 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1,1-Trifluoropentane-2,4-dione | |
| Other names
1,1,1-Trifluoro-2,4-pentanedione, (trifluoroacetyl)acetone, 1,1,1-(trifluoroacetyl)acetone, 1,1,1-TFAA | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.090 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H4F3O2 | |
| Molar mass | 153.080 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.27 g/cm3 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H226, H302, H312, H315, H319, H332 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
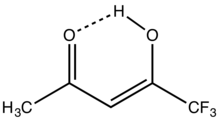
1,1,1-Trifluoroacetylacetone is the organofluorine compound with the formula CF3C(O)CH2C(O)CH3. It is a colorless liquid. Like other 1,3-diketones, it is used as a precursor to heterocycles, e.g. pyrazoles, and metal chelates.[1] It is prepared by condensation of esters of trifluoroacetic acid with acetone.[2]
According to an analysis by proton NMR spectroscopy, the compound exists predominantly (97% at 33 °C, neat) as the enol. For comparison under the same conditions, the percent enol for acetylacetone and hexafluoroacetylacetone are 85 and 100%, respectively.[3]
References
- ↑ Morris, M. L.; Moshier, Ross W.; Sievers, Robert E. (1967). "Tetrakis(1,1,1-trifluoro-2,4-pentanedionato)zirconium(and Hafnium)". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 9. pp. 50–52. doi:10.1002/9780470132401.ch15. ISBN 9780470132401.
- ↑ Henne, Albert L.; Newman, Melvin S.; Quill, Laurence L.; Staniforth, Robert A. (1947). "Alkaline condensation of fluorinated esters with esters and ketones". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 69 (7): 1819–20. doi:10.1021/ja01199a075.
- ↑ Jane L. Burdett; Max T. Rogers (1964). "Keto-Enol Tautomerism in β-Dicarbonyls Studied by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. I. Proton Chemical Shifts and Equilibrium Constants of Pure Compounds". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 86: 2105–2109. doi:10.1021/ja01065a003.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.