2023 in arthropod paleontology is a list of new arthropod fossil taxa, including arachnids, crustaceans, trilobites, and other arthropods (except insects, which have their own list) that were announced or described, as well as other significant arthropod paleontological discoveries and events which occurred in 2023.
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
Chelicerates
Arachnids
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Type locality | Country | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ajkagarypinus[1] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Novák et al. |
Ajka Coal Formation |
A pseudoscorpion belonging to the family Garypinidae. The type species is A. stephani. |
||||
|
Archaeocroton kaufmani[2] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Chitimia-Dobler, Mans & Dunlop in Chitimia-Dobler et al. |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A hard tick. Announced in 2022; the final article version was published in 2023. |
||
|
Archaeoscorpiops grossei[3] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Lourenço in Lourenço & Velten |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A scorpion belonging to the family Palaeoeuscorpiidae. |
||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Dunlop |
Carboniferous (Moscovian) |
Osnabrück Formation |
A spider belonging to the family Arthrolycosidae. |
|||
|
Baltamblyolpium[5] |
Gen. et 2 sp. nov |
Valid |
Stanczak et al. |
Eocene |
A pseudoscorpion belonging to the family Garypinidae. The type species is B. gizmotum from the Baltic amber; genus also includes B. grabenhorsti from the Bitterfeld amber. |
|||
|
Balticonopsis duplo[6] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A spider belonging to the family Anapidae. |
|
|
Betaburmesebuthus fuscus[7] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Xuan, Cai & Huang |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A scorpion belonging to the family Palaeoburmesebuthidae. |
||
|
Betaburmesebuthus villosus[7] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Xuan, Cai & Huang |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A scorpion belonging to the family Palaeoburmesebuthidae. |
||
|
Bothriocroton muelleri[2] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Chitimia-Dobler, Mans & Dunlop in Chitimia-Dobler et al. |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A hard tick. Announced in 2022; the final article version was published in 2023. |
||
|
Cerachipteria ahsokatanoae[8] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Arillo, Subías & Huang |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A mite belonging to the family Achipteriidae. |
||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
||||
|
Chimerarachne patrickmueller[9] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
|||
|
Chimerarachne spiniflagellum[9] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
|||
|
Chthonius marusiki[10] |
Sp. nov |
Turbanov et al. |
Eocene |
Rovno amber |
A pseudoscorpion, a species of Chthonius. |
|||
|
Congovidia glesoconomorphi[11] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Kolesnikov et al. |
Eocene |
Rovno amber |
A mite belonging to the family Hemisarcoptidae |
||
|
?Cornicaraneus unuspedipalpus[9] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A spider belonging to the family Zarqaraneidae. |
||
|
Cretaceousbuthus petersi[12] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Lourenço in Lourenço & Velten |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A scorpion belonging to the superfamily Buthoidea. |
||
|
Cretaceoushormiops elegans[13] |
Sp. nov |
Xuan et al. |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A scorpion belonging to the family Protoischnuridae. |
|||
|
Crethypoctonus[14] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Zhou et al. |
Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) |
Burmese amber |
A member of Uropygi belonging to the family Thelyphonidae. The type species is C. kachinus. |
|||
|
Curvitibia pellucidus[9] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A spider belonging to the family Zarqaraneidae. |
||
|
Electroblemma retroflectum[9] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A spider belonging to the family Tetrablemmidae. |
||
|
