| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 110 seats in the Landtag of Hesse 56 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 3,450,090 (87.7% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
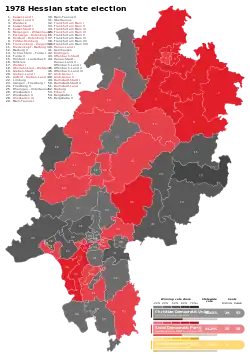 Results for the single-member constituencies. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1978 Hessian state election was held on 8 October 1978 to elect the 9th Landtag of Hesse. The outgoing government was a coalition of the Social Democratic Party (SPD) and Free Democratic Party (FDP) led by Minister-President Holger Börner.
The opposition Christian Democratic Union (CDU) remained the largest party with 46%, but the SPD narrowed the gap with a swing of about one percentage point. The FDP recorded a small decline. Overall, the incumbent coalition retained its majority with a net shift of one seat from the FDP to the SPD, and was renewed for a third term.
Electoral system
The Landtag was elected via mixed-member proportional representation. 55 members were elected in single-member constituencies via first-past-the-post voting, and 55 then allocated using compensatory proportional representation. A single ballot was used for both. An electoral threshold of 5% of valid votes is applied to the Landtag; parties that fall below this threshold are ineligible to receive seats.
Background
In the previous election held on 27 October 1974, the CDU overtook the SPD to become the largest party in Hesse for the first time on a swing of 7.6 percentage points. Despite losses, the incumbent SPD and FDP coalition narrowly retained its majority and was renewed for a second term. On 3 October 1976, incumbent Minister-President Albert Osswald resigned after a financial scandal involving public bank Helaba and was replaced by Kassel's MdB Holger Börner, and the social-liberal coalition continued.
A hot topic was the city of Lahn in Central Hesse, which had been created by the merger of the cities of Giessen and Wetzlar, that were 15 kilometers apart. Osswald, a former Mayor of Giessen, was a supporter of the new city, which was however unpopular with the public, thus leading to SPD losing some support in the center of the state. Despite Lahn being the creation of his party, Börner announced that he would eliminate Lahn and restore the status quo with Giessen and Wetzlar.[1][2]
Parties
The table below lists parties represented in the 8th Landtag of Hesse.
| Name | Ideology | Lead candidate |
1974 result | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes (%) | Seats | |||||
| CDU | Christian Democratic Union of Germany Christlich Demokratische Union Deutschlands |
Christian democracy | Alfred Dregger | 47.3% | 53 / 110 | |
| SPD | Social Democratic Party of Germany Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands |
Social democracy | Holger Börner | 43.2% | 49 / 110 | |
| FDP | Free Democratic Party Freie Demokratische Partei |
Classical liberalism | Ekkehard Gries | 7.4% | 8 / 110 | |
Results
| Party | Votes | % | +/– | Seats | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Con. | List | Total | +– | ||||||
| Christian Democratic Union | 1,575,445 | 46.03 | –1.30 | 29 | 24 | 53 | 0 | ||
| Social Democratic Party | 1,515,953 | 44.29 | +1.13 | 26 | 24 | 50 | +1 | ||
| Free Democratic Party | 225,044 | 6.57 | –0.82 | 0 | 7 | 7 | –1 | ||
| Green List Hesse | 37,758 | 1.10 | New | 0 | 0 | 0 | New | ||
| Green Action Future | 30,787 | 0.90 | New | 0 | 0 | 0 | New | ||
| German Communist Party | 14,531 | 0.42 | –0.46 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| National Democratic Party | 12,507 | 0.37 | –0.65 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Free Voters | 7,452 | 0.22 | New | 0 | 0 | 0 | New | ||
| Communist League of West Germany | 2,638 | 0.08 | –0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| European Workers' Party | 511 | 0.01 | New | 0 | 0 | 0 | New | ||
| Green List Environmental Protection | 274 | 0.01 | New | 0 | 0 | 0 | New | ||
| Justice Party | 39 | 0.00 | New | 0 | 0 | 0 | New | ||
| Action Group Fourth Party | 12 | 0.00 | New | 0 | 0 | 0 | New | ||
| Independents | 16 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | – | 0 | 0 | ||
| Total | 3,422,967 | 100.00 | – | 55 | 55 | 110 | 0 | ||
| Valid votes | 3,422,967 | 99.21 | |||||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 27,123 | 0.79 | |||||||
| Total votes | 3,450,090 | 100.00 | |||||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 3,933,990 | 87.70 | |||||||
External links
- "Final Results for the Landtag election of 8 October 1978" (PDF). Parliamentary Data Bank of the Hessian Landtag (in German). 24 October 1978. Retrieved 15 September 2023.
- "Elections for the 9th Hessian state parliament, October 8, 1978". Hessian Regional History Information System (in German). Retrieved 15 September 2023.
- "The election of the Hessian Landtag on 8 October 1978" (PDF). Parliamentary Data Bank of the Hessian Landtag (in German). 1979. Retrieved 15 September 2023.
Notes
References
- ↑ "Hessen-Wahl: »Es ist unser Kopf, der wackelt«". Der Spiegel (in German). 1978-10-01. ISSN 2195-1349. Retrieved 2023-10-17.
- ↑ "Stadt Lahn: Schnelles Ende einer Großstadt". www.giessener-allgemeine.de (in German). 2019-08-01. Retrieved 2023-10-17.


.jpg.webp)