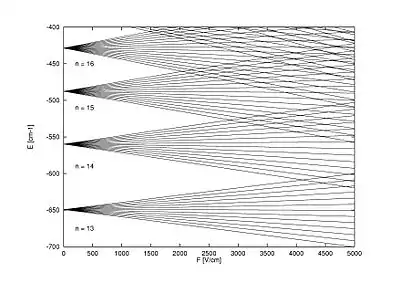
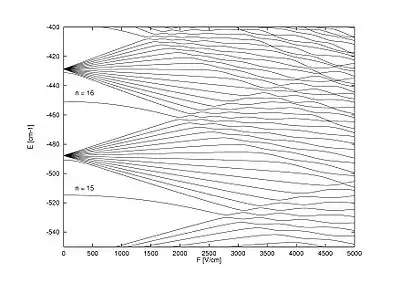
斯塔克效应
斯塔克效应(英語:)是原子和分子光譜譜線在外加電場中發生位移和分裂的現象。分裂和位移量稱為斯塔克分裂或斯塔克位移。斯塔克效應又可分為一階和二階斯塔克效應。一階的情況下光譜分裂或位移是與電場強度呈線性關係,二階則是和電場強度呈二次方關係。
斯塔克效應對應於帶電粒子譜線的壓力增寬(斯塔克增寬)。當譜線的分裂或位移在吸收線發生時則稱為逆斯塔克效應(Inverse Stark effect)。
由電場造成的斯塔克效應與由磁場造成譜線分裂成數個部分的塞曼效應相似。
參見
- 塞曼效应
- Autler-Townes效應
- 斯塔克光譜學
- 英格利斯-泰勒方程式
注釋
- Classical, semiclassical, and quantum dynamics of lithium in an electric field, M Courtney, N Spellmeyer, H Jiao, D Kleppner, Phys Rev A 51, 3604 (1995).
- See for the early history of the Stark effect: E. Whitaker, A History of the Theories of Aether and Electricity, vol. II; The Modern Theories, American Institute of Physics (1987).
參考資料
- E. U. Condon and G. H. Shortley. . Cambridge University Press. 1935. ISBN 0-521-09209-4. (Chapter 17 provides a comprehensive treatment, as of 1935.)
- H. W. Kroto. . Dover, New York. 1992. ISBN 0-486-67259-X. (Stark effect for rotating molecules)
- H. Friedrich. . Springer-Verlag, Berlin. 1990. ISBN 0-387-54179-9. (Stark effect for atoms)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.