Eocryphoeca amputata[6] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A spider belonging to the family Cybaeidae. |
|
|
Eocryphoeca laesa[6] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A spider belonging to the family Cybaeidae. |
|
|
Eognosippus[15] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Dunlop, Erdek & Bartel |
Eocene (Lutetian) |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region, possibly Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia) |
A camel spider. The type species is E. fahrenheitiana. |
|
|
Eomysmauchenius cretaceominimus[16] |
Sp. nov |
Peng et al. |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A spider belonging to the family Archaeidae. |
|||
|
Esuritor duospinae[6] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
||
|
Esuritor nonincisio[6] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A nursery web spider. |
|
|
Esuritor rovnoensis[6] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Rovno amber |
A nursery web spider. |
||
|
Foveacorpus[17] |
Gen. et 2 sp. nov |
Valid |
Bartel, Dunlop & Giribet |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A member of Opiliones belonging to the group Cyphophthalmi. Genus includes F. cretaceus and F. parvus. |
||
|
Gibberaraneoid[9] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A spider, probably a member of the family Zarqaraneidae. The type species is G. furcula. |
||
|
Insecutor angustidentes[6] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A spider belonging to the family Insecutoridae. |
|
|
Insecutor cymbiumseta[6] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A spider belonging to the family Insecutoridae. |
|
|
Kachinblemma[9] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A spider belonging to the family Tetrablemmidae. The type species is K. constrictum. |
||
|
Leptopsalis breyeri[17] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Bartel, Dunlop & Giribet |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A member of Opiliones belonging to the family Stylocellidae. |
||
|
Megamonodontium[18] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
McCurry, Frese & Raven |
Miocene |
McGraths Flat site |
A spider belonging to the family Barychelidae. The type species is M. mccluskyi. |
||
|
Mesopsalis[17] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Bartel, Dunlop & Giribet |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A member of Opiliones belonging to the group Cyphophthalmi. Genus includes M. oblongus. |
||
|
Myanmarmysmena[9] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A spider, possibly a member of the family Mysmenidae. The type species is M. grandipalpus. |
||
|
Nanoaenigma[9] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A spider belonging to the symphytognathidan branch of the Araneoidea, the type genus of the new family Nanoaenigmatidae. The type species is N. pumilio. |
||
|
Opellianus fissura[6] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A spider belonging to the family Uloboridae. |
|
|
Palaeophantes[6] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A spider belonging to the family Linyphiidae. The type species is P. paracymbium. |
|
|
Parakachin[9] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A spider belonging to the family Uloboridae. The type species is P. pectunculus. |
||
|
Parilisthelyphonus[19] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Knecht et al. |
Carboniferous (Moscovian) |
Rhode Island Formation |
A whip scorpion. The type species is P. bryantae. |
|||
|
Parvimegasetae[9] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A spider belonging to the family Megasetidae. The type species is P. araneoides. |
||
|
Promacrothele[20] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Tang, Engel & Yang in Tang et al. |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A spider belonging to the family Macrothelidae. The type species is P. polyacantha. |
|||
|
Protobuthus ziliolii[21] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Viaretti, Bindellini & Dal Sasso |
Middle Triassic |
A scorpion belonging to the superfamily Buthoidea and the family Protobuthidae. |
|||
|
Sarcoptes kutchensis[22] |
Sp. nov |
Agnihotri et al. |
Eocene |
A sarcoptid mite. |
||||
|
Scutcybaeus[6] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A spider belonging to the family Cybaeidae. The type species is S. brevitricha. |
|
|
