帕里克-德林氧化反应
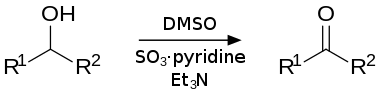
帕里克-德林氧化反应(Parikh-Doering oxidation)以二甲亚砜为氧化剂,三氧化硫-吡啶络合物为活化剂,三乙胺为碱而将伯醇和仲醇转化为相应的醛酮。
帕里克-德林反应
反应在近环境温度(一般为0℃)下进行时,可以只产生少量的甲硫甲基醚副产物。[1]
反应机理
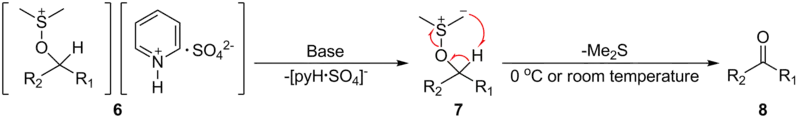
二甲亚砜与三氧化硫在0℃或室温下发生加成,并受到醇进攻,生成关键的烷氧基锍离子中间体(6)。

该中间体接下来被碱去质子化为相应的硫叶立德,然后硫叶立德经五元环过渡态、分解放出二甲硫醚,得到醛酮。
应用
埃文斯等在合成(–)-kumausallene 时就用到了帕里克-德林氧化反应。(注意所用的典型反应条件)[2]
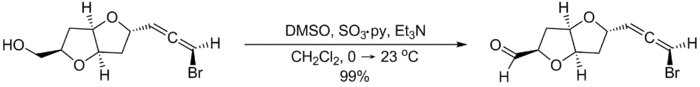
帕里克-德林氧化
尼科拉乌的cortistatin全合成中也使用了该反应。[3]

参考资料
- J. R. Parikh and W. v. E. Doering. . Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1967, 89: 5505–5507. doi:10.1021/ja00997a067.
- P. A. Evans, V. S. Murthy, J. D. Roseman, A. L. Rheingold. . Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 1999, 38: 3175–3177. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19991102)38:21<3175::AID-ANIE3175>3.0.CO;2-M.
- K. C. Nicolaou, Xiao-Shui Peng, Ya-Ping Sun, Damien Polet, Bin Zou, Chek Shik Lim, and David Y.-K. Chen. . Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2009, 131: 10587–10597. doi:10.1021/ja902939t.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.