 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
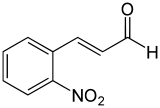
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2E)-3-(2-Nitrophenyl)prop-2-enal | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H7O3N | |
| Appearance | Pale yellow crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 124 to 126 °C (255 to 259 °F; 397 to 399 K) |
| Slightly soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
2-Nitrocinnamaldehyde, ortho-nitrocinnamaldehyde or o-nitrocinnamaldehyde is an organic aromatic compound containing a nitro group ortho- to the 1-position of cinnamaldehyde.
Synthesis
2-Nitrocinnamaldehyde can be synthesized by dissolving cinnamaldehyde to a solution of acetic anhydride in acetic acid, and adding a stoichiometric amount of concentrated nitric acid at 0–5 °C. Yields are around 36-46% of theoretical.
Nitration of cinnamaldehyde via acidification of a nitrate salt with H2SO4 also yields the ortho-nitro compound, however it also yields some of the para-nitro compound, which is generally undesired.
2-Nitrocinnamaldehyde can also be prepared by reacting 2-nitrobenzaldehyde with acetaldehyde in a condensation reaction.[2]
Uses
2-Nitrocinnamaldehyde can be oxidized to 2-nitrocinnamic acid which can be used in the Baeyer-Emmerling indole synthesis to produce indole and substituted indoles.
References
- ↑ http://www.21cnlab.com/chemdict/MSDS/62967.html 2-Nitrocinnamaldehyde MSDS
- ↑ "Organic Syntheses".