Scytodes daniloharms[6] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A species of Scytodes. |
|
|
?Scytodes nonalta[9] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
|||
|
Sirocellus[17] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Bartel, Dunlop & Giribet |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A member of Opiliones belonging to the group Cyphophthalmi, with a combination of sironid and stylocellid traits. Genus includes S. iunctus. |
||
|
Spinatibia[6] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A spider belonging to the family Liocranidae. The types species is S. curvitibia. |
|
|
Spinipalpitibia occulta[9] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A spider belonging to the family Protoaraneoididae. |
||
|
Succinaria[6] |
Gen. et 2 sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A spider belonging to the family Cybaeidae. The type species is S. lingua; genus might also include S? adcoccinoidea. |
|
|
Tyrannobunus[23] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Bartel & Dunlop |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A eupnoid harvestman. The type species is T. aculeus. |
||
|
Unguicheylus[24] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Khaustov, Vorontsov & Lindquist |
Cretaceous (Albian–Cenomanian) |
Taimyr amber |
A mite belonging to the new family Unguicheylidae, which might belong to the superfamily Anystoidea. The type species is U. quadriocellatus. |
||
|
Unguistegenaria[6] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wunderlich |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A spider belonging to the family Agelenidae. The type species is U. sinemammillae. |
|
|
Uropodella hoffeinsorum[25] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Lindquist & Vorontsov |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
A mite, a species of Uropodella. |
||
Arachnid research
- New specimens of Compluriscutula vetulum, providing new information on the morphology of this tick, are described from the Cretaceous amber from Myanmar by Chitimia-Dobler et al. (2023).[26]
- Dunlop & Garwood (2023) reevaluate purported Paleozoic scorpion taxa Palaeophonus arctus and Palaeophonus lightbodyi, considering them both to be nomina dubia, and consider the genus Allopalaeophonus to be a junior synonym of the genus Palaeophonus.[27]
- A trigonotarbid arachnid specimen is described from the Carboniferous (Moscovian) Almazna Formation (Donetsk Oblast) by Dunlop & Dernov (2023), extending known distribution of trigonotarbids in Europe.[28]
- A study on the anatomy and affinities of Geralinura brittanica and Proschizomus petrunkevitchi is published by Garwood & Dunlop (2023), who reinterpret P. petrunkevitchi as a whip scorpion rather than a stem-schizomid.[29]
- Probable new specimen of Mesoproctus rowlandi, representing the first fossil whip scorpion specimen preserved with book lungs, is described from the Lower Cretaceous Crato Formation (Brazil) by Alberto et al. (2023).[30]
- The first known male specimen of Strotarchus paradoxus is described from the Miocene Mexican amber by García-Villafuerte & Ibarra-Núñez (2023).[31]
- A study on the phylogenetic relationships of extant and fossil members of Palpimanoidea is published by Wood & Wunderlich (2023), who interpret their findings as indicative of closer relationships of palpimanoids from the Cretaceous amber from Myanmar with the Gondwanan taxa, and indicative of dispersal of Gondwanan lineages through the Burma Terrane into the Holarctic in the Cretaceous.[32]
- Richardson, McCurry & Frese (2023) describe fossil material of a member of the genus Simaetha from the Miocene of Australia, interpreted as consistent with the molecular-based studies indicating that the radiation of the astioid jumping spiders at the Oligocene/Miocene transition happened in Australasia.[33]
Eurypterids
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Type locality | Country | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Archopterus[34] |
Gen et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wang et al. |
Ordovician |
Wenchang Formation |
Likely the oldest adelophthalmid. |
||
Eurypterid research
- Braddy (2023) reviews evidence for the predatory abilities of pterygotid eurypterids, and interprets them as likely slow swimming vagrant and ambush predators, with different taxa adapted to feeding on different types of prey.[35]
