 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
R-132c, HCFC-132c | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UN number | 3082 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H2Cl2F2 | |
| Molar mass | 134.93 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Melting point | −106.5 °C (−159.7 °F; 166.7 K) |
| Boiling point | 45.1 °C (113.2 °F; 318.2 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Inhalation |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
 | |
| Danger | |
| H301, H331 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P301+P316, P304+P340, P316, P321, P330, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
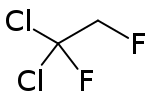
1,1-Dichloro-1,2-difluoroethane (also known as HCFC-132c or R-132c) is a hydrochlorofluorocarbon. It is a volatile derivative of ethane. It appears as a colourless, odorless non-flammable liquid.[2] The use of HCFC-132c is restricted by the US EPA through the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990 which intend to phase-out the use of substances that deplete the ozone layer. HCFC-132c is cited as an ozone depleting substance; it is considered as a class II substance by the EPA.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "System of Registries | US EPA". sor.epa.gov. Retrieved Sep 26, 2022.
- ↑ "1,1-Dichloro-1,2-difluoroethane". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved Sep 26, 2022.
- ↑ "System of Registries | US EPA". sor.epa.gov. Retrieved Sep 26, 2022.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.