桶排序
桶排序(英語:)或所謂的箱排序,是一個排序演算法,工作的原理是將陣列分到有限數量的桶裡。每個桶再個別排序(有可能再使用別的排序演算法或是以遞迴方式繼續使用桶排序進行排序)。桶排序是鴿巢排序的一種歸納結果。當要被排序的陣列內的數值是均勻分配的時候,桶排序使用線性時間()。
| 桶排序 | |
|---|---|
| 概况 | |
| 類別 | 排序算法 |
| 資料結構 | 数组 |
| 复杂度 | |
| 平均時間複雜度 | ,為桶數 |
| 最坏时间复杂度 | |
| 空間複雜度 | |
| 最佳解 | |
| 相关变量的定义 | |
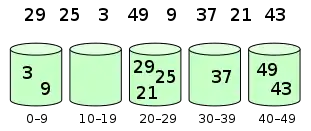
元素分配到桶中

对桶中元素排序
桶排序以下列程序進行:
- 設置一個定量的陣列當作空桶子。
- 尋訪序列,並且把項目一個一個放到對應的桶子去。
- 對每個不是空的桶子進行排序。
- 從不是空的桶子裡把項目再放回原來的序列中。
伪代码
function bucket-sort(array, n) is
buckets ← new array of n empty lists
for i = 0 to (length(array)-1) do
insert array[i] into buckets[msbits(array[i], k)]
for i = 0 to n - 1 do
next-sort(buckets[i])
return the concatenation of buckets[0], ..., buckets[n-1]
C++实现算法
假设数据分布在[0,100)之间,每个桶内部用链表表示,在数据入桶的同时插入排序。然后把各个桶中的数据合并。
#include<iterator>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int BUCKET_NUM = 10;
struct ListNode{
explicit ListNode(int i=0):mData(i),mNext(NULL){}
ListNode* mNext;
int mData;
};
ListNode* insert(ListNode* head,int val){
ListNode dummyNode;
ListNode *newNode = new ListNode(val);
ListNode *pre,*curr;
dummyNode.mNext = head;
pre = &dummyNode;
curr = head;
while(NULL!=curr && curr->mData<=val){
pre = curr;
curr = curr->mNext;
}
newNode->mNext = curr;
pre->mNext = newNode;
return dummyNode.mNext;
}
ListNode* Merge(ListNode *head1,ListNode *head2){
ListNode dummyNode;
ListNode *dummy = &dummyNode;
while(NULL!=head1 && NULL!=head2){
if(head1->mData <= head2->mData){
dummy->mNext = head1;
head1 = head1->mNext;
}else{
dummy->mNext = head2;
head2 = head2->mNext;
}
dummy = dummy->mNext;
}
if(NULL!=head1) dummy->mNext = head1;
if(NULL!=head2) dummy->mNext = head2;
return dummyNode.mNext;
}
void BucketSort(int n,int arr[]){
vector<ListNode*> buckets(BUCKET_NUM,(ListNode*)(0));
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
int index = arr[i]/BUCKET_NUM;
ListNode *head = buckets.at(index);
buckets.at(index) = insert(head,arr[i]);
}
ListNode *head = buckets.at(0);
for(int i=1;i<BUCKET_NUM;++i){
head = Merge(head,buckets.at(i));
}
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
arr[i] = head->mData;
head = head->mNext;
}
}
Java實現算法
private int indexFor(int a, int min, int step) {
return (a - min) / step;
}
public void bucketSort(int[] arr) {
int max = arr[0], min = arr[0];
for (int a : arr) {
if (max < a)
max = a;
if (min > a)
min = a;
}
// 該值也可根據實際情況選擇
int bucketNum = max / 10 - min / 10 + 1;
List buckList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
// create bucket
for (int i = 1; i <= bucketNum; i++) {
buckList.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
// push into the bucket
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int index = indexFor(arr[i], min, 10);
((ArrayList<Integer>) buckList.get(index)).add(arr[i]);
}
ArrayList<Integer> bucket = null;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < bucketNum; i++) {
bucket = (ArrayList<Integer>) buckList.get(i);
insertSort(bucket);
for (int k : bucket) {
arr[index++] = k;
}
}
}
// 把桶內元素插入排序
private void insertSort(List<Integer> bucket) {
for (int i = 1; i < bucket.size(); i++) {
int temp = bucket.get(i);
int j = i - 1;
for (; j >= 0 && bucket.get(j) > temp; j--) {
bucket.set(j + 1, bucket.get(j));
}
bucket.set(j + 1, temp);
}
}
JavaScript实现算法
Array.prototype.bucketSort = function(num) {
function swap(arr, i, j) {
const temp = arr[i]
arr[i] = arr[j]
arr[j] = temp
}
const max = Math.max(...this)
const min = Math.min(...this)
const buckets = []
const bucketsSize = Math.floor((max - min) / num) + 1
for(let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
const index = ~~(this[i] / bucketsSize)
!buckets[index] && (buckets[index] = [])
buckets[index].push(this[i])
let l = buckets[index].length
while(l > 0) {
buckets[index][l] < buckets[index][l - 1] && swap(buckets[index], l, l - 1)
l--
}
}
let wrapBuckets = []
for(let i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
buckets[i] && (wrapBuckets = wrapBuckets.concat(buckets[i]))
}
return wrapBuckets
}
const arr = [11, 9, 6, 8, 1, 3, 5, 1, 1, 0, 100]
console.log(arr.bucketSort(10))
JavaScript实现递归算法
Array.prototype.bucketSort = function()
{
var start = 0;
var size = this.length;
var min = this[0];
var max = this[0];
for (var i = 1; i < size; i++){
if (this[i] < min){min = this[i];}
else{ if(this[i] > max){max = this[i];} }
}
if (min != max){
var bucket = new Array(size);
for (var i = 0; i < size; i++){bucket[i] = new Array();}
var interpolation = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < size; i++){
interpolation = Math.floor(((this[i] - min) / (max - min)) * (size - 1));
bucket[interpolation].push(this[i]);
}
for (var i = 0; i < size; i++){
if (bucket[i].length > 1){bucket[i].bucketSort();}//遞歸
for(var j = 0; j < bucket[i].length; j++){this[start++] = bucket[i][j];}
}
}
};
Python 3.10 實現演算法
def is_sort(arr: list) -> bool:
for i in range(len(arr) - 1):
if arr[i] > arr[i + 1]:
return False
return True
def bucket_sort(arr: list, is_sub_bucket: bool = False):
if is_sort(arr):
return
bucket_num: int = max(arr) // 10 + 1 if not is_sub_bucket else 10
buckets: list[list] = [[] for _ in range(bucket_num)]
for a in arr:
i: int = a // 10 if not is_sub_bucket else a % 10
buckets[i].append(a)
arr.clear()
for bucket in buckets:
bucket_sort(bucket, is_sub_bucket=True)
arr += bucket
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [29, 25, 3, 49, 9, 37, 21, 43]
bucket_sort(arr)
print(arr)
參考
- Thomas H. Cormen,Charles E. Leiserson,Ronald L. Rivest,and Clifford Stein。Introduction to Algorithms, Second Edition. MIT Press and McGraw-Hill, 2001. ISBN 0-262-03293-7. Section 8.4: Bucket sort, pp.174–177.
- Paul E. Black "Postman's Sort" (页面存档备份,存于) from Dictionary of Algorithms and Data Structures at NIST。
- Robert Ramey The Postman's Sort (页面存档备份,存于) C Users Journal Aug. 1992
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.