- Bicknell, Kenny & Plotnick (2023) present a new, three-dimensional reconstruction of Acutiramus.[36]
Xiphosurans
Xiphosuran research
- A study on the evolution of the developmental patterns of xiphosurans is published by Lustri et al. (2023), who find evidence of changes in the allometric growth of xiphosurans related to adaptations to different environments, but also report that the studied changes were relatively minor compared to the diversity of patterns of allometric growth observed in eurypterids and chasmataspidids.[37]
- Klompmaker et al. (2023) describe a specimen of Limulitella bronnii from the Anisian Muschelkalk sediments of the Vossenveld Formation (Netherlands), extending known temporal range of this species, and provide the diagnosis of L. bronnii for the first time.[38]
Other chelicerates
- Siveter et al. (2023) describe two new specimens of Haliestes dasos from the Silurian Coalbrookdale Formation (United Kingdom), interpret their anatomy as indicative of adaptation of the studied species to a different mode of feeding than in living sea spiders, as well as possibly indicative of the presence of sexual dimorphism, and assign H. dasos to the stem group rather than the crown group of Pycnogonida.[39]
- Revision of the Callovian sea spider taxa from the La Voulte-sur-Rhône (France) is published by Sabroux et al. (2023), who assign the studied fossil to Pantopoda, crown-group Pycnogonida, assign Palaeopycnogonides gracilis to the new family Palaeopycnogonididae, and interpret Colossopantopodus boissinensis and Palaeoendeis elmii as members of the families Colossendeidae and Endeidae, respectively.[40]
General chelicerate research
Crustaceans
Malacostracans
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Type locality | Country | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Albaidaplax[41] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Garassino, Pasini & Castro |
Pliocene to early Pleistocene |
A goneplacid crab. The type species is Albaidaplax ispalensis. Announced in 2013;[42] validated in 2023. |
|||
|
Annieporcellana paleocenica[43] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Yost, Feldmann & Schweitzer |
Paleocene |
A member of Galatheoidea belonging to the family Catillogalatheidae. |
|||
|
Anthracophausia rheamsi[44] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Vohs, Feldmann & Schweitzer |
Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) |
A malacostracan of uncertain affinities. |
|||
|
Austropotamobius plenicari[45] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Gašparič et al. |
Miocene (Messinian) |
A species of Austropotamobius. |
|||
|
Bahiacaris[46] |
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Schweitzer et al. |
Early Cretaceous (Aptian) |
A caridean shrimp; a new genus for "Atyoida" roxoi Beurlen (1950). Announced in 2019;[47] validated in 2023. |
|||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
De Mazancourt, Wappler & Wedmann |
Eocene |
Possibly a member of the family Palaemonidae. Announced in 2022; the correction including evidence of registration in ZooBank was published in 2023.[49] |
||||
|
Bericorystes[50] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
De Angeli |
Eocene |
A crab belonging to the family Corystidae. The type species is B. caporiondoi. |
|||
|
Bournelyreidus paredonensis[51] |
Sp. nov |
Vega, Nyborg & Garassino |
Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) |
A crab belonging to the family Lyreididae. |
||||
|
Braggicarpilius wanzenboecki[52] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Miller, Schweitzer & Feldmann |
Paleocene |
Kambühel Formation |
A crab belonging to the family Carpiliidae. |
||
|
Callianassa ocozocoautlaensis[53] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Hyžný, Vega & Coutiño |
Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) |
A member of Callianassidae, a species of Callianassa (sensu lato). Announced in 2013;[54] validated in 2023. |
|||
|
Campanaxius[55] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Nyborg, Hyžný & Haggart |
Late Cretaceous (Campanian) |
A member of Axiidea. The type species is C. raffi. |
|||
|
Cancer zameniscus[56] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Feldmann, Schweitzer & Casadío |
Miocene |
A species of Cancer. |
