冰立方中微子天文台
冰立方微中子觀測站(英語:,或簡稱)是一個位於阿蒙森-斯科特南極站的微中子觀測站[1]。這個計劃由威斯康辛大學所主導,集合了來自十多個國家超過300名科學家投入其中[2]。
| 冰立方微中子觀測站 IceCube Neutrino Observatory | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
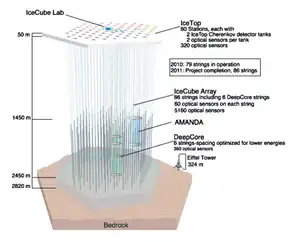 冰立方微中子觀測站的結構示意圖。 | |||||
.svg.png.webp) 冰立方微中子觀測站 IceCube Neutrino Observatory的位置 | |||||
| 組織 | 威斯康辛大學 | ||||
| 位置 | 阿蒙森-斯科特南極站 | ||||
| 座標 | 89°59′24″S 63°27′11″W | ||||
| 網址 | icecube | ||||
| 望遠鏡 | |||||
| |||||
| |||||
[编辑维基数据] | |||||
觀測站的數千個探測器位於南極的冰層之下,分佈範圍超過一立方公里。類似其前身南極緲子和微中子觀測陣列,的組成包含帶有光電倍增管的球型數位光學模組(DOM)[3],以及數據擷取面板。光學模組佈署在86條深度介於1450到2450公尺深的觀測鍊上,觀測到的資料由則面板傳送位於陣列之上的計算中心[4]。被設計作用來觀測能量約 1TeV的微中子,以用來研究宇宙中極高能量的天文物理現象。的建造完成於2010年12月8日[5]。
DOM模块被部署成每条有六十个模块的“链条”放在从1450米到2450米深度范围,用热水钻头融化冰来钻孔。的目的是寻找在TeV的范围内中微子的点源,探索能量最高的天体物理过程。
建設過程

的鑽孔設備 ,2009年12月。
冰立方微中子觀測站的只能於夏季進行建造,永晝的11月到2月使工程能二十四小時持續進行。最初的建設始於2005年,第一條觀測鏈被埋設以確認光學模組能正確運作。[8]之後2005年到2006年夏季期間完成另外8條觀測鏈,使成為全球最大的中微子探测器。
| 設置數量 | 累計數量 | |
|---|---|---|
| 2005年 | 1 | 1 |
| 2005–2006年 | 8 | 9 |
| 2006–2007年 | 13 | 22 |
| 2007–2008年 | 18 | 40 |
| 2008–2009年 | 19 | 59 |
| 2009–2010年 | 20 | 79 |
| 2010–2011年 | 7 | 86 |
分探测器

"Taklampa", 85號坑的其中一個DOM(數字光學模塊)。
冰立方中微子观测站是由主阵列与几个分探测器组成。
阵列探测器
低能量扩展探测器
- 低能量扩展探测器,是阵列的仪器密集的区域,延伸到低于100 GeV的可观察到的能量。链被部署在更大阵列的中心位置(在表面平面),深入到底部阵列(从1760到2450米之间的深度)中最清澈的冰。在从1850米到2107米的深度之间是没有的DOM(数字光学模块),因为冰没有这些层的清澈。
PINGU
- PINGU(精密冰立方中微子觀測站下一代升级),是一个计划中的扩展,将检测到低能量中微子(〜GeV),用于包括确定中微子质量等级,检测陶中微子,并寻找大質量弱相互作用粒子湮灭[12]。,作为一个更大观测站的远景规划已经被提出了[13]。
參考資料
- . 威斯康辛大學. 2009-06-30 [2009-10-15]. (原始内容存档于2010-03-14).
- . 威斯康辛大學. [2015-01-12]. (原始内容存档于2014-12-27).
- Abbasi, R.; Abdou, Y.; Abu-Zayyad, T.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Andeen, K.; Auffenberg, J.; Bai, X. . Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment. 2010-06, 618 (1-3): 139–152 [2022-04-21]. Bibcode:2010NIMPA.618..139A. arXiv:1002.2442
 . doi:10.1016/j.nima.2010.03.102. (原始内容存档于2022-06-16) (英语).
. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2010.03.102. (原始内容存档于2022-06-16) (英语). - Abbasi, R.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, J.; Andeen, K.; Auffenberg, J.; Bai, X.; Baker, M. . Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment. 2009-04, 601 (3): 294–316. Bibcode:2009NIMPA.601..294T. arXiv:0810.4930
 . doi:10.1016/j.nima.2009.01.001 (英语).
. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2009.01.001 (英语). - . [2015-01-13]. (原始内容存档于2015-01-12).
- IceCube Collaboration*. . Science. 2013-11-22, 342 (6161): 1242856. ISSN 0036-8075. doi:10.1126/science.1242856 (英语).
- . ScienceDaily. [2022-04-21]. (原始内容存档于2018-07-17) (英语).
- . SpaceRef. [2022-04-21].
- . [2011-01-09]. (原始内容存档于2010-12-25).
- . [2015-01-13]. (原始内容存档于2015-01-13).
- Aartsen, M.G.; Abbasi, R.; Abdou, Y.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Altmann, D.; Auffenberg, J. . Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment. 2013-05, 711: 73–89 [2022-04-21]. Bibcode:2013NIMPA.711...73A. arXiv:1301.5361
 . doi:10.1016/j.nima.2013.01.054. (原始内容存档于2022-06-29) (英语).
. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2013.01.054. (原始内容存档于2022-06-29) (英语). - . 2013-12-30. (原始内容存档于2015-10-06).
- Gen2 Collaboration; Aartsen, M. G.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J. A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Altmann, D.; Anderson, T. . 2014 [2022-04-21]. arXiv:1412.5106
 . doi:10.48550/ARXIV.1412.5106. (原始内容存档于2022-07-07).
. doi:10.48550/ARXIV.1412.5106. (原始内容存档于2022-07-07).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.