集群錯覺
集群错觉(英語:)是人类的一种错觉,指的是人类会倾向将小样本中随机出现的集群或者条纹认为是非随机的[1][2]。这种错觉是由于人们低估随机或半随机数据小样本中的变异量所致[3]。
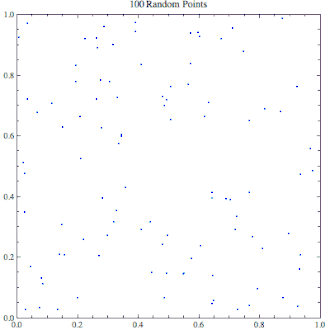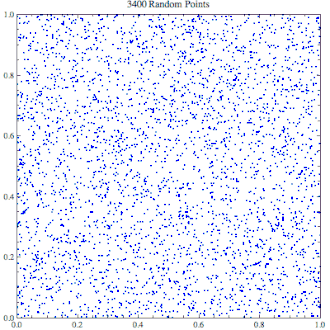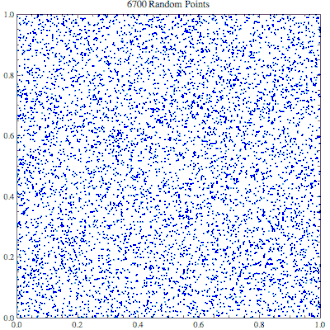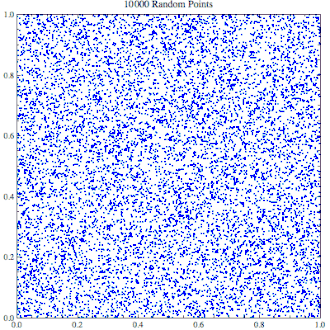
逐渐上升到10,000个点的随机点生成器,看起来里面似乎充满了集群
例子
相关课题研究者、社会科学家托马斯·吉洛维奇认为集群错觉在生活中无处不在,甚至人们对二维数据也会有集群错觉:例如第二次世界大战中V-1火箭击中伦敦的位置看起来就像是若干个集群,股票市场价格随时间波动的模式看起来也像是若干个集群[3][4]。尽管伦敦人对于火箭攻击的情况有许多猜测,数据分析师R.克拉克最初于1946年发表的分析显示V-2火箭击中伦敦的位置实际上符合一定范围内的随机分布[5][6][7][8][9]。
类似偏误
在因果推理中受到该認知偏誤的影响可能导致德州神槍手謬誤,有时两者干脆就是混用的[10][11]。该谬误的更普遍形式是空想性错视和幻想性错觉。相关谬误还包括集群错觉可能导致的控制错觉以及对数据集大小的不敏感。该谬误在概率学上常常与賭徒謬誤错用。
参考文献
- the free dictionary. . . [2020-03-26]. (原始内容存档于2020-11-26).
- Tilli, Michele Orazio. .
- Gilovich, Thomas. . New York: The Free Press. 1991. ISBN 978-0-02-911706-4.
- Kahneman, Daniel; Amos Tversky. . Cognitive Psychology. 1972, 3 (3): 430–454. doi:10.1016/0010-0285(72)90016-3.
- Clarke, R. D. . Journal of the Institute of Actuaries. 1946, 72 (3): 481. doi:10.1017/S0020268100035435.
- Gilovich, 1991 p. 19
- Mori, Kentaro. . [3 March 2012]. (原始内容存档于2020-02-24).
- . [3 March 2012]. (原始内容存档于2012-02-21).
- Tierney, John. (October 3, 2008). TierneyLab (New York Times). 3 October 2008 [3 March 2012]. (原始内容存档于2020-12-18).
- . . [2020-03-26]. (原始内容存档于2021-03-04).
- Laurie Johnson. .
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.