|||
|
Chaceon marcorilobus[56] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Feldmann, Schweitzer & Casadío |
Miocene |
A species of Chaceon. |
|||
|
Cherusius marangoni[50] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
De Angeli |
Eocene |
A crab belonging to the family Domeciidae. |
|||
|
Coahuilanina[51] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Vega, Nyborg & Garassino |
Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) |
Potrerillos Formation |
A crab belonging to the family Raninidae. The type species is C. difuntaensis. |
|||
|
Chronocancer[57] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Santana et al. |
Early Cretaceous (Aptian-Albian) |
A crab, probably a member of the family Orithopsidae. The type species is C. camilosantanai. Announced in 2022 in an online-only journal, and the publication did not include a ZooBank registration number;[58] validated in 2023. |
|||
|
Corystites orgianensis[50] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
De Angeli |
Eocene |
A crab belonging to the family Corystidae. |
|||
|
Costacopluma squiresi[59] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Nyborg, Vega & Filkorn |
Paleocene |
A retroplumid crab. Announced in 2009;[60] validated in 2023. |
|||
|
Cretacocalcinus fortis[61] |
Sp. nov |
Ferratges & Zamora in García-Penas et al. |
Early Cretaceous |
Maestrazgo Basin |
A hermit crab. |
|||
|
Cretalamoha[62] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Nyborg, Garassino & Vega |
Late Cretaceous (Campanian) |
A member of Homolidae. The type species is C. boweni. Announced in 2017;[63] validated in 2023. |
|||
|
Cugocaris[64] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Liu et al. |
Silurian |
Fentou Formation |
A member of Phyllocarida belonging to the group Archaeostraca. Genus includes new species C. future. |
||
|
Dardanus cyprioticus[65] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wallaard et al. |
Miocene (Serravallian-Messinian) |
Pakhna Formation |
A species of Dardanus. |
||
|
Dardanus plevrotos[65] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wallaard et al. |
Miocene (Serravallian-Messinian) |
Pakhna Formation |
A species of Dardanus. |
||
|
Diaulax rosablanca[66] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Gómez-Cruz, Bermúdez & Vega |
Early Cretaceous (Valanginian) |
||||
|
Dinocarcinus[68] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Van Bakel et al. |
Late Cretaceous (late Campanian) |
A crab, a member of Portunoidea sensu lato. The type species is D. velauciensis. Announced in 2019;[69] validated in 2023. |
|||
|
Disspinamithrax[56] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Feldmann, Schweitzer & Casadío |
Oligocene |
A member of the family Mithracidae. The type species is D. santacruzensis. |
|||
|
Dromiopsis aedicula[52] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Miller, Schweitzer & Feldmann |
Paleocene |
Kambühel Formation |
A crab belonging to the family Dromiidae. |
||
|
Dromiopsis bullamelga[52] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Miller, Schweitzer & Feldmann |
Paleocene |
Kambühel Formation |
A crab belonging to the family Dromiidae. |
||
|
Dubiostenopus[70] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Alencar et al. |
Early Cretaceous (Aptian-Albian) |
A member of Stenopodidea of uncertain affinities. The type species is D. parvus. |
|||
|
Enoploclytia tepeyacensis[71] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Vega, Garassino & Zapata-Jaime |
Late Cretaceous (Campanian) |
An erymid, a species of Enoploclytia. Announced in 2013;[72] validated in 2023. |
|||
|
Eobooralana[73] |
Gen. et comb. nov |
Schädel, Nagler & Hyžný |
Middle Jurassic (Callovian) |
An isopod belonging to the group Scutocoxifera. The type species is "Urda" rhodanica Van Straelen (1928). |
||||
|
Eomunidopsis kinokunica[74] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Karasawa, Ohara & Kato |
Early Cretaceous (Barremian) |
Arida Formation |
A member of the family Galatheidae. Announced in 2008 in an online-only journal, prior to electronic-only publications being allowed under ICZN; validated in 2023.[74] |
||
|
Eoparanaxia[75] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Ferratges et al. |
Eocene |
Pamplona Marls Formation |
A crab belonging to the family Epialtidae and the subfamily Pisinae. The type species is E. eocenica. |
