| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 658 seats in the House of Commons 330 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Colours denote the winning party | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Composition of the Commons after the election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In the 1841 United Kingdom general election, there was a big swing as Sir Robert Peel's Conservatives took control of the House of Commons. Melbourne's Whigs had seen their support in the Commons erode over the previous years. Whilst Melbourne enjoyed the firm support of the young Queen Victoria, his ministry had seen increasing defeats in the Commons, culminating in the defeat of the government's budget in May 1841 by 36 votes, and by 1 vote in a 4 June 1841 vote of no confidence put forward by Peel. According to precedent, Melbourne's defeat required his resignation. However, the cabinet decided to ask for a dissolution, which was opposed by Melbourne personally (he wished to resign, as he had attempted in 1839), but he came to accept the wishes of the ministers. Melbourne requested the Queen dissolve Parliament, leading to an election.[1] The Queen thus prorogued Parliament on 22 June.[2]
The Conservatives campaigned mainly on an 11-point programme modified from their previous electoral effort and designed by Peel, whilst the Whigs emphasised reforming the import duties on corn, replacing the existing sliding scale with a uniform rate. The Whig position lost them support amongst protectionists, and the Whigs saw heavy losses in constituencies like the West Riding, where aristocratic Whig families who held a strong tradition of unbroken representation in Parliament were rejected by the electorate.
O'Connell, who had been governing with the Whigs through a compact, felt the government's unpopularity rub off on him. His own party was shattered in the election. Barely a dozen Repealers retained their seats, and O'Connell himself lost in Dublin while his son was defeated in Carlow.[3] The Chartists picked up only a few votes.
Results
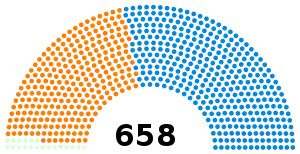
| UK General Election 1841 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidates | Votes | |||||||||||||
| Stood | Elected | Gained | Unseated | Net | % of total | % | No. | Net % | |||||||
| Conservative | 498 | 367 | +53 | 55.78 | 51.62 | 306,314 | +2.6 | ||||||||
| Whig | 388 | 271 | −73 | 41.19 | 46.15 | 273,902 | −4.8 | ||||||||
| Irish Repeal | 22 | 20 | 20 | 0 | +20 | 3.04 | 2.11 | 12,537 | N/A | ||||||
| Chartist | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.12 | 692 | N/A | ||||||
Voting summary
Seats summary
Regional results
Great Britain
| Party | Candidates | Unopposed | Seats | Seats change | Votes | % | % change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conservative | 439 | 185 | 326 | +42 | 286,650 | 52.7 | +4.5 | |
| Whig | 333 | 83 | 229 | −42 | 256,774 | 47.2 | −4.6 | |
| Chartist | 8 | 0 | 0 | 692 | 0.1 | |||
| Total | 780 | 268 | 555 | 544,116 | 100 | |||
England
| Party | Candidates | Unopposed | Seats | Seats change | Votes | % | % change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conservative | 374 | 147 | 277 | 272,755 | 53.1 | |||
| Whig | 277 | 62 | 187 | 236,813 | 46.8 | |||
| Chartist | 4 | 0 | 0 | 307 | 0.1 | |||
| Total | 655 | 209 | 464 | 509,875 | 100 | |||
Scotland
| Party | Candidates | Unopposed | Seats | Seats change | Votes | % | % change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whig | 40 | 13 | 31 | -2 | 16,356 | 60.8 | ||
| Conservative | 35 | 16 | 22 | +2 | 9,793 | 38.3 | ||
| Chartist | 3 | 0 | 0 | 385 | 0.9 | |||
| Total | 78 | 29 | 53 | 26,534 | 100 | |||
Wales
| Party | Candidates | Unopposed | Seats | Seats change | Votes | % | % change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conservative | 24 | 16 | 21 | 4,102 | 53.2 | |||
| Whig | 16 | 8 | 11 | 3,605 | 46.8 | |||
| Chartist | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | |||
| Total | 41 | 24 | 32 | 7,707 | 100 | |||
Ireland
| Party | Candidates | Unopposed | Seats | Seats change | Votes | % | % change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whig | 55 | 30 | 42 | 17,128 | 35.1 | |||
| Irish Conservative | 59 | 27 | 41 | 19,664 | 40.1 | |||
| Irish Repeal | 22 | 12 | 20 | 12,537 | 24.8 | |||
| Total | 136 | 69 | 103 | 49,329 | 100 | |||
Universities
| Party | Candidates | Unopposed | Seats | Seats change | Votes | % | % change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conservative | 6 | 6 | 6 | Uncontested | Uncontested | |||
| Total | 6 | 6 | 6 | Uncontested | Uncontested | |||
Notable Whig MPs who lost their seats
References
- ↑ Kemp, Betty (June 1952), "The General Election of 1841", History, 37 (130): 146–157, doi:10.1111/j.1468-229X.1952.tb00231.x, JSTOR 24402876
- ↑ Saint James's Chronicle Tuesday 22 June 1841, p.2.
- ↑ Marriott, John (1913). England since Waterloo. p. 143. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ↑ British Electoral Facts 1832–2006, compiled and edited by Colin Rallings and Michael Thrasher (Parliamentary Research Services, 2007)
Further reading
- Craig, F. W. S. (1989), British Electoral Facts: 1832–1987, Dartmouth: Gower, ISBN 0900178302
- Gash, Norman (1972), Sir Robert Peel: The life of Sir Robert Peel after 1830, pp. 234–72
- Rallings, Colin; Thrasher, Michael, eds. (2000), British Electoral Facts 1832–1999, Ashgate Publishing Ltd


_(14587944860).jpg.webp)