| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 County Results
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Utah |
|---|
 |
The 1936 United States presidential election in Utah took place on November 3, 1936, as part of the 1936 United States presidential election. All contemporary forty-eight states took part in the national election, and Utah voters selected four voters to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
Since its landslide endorsement of William Jennings Bryan's "free silver" in its inaugural 1896 election, Utah had been a swing state apart from its support for embattled President William Howard Taft in 1912. Woodrow Wilson had carried the state easily in 1916 due to strong anti-war sentiment,[1] but James M. Cox, John W. Davis and Robert M. La Follette did not win a single county between them in the 1920 and 1924 Republican landslides.
Vis-à-vis the rest of the nation, the Beehive State had shown only a small anti-Hoover trend in 1932. During Landon's summer campaigning, Utah was targeted strongly as a state the GOP needed to carry to have a chance at the presidency.[2] However, FDR's western public works programs, most notably Boulder Dam,[3] had made him exceptionally popular in the rugged, arid West.[4] Along with the potent campaigning of James Farley meant that, by the last week of October the Republicans were showing no interest in the Beehive State,[5] and this despite the opposition of the leadership of Utah's dominant Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints to Roosevelt's candidacy and policies, chiefly regarding the church's desire to remove Mormons from welfare rolls.[6]
Utah, like every other state west of the Appalachian Mountains, voted for Franklin D. Roosevelt over Alf Landon by a substantial margin, making FDR the first (and only) Democrat to win the state more than once. Roosevelt won Utah by a landslide with 69.34 percent of the vote, which remains the second best Democratic result from the state behind William Jennings Bryan in the state's inaugural election of 1896.
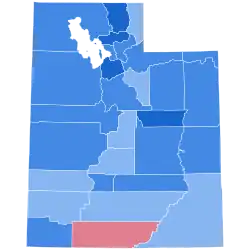
Like Bryan, FDR won every county in the state except strongly Republican Kane County in the far south, which has only voted Democratic for Woodrow Wilson in 1916.[1] Kane County was the westernmost county in the nation to vote for Landon, and one of only three west of the Continental Divide to do so.[lower-alpha 1]
As of the 2020 presidential election, this is the last election in which Iron County, Sanpete County, Sevier County, San Juan County, and Garfield County have voted for a Democratic presidential candidate.[7]
Results
| 1936 United States presidential election in Utah[8] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | Percentage | Electoral votes | |
| Democratic | Franklin D. Roosevelt (incumbent) | 150,246 | 69.34% | 4 | |
| Republican | Alf Landon | 64,555 | 29.79% | 0 | |
| Union[lower-alpha 2] | William Lemke | 1,121 | 0.52% | 0 | |
| Socialist[lower-alpha 2] | Norman Thomas | 432 | 0.20% | 0 | |
| Write-ins[lower-alpha 2] | — | 323 | 0.15% | 0 | |
| Totals | 216,677 | 100.00% | 4 | ||
Results by county
| County | Franklin Delano Roosevelt Democratic |
Alfred Mossman Landon Republican |
Various candidates Other parties |
Margin | Total votes cast[9] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | % | # | % | # | % | # | % | ||
| Beaver | 1,337 | 59.13% | 913 | 40.38% | 11 | 0.49% | 424 | 18.75% | 2,261 |
| Box Elder | 5,001 | 69.16% | 2,180 | 30.15% | 50 | 0.69% | 2,821 | 39.01% | 7,231 |
| Cache | 8,606 | 71.97% | 3,258 | 27.25% | 93 | 0.78% | 5,348 | 44.72% | 11,957 |
