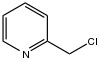
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(Chloromethyl)pyridine | |
| Other names
2-Picolinyl chloride; 2-Picolyl chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H6ClN | |
| Molar mass | 127.57 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 79 °C (174 °F; 352 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H302, H314 | |
| P260, P264, P270, P280, P301+P312+P330, P301+P330+P331, P310, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
2-Chloromethylpyridine is an organohalide that consists of a pyridine core bearing a chloromethyl group. It is one of three isomeric chloromethylpyridines, along with 3- and 4-chloromethylpyridine. It is an alkylating agent. 2-Chloromethylpyridine is a precursor to pyridine-containing ligands.[1][2]
Safety
2-Chloromethylpyridine is an analogue of nitrogen mustards, and has been investigated for its mutagenicity.
References
- ↑ Buhaibeh, Ruqaya; Duhayon, Carine; Valyaev, Dmitry A.; Sortais, Jean-Baptiste; Canac, Yves (2021). "Cationic PCP and PCN NHC Core Pincer-Type Mn(I) Complexes: From Synthesis to Catalysis". Organometallics. 40 (2): 231–241. doi:10.1021/acs.organomet.0c00717. S2CID 234156476.
- ↑ Rapko, B. M.; Duesler, E. N.; Smith, P. H.; Paine, R. T.; Ryan, R. R. (1993). "Chelating Properties of 2-((Diphenylphosphino)methyl)pyridine N,P-dioxide and 2,6-Bis((diphenylphosphino)methyl)pyridine N,P,P'-trioxide Toward f-Element Ions". Inorganic Chemistry. 32 (10): 2164–2174. doi:10.1021/ic00062a047.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.