||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Karasawa, Ohara & Kato |
Early Cretaceous (Barremian) |
Arida Formation |
Announced in 2008 in an online-only journal, prior to electronic-only publications being allowed under ICZN; validated in 2023.[74] |
|||
|
Eurynome bandurriasensis[56] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Feldmann, Schweitzer & Casadío |
Miocene |
A member of the family Majidae. |
|||
|
Garrafosopon[76] |
Gen. et comb. nov |
Ossó, van Bakel & Artal in Ossó et al. |
Early Cretaceous (Aptian) |
The type species is G. angustus (Wright & Collins, 1972) |
||||
|
Gladiocaris[77] |
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Garassino et al. |
Middle Triassic |
A member of the family Penaeidae. Genus includes "Antrimpos" germanicus Brandt & Schulz (2013) |
|||
|
Sp. nov |
Charbonnier, Garassino & López-Horgue |
Early Jurassic (Pliensbachian–Toarcian) |
||||||
|
Gonatocaris wuhanensis[64] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Liu et al. |
Silurian |
Fentou Formation |
A member of Phyllocarida belonging to the group Archaeostraca. |
||
|
Hepatus beurleni[79] |
Nom. nov |
Valid |
Lima et al. |
Miocene |
Pirabas Formation |
A species of Hepatus; a replacement name for Cyclocancer tuberculatus Beurlen (1958). |
||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Karasawa, Ohara & Kato |
Early Cretaceous (Barremian) |
Arida Formation |
Announced in 2008 in an online-only journal, prior to electronic-only publications being allowed under ICZN; validated in 2023.[74] |
|||
|
Iberodorippe[76] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Ossó, van Bakel & Artal in Ossó et al. |
Early Cretaceous (Aptian) |
The type species is I. vinea. |
||||
|
Jaliscosphaera[80] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
García-Vázquez, Alvarado-Ortega & Vega |
An isopod belonging to the family Sphaeromatidae. The type species is J. pliocenica. |
|||||
|
Laeviprosopon ewakrzeminskae[81] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Starzyk et al. |
Late Jurassic (Tithonian) |
A crab belonging to the family Homolidae. |
|||
|
Laeviprosopon joecollinsi[81] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Starzyk et al. |
Late Jurassic (Oxfordian) |
A crab belonging to the family Homolidae. |
|||
|
Laeviprosopon lanceatum[81] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Starzyk et al. |
Late Jurassic (Oxfordian) |
A crab belonging to the family Homolidae. |
|||
|
Litorepagurus[82] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Fraaije et al. |
Early Cretaceous (Albian) |
A hermit crab. Genus includes new species L. wissantensis. |
|||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Charbonnier et al. |
Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) |
A member of the family Mecochiridae. |
||||
|
Meroncarcinus[84] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
In press |
Van Bakel & Guinot |
Middle Jurassic (Callovian) |
A crab belonging to the family Glaessneropsidae. The type species is M. boursicoti. |
|||
|
Mesodromilites prietoi[76] |
Sp. nov |
Ossó, van Bakel & Artal in Ossó et al. |
Early Cretaceous (Aptian) |
|||||
|
Mesolambrus vallionensis[50] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
De Angeli |
Eocene |
A crab belonging to the family Parthenopidae. |
|||
|
Metacirolana jimlowryi[85] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Bruce & Rodcharoen |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
An isopod belonging to the family Cirolanidae. |
||
|
Metanephrops serendipitus[86] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Gašparič et al. |
Miocene |
A species of Metanephrops. Announced in 2021;[87] validated in 2023. |
|||
|
Meyeria hurtrelleorum[88] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Charbonnier et al. |
Late Jurassic (Oxfordian) |
A member of the family Mecochiridae. |
|||
|
Miohepatus amazonicus[79] |
Comb. nov |
Valid |
Lima et al. |
Miocene |
Pirabas Formation |
A crab belonging to the family Aethridae. Moved from Hepatella amazonica Beurlen (1958). The type species of the new genus Miohepatus, which also includes extant species Miohepatus peruvianus (originally Hepatella peruviana Rathbun, 1933) |
||
|
Mutotylaspis[89] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Fraaije et al. |
Early Cretaceous (Albian) |