| Carbon | 5,140 | 77.76% | 1,348 | 20.39% | 122 | 1.85% | 3,792 | 57.37% | 6,610 |
| Daggett | 128 | 61.54% | 78 | 37.50% | 2 | 0.96% | 50 | 24.04% | 208 |
| Davis | 3,920 | 67.80% | 1,841 | 31.84% | 21 | 0.36% | 2,079 | 35.96% | 5,782 |
| Duchesne | 1,970 | 63.86% | 1,070 | 34.68% | 45 | 1.46% | 900 | 29.16% | 3,085 |
| Emery | 1,909 | 66.54% | 938 | 32.69% | 22 | 0.77% | 971 | 33.85% | 2,869 |
| Garfield | 928 | 52.37% | 842 | 47.52% | 2 | 0.11% | 86 | 4.85% | 1,772 |
| Grand | 521 | 64.40% | 272 | 33.62% | 16 | 1.98% | 249 | 30.78% | 809 |
| Iron | 1,844 | 56.07% | 1,396 | 42.44% | 49 | 1.49% | 448 | 13.63% | 3,289 |
| Juab | 2,319 | 68.67% | 1,027 | 30.41% | 31 | 0.92% | 1,292 | 38.26% | 3,377 |
| Kane | 395 | 43.03% | 519 | 56.54% | 4 | 0.44% | -124 | -13.51% | 918 |
| Millard | 2,313 | 60.34% | 1,466 | 38.25% | 54 | 1.41% | 847 | 22.09% | 3,833 |
| Morgan | 739 | 60.18% | 483 | 39.33% | 6 | 0.49% | 256 | 20.85% | 1,228 |
| Piute | 611 | 64.25% | 339 | 35.65% | 1 | 0.11% | 272 | 28.60% | 951 |
| Rich | 488 | 55.45% | 388 | 44.09% | 4 | 0.45% | 100 | 11.36% | 880 |
| Salt Lake | 62,386 | 71.77% | 23,819 | 27.40% | 724 | 0.83% | 38,567 | 44.37% | 86,929 |
| San Juan | 520 | 54.11% | 432 | 44.95% | 9 | 0.94% | 88 | 9.16% | 961 |
| Sanpete | 3,959 | 58.67% | 2,738 | 40.57% | 51 | 0.76% | 1,221 | 18.10% | 6,748 |
| Sevier | 2,816 | 59.07% | 1,899 | 39.84% | 52 | 1.09% | 917 | 19.23% | 4,767 |
| Summit | 2,344 | 61.95% | 1,422 | 37.58% | 18 | 0.48% | 922 | 24.37% | 3,784 |
| Tooele | 2,361 | 69.46% | 1,029 | 30.27% | 9 | 0.26% | 1,332 | 39.19% | 3,399 |
| Uintah | 1,986 | 60.96% | 1,193 | 36.62% | 79 | 2.42% | 793 | 24.34% | 3,258 |
| Utah | 14,387 | 69.52% | 6,173 | 29.83% | 135 | 0.65% | 8,214 | 39.69% | 20,695 |
| Wasatch | 1,299 | 55.66% | 1,029 | 44.09% | 6 | 0.26% | 270 | 11.57% | 2,334 |
| Washington | 2,005 | 63.37% | 1,145 | 36.19% | 14 | 0.44% | 860 | 27.18% | 3,164 |
| Wayne | 522 | 61.12% | 329 | 38.52% | 3 | 0.35% | 193 | 22.60% | 854 |
| Weber | 17,594 | 77.08% | 4,989 | 21.86% | 243 | 1.06% | 12,605 | 55.22% | 22,826 |
| Totals | 150,246 | 69.34% | 64,555 | 29.79% | 1,876[lower-alpha 2] | 0.87% | 85,691 | 39.55% | 216,677 |
See also
Notes
- ↑ The others were Clark County, Idaho and Rio Blanco County, Colorado
- 1 2 3 4 These individual third-party totals were not separated by county in any available source.
References
- 1 2 Menendez, Albert J.; The Geography of Presidential Elections in the United States, 1868-2004, p. 47 ISBN 0786422173
- ↑ Sheppard, Si; The Buying of the Presidency?: Franklin D. Roosevelt, the New Deal, and the Election of 1936 (Praeger Series on American Political Culture) , pp. 52-53 ISBN 144083105X
- ↑ Wrobel, David M.; America's West: A History, 1890–1950, p. 139 ISBN 0521150132
- ↑ Murrin, John; Johnson, Paul; McPherson, James; Fahs, Alice and Gerstle, Gary; Liberty, Equality, Power: A History of the American People (Enhanced Concise Edition), p. 151 ISBN 9780495565987
- ↑ Sheppard; The Buying of the Presidency, pp. 191-192
- ↑ Cannon, Brian Q. and Embry, Jessie L. (editors); Utah in the Twentieth Century, pp. 167-169 ISBN 087421744X
- ↑ Sullivan, Robert David; ‘How the Red and Blue Map Evolved Over the Past Century’; America Magazine in The National Catholic Review; June 29, 2016
- ↑ "1936 Presidential General Election Results – Utah". Dave Leip's U.S. Election Atlas. Retrieved 2017-02-13.
- ↑ Scammon, Richard M. (compiler); America at the Polls: A Handbook of Presidential Election Statistics 1920-1964; p. 459 ISBN 0405077114
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)