 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Nitronaphthalene | |
| Other names
α-Nitronaphthalene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1867714 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.531 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2538 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H7NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 173.171 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | pale yellow solid |
| Density | 1.332 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 52–61 °C (126–142 °F; 325–334 K) |
| Boiling point | 304 °C (579 °F; 577 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
     | |
| Danger | |
| H228, H301, H315, H319, H335, H351, H411 | |
| P201, P202, P210, P240, P241, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P281, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P370+P378, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
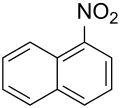
1-Nitronaphthalene is an organic compound with the formula C10H7NO2. It is one of two isomers of nitronaphthalene. A pale yellow, sublimable solid, 1-nitronaphthalene is the main product of the direct nitration of naphthalene. It is an intermediate in the production of naphthylamine, a precursor to dyes.[1] The conversion to the amine is effected by hydrogenation.[2]
Safety
References
- ↑ Booth, Gerald (2005). "Nitro Compounds, Aromatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_411. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ↑ Westerhaus, Felix A.; Jagadeesh, Rajenahally V.; Wienhöfer, Gerrit; Pohl, Marga-Martina; Radnik, Jörg; Surkus, Annette-Enrica; Rabeah, Jabor; Junge, Kathrin; Junge, Henrik; Nielsen, Martin; Brückner, Angelika; Beller, Matthias (2013). "Heterogenized Cobalt Oxide Catalysts for Nitroarene Reduction by Pyrolysis of Molecularly Defined Complexes". Nature Chemistry. 5 (6): 537–543. Bibcode:2013NatCh...5..537W. doi:10.1038/nchem.1645. PMID 23695637. S2CID 3273484.
- ↑ Martin, Todd M.; Young, Douglas M. (2001). "Prediction of the Acute Toxicity (96-h LC50) of Organic Compounds to the Fathead Minnow ( Pimephales promelas ) Using a Group Contribution Method". Chemical Research in Toxicology. 14 (10): 1378–1385. doi:10.1021/tx0155045. PMID 11599929.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.