茉莉酮酸
茉莉酮酸(英語:,缩写JA)是一类帮助植物均匀生长发育的植物激素。茉莉酮酸包括茉莉酸及其酯,例如茉莉酸甲酯。如同哺乳动物体内的前列腺素,茉莉酮酸是由环戊酮和脂肪酸通过生物合成作用合成的环戊酮衍生物。他们是从亚麻酸通过C18路径合成得到的。

茉莉酸
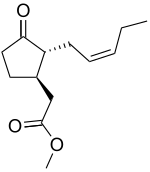
茉莉酸甲酯
植物体内的茉莉酮酸含量随着组织功能、细胞种类、生长发育时期的变化而不同[1]。植物受到某些外界刺激而做出响应时,茉莉酮酸的含量也会有所变化[1]。高水平的茉莉酮酸含量也会出现在花与果实等正在生长的生殖器官中,以及受到光照的植物的叶绿体内。茉莉酮酸的含量还会因为卷须缠绕、植物受伤等机械摄动而迅速增长[2][3]。
茉莉酮酸在植物体内已知的作用包括:
- 抑制种子的萌发或刺激潜伏期种子的萌发[1]
- 高水平的茉莉酮酸会促进蛋白质储存;编码植物性储存蛋白的基因会对茉莉酸有响应,且tuberonic酸(一种茉莉酮酸衍生物)被认为在块茎的形成中起作用[4][5]
- 植物体内的茉莉酮酸可以引起叶绿素的减少并抑制编码光合作用相关蛋白基因的表达。尽管这一现象的原因尚不知晓,人们认为这样的反应可以降低植物在过量光照和二氧化碳的情况下的同化能力。[1]
- 茉莉酮酸在花和果实中积累的作用尚未知晓,但它可能和果实成熟(通过乙烯)、果实中的类胡萝卜素的合成、编码种子和植物性储存蛋白的基因的表达相关[1]
- 茉莉酮酸在植物对昆虫和疾病的抵抗中起着重要作用。许多与植物抗性相关的基因都是由茉莉酸诱导表达的,而茉莉酸和乙烯也在抵抗反应中有着共同的作用[6]
像生长素一样,茉莉酮酸也是通过泛素系统而被感觉到的。当茉莉酮酸和异亮氨酸结合后,会导致SCFCOI1联合体分解被泛素蛋白标记的JAZ蛋白,然后联合体会发出一些其他转录因子的转录。[7]
参考文献
- Creelman RA and Mullet ME. 1997. Biosynthesis and action of jasmonsates in plants. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology 48: 355-381
- Falkenstein E et al. 1991. Methyljasmonate and α-linolenic acid are potent inducers of tendril coiling. Planta 185: 316– 22
- Creelman RA etal. 1992. Jasmonic acid/methyl jasmonate accumulate in wounded soybean hypocotyls and modulate wound gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:4938– 41
- Anderson JM. 1988. Jasmonic acid-dependent increases in the level of specific polypeptides in soybean suspension cultures and seedlings. Journal of Plant Growth and Regulation. 7: 203– 11
- Pelacho AM and Mingo-Castel AM. 1991. Jasmonic acid induces tuberization of potato stolons cultured in vitro. Plant Physiology 97: 1253– 55
- Xu Y et al. 1994. Plant defense genes are synergistically induced by ethylene and methyl jasmonate. Plant Cell 6: 1077– 85
- Farmer EE. . Nature. 2007, 448: 659–660. doi:10.1038/448659a.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.