參見:
英语
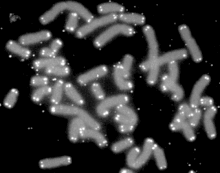
人类的染色体(灰色部分)及其尾部的端粒(白色部分)
词源
(“末,尾”) + (“部分”)。
发音
國際音標(幫助):/ˈtɛləmɪəɹ/, /ˈtiːləmɪəɹ/
名词
(複數)
- (遺傳學) 端粒
- 2004, Peter M. Lansdorp, 11: Telomeres and Telomere Regulation, Robert Paul Lanza (editor), Handbook of Stem Cells, Volume 2: Adult and Fetal Stem Cells, page 127,
- Chromosome ends or telomeres are composed of guanine-rich repeat sequences and associated proteins. A minimum number of repeats is essential for proper telomere function and to avoid sustained activation of DNA damage pathways that may result in replicative senescence or cell death.
- 2007, Peter Sutovsky, Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer,頁號 78:
- Previous studies have examined telomere lengths as an indirect measure of aging in cloned animals. Sheep were reported to have shorter telomeres suggestive of premature aging while cattle had either age-appropriate or longer telomeres.
- (請為本引文添加中文翻譯)
- 2004, Peter M. Lansdorp, 11: Telomeres and Telomere Regulation, Robert Paul Lanza (editor), Handbook of Stem Cells, Volume 2: Adult and Fetal Stem Cells, page 127,
相关词汇
This article is issued from Wiktionary. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.