SNARE蛋白
可溶性N-乙基順丁烯二醯亞胺敏感性因子附著蛋白受體(英語:,即SNAP受體,又稱可溶性NSF附著蛋白受體),又稱SNARE蛋白,是一個大的蛋白質家族,由酵母菌中的至少24個成員和哺乳動物細胞中的60個以上的成員組成。[2][3]SNARE蛋白的主要作用是介導囊泡融合以及囊泡與靶膜的融合。這尤其介導胞吐作用,但也可以介導囊泡與膜結合區室(如溶體)的融合。研究最深入的SNARE是介導神經元中突觸小泡的神經遞質釋放。這些神經元SNAREs是負責某些細菌產生的肉毒桿菌中毒和破傷風的等神經毒素的標靶。
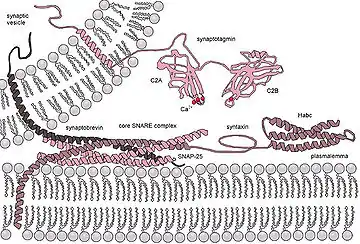
Molecular machinery driving vesicle fusion in neuromediator release. The core SNARE complex is formed by four α-helices contributed by synaptobrevin, syntaxin and SNAP-25, synaptotagmin serves as a calcium sensor and closely regulates the SNARE zipping.[1]
| SNARE-fusion membrane complex proteins | |
|---|---|
| 鑑定 | |
| 標誌 | SNARE |
| InterPro | IPR010989 |
| SCOP | 1kil / SUPFAM |
| TCDB | 1.F.1 |
| OPM家族 | 197 |
| OPM蛋白 | 3hd7 |
| 膜蛋白數據庫 | 198 |
參考資料
- Georgiev, Danko D; James F . Glazebrook. . Lyshevski, Sergey Edward (编). . Nano and Microengineering Series. CRC Press. 2007: 17–1–17–41 [2020-10-09]. ISBN 978-0-8493-8528-5. doi:10.1201/9781420008142.ch17 (不活跃 2020-09-09). (原始内容存档于2016-01-16).
- Burri, Lena; Lithgow, Trevor. . Traffic. 2004-01-01, 5 (1): 45–52. ISSN 1398-9219. PMID 14675424. doi:10.1046/j.1600-0854.2003.00151.x.
- Gerald K. 4th. John Wiley & Sons. 2002.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.