovits , 编, , Advances in computers (Academic Press), 1984, 23: 295–351, ISBN 9780120121236
- Robert Sedgewick. 3rd. Addison-Wesley Professional. 2003: 454–464. ISBN 9780201361209.
- Allen Kent and James G. Williams. . CRC Press. 1993: 33–38. ISBN 9780824722821.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.