 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde | |
| Other names
β-Resorcylaldehyde 3,4-dihydroxybenzyl aldehyde[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 878548 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.167 |
| EC Number |
|
| 218304 | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 138.12 g/mol |
| Melting point | 135 °C (275 °F; 408 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 226 °C (439 °F; 499 K)[1] |
| soluble[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[2] | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P264+P265, P270, P271, P280, P301+P317, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P319, P321, P330, P332+P317, P337+P317, P362+P364, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
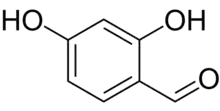
2,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde or β-resorcylaldehyde is a phenolic aldehyde, a chemical compound with the formula C7H6O3. It is an isomer of protocatechuic aldehyde (3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde).
References
- 1 2 3 4 Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. p. 3.190. ISBN 9781498754293.
- ↑ "2,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.