A hermit crab belonging to the family Probeebeidae. The type species is M. tripudium. |
||||
|
Necrocarcinus gorbenkoi[90] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Mychko et al. |
Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) |
Lyamino Formation |
A crab belonging to the group Raninoida. |
||
|
Necrocarcinus mariae[76] |
Sp. nov |
Ossó, van Bakel & Artal in Ossó et al. |
Early Cretaceous (Aptian) |
|||||
|
Nectocarcinus verruculus[56] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Feldmann, Schweitzer & Casadío |
Miocene |
||||
|
Ophthalmoplax andina[91] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Guzmán et al. |
Late Cretaceous (Campanian) |
Lodolitas de Aguacaliente Formation |
A member of Macropipidae, a species of Ophthalmoplax. Announced in 2016;[92] validated in 2023. |
||
|
Oregonina[93] |
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Nyborg, Garassino & Nyborg |
Eocene |
Yamhill Formation |
A lyreidid crab. |
||
|
Osonacarcinus[94] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Artal, Onetti & Ossó |
Eocene (Lutetian) |
A crab belonging to the family Pseudoziidae. The type species is O. lenis. |
|||
|
Ostenosculda[95] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Braig et al. |
Early Jurassic |
A mantis shrimp belonging to the group Unipeltata. The type species is O. teruzzii. |
|||
|
Paguristes timoni[96] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wallaard et al. |
Miocene |
A hermit crab, a species of Paguristes. |
|||
|
Pagurus? garrafensis[76] |
Sp. nov |
Ossó, van Bakel & Artal in Ossó et al. |
Early Cretaceous (Aptian) |
A hermit crab, possibly a species of Pagurus. |
||||
|
Pagurus hazenorum[96] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wallaard et al. |
Miocene |
St. Marys Formation |
A hermit crab, a species of Pagurus. |
||
|
Palaega yamadai[74] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Karasawa, Ohara & Kato |
Early Cretaceous (Barremian) |
Arida Formation |
An isopod belonging to the family Cirolanidae. Announced in 2008 in an online-only journal, prior to electronic-only publications being allowed under ICZN; validated in 2023.[74] |
||
|
Palaeodromites pimientai[61] |
Sp. nov |
Ferratges & Zamora in García-Penas et al. |
Early Cretaceous |
Maestrazgo Basin |
A crab. |
|||
|
Palaeosynaxes[97] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Fraaije et al. |
Late Jurassic (Oxfordian) |
A furry lobster. The type species is P. montserratae. |
|||
|
Paromola roseburgensis[98] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Nyborg, Garassino & Vega |
Early Eocene |
A member of Homolidae. Announced in 2017;[63] validated in 2023. |
|||
|
Percnon paleogenicus[50] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
De Angeli |
Eocene |
A species of Percnon. |
|||
|
Petersbuchia[99] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Schweigert |
Treuchtlingen Formation |
A crab belonging to the group Homolodromioidea and the family Prosopidae. The type species is P. thauckei. Announced in 2021 in an online-only journal;[100] validated in 2023.[99] |
|||
|
Petrolisthes mitseroensis[65] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wallaard et al. |
Miocene (Serravallian-Messinian) |
Pakhna Formation |
A species of Petrolisthes. |
||
|
Phrynolambrus sagittalis[101] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Ferratges et al. |
Eocene |
Pamplona Formation |
A crab belonging to the family Parthenopidae and the subfamily Dairoidinae. |
||
|
Pirabacarcinus[102] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Lima et al. |
Miocene |
Pirabas Formation |
A crab belonging to the family Pilumnidae. The type species is P. iara. |
|||
|
Planobranchia elongata[75] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Ferratges et al. |
Eocene |
Pamplona Marls Formation |
A crab belonging to the family Epialtidae and the subfamily Pisinae. |
||
|
Protomunida kambuehelensis[43] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Yost, Feldmann & Schweitzer |
Paleocene |
Kambühel Formation |
A member of the family Munididae. |
||
|
Pseudoglyphea anisica[103] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Pasini, Garassino & Charbonnier |
Middle Triassic (Anisian) |
A litogastrid lobster. |
|||
|
Rogueus belgodereae[104] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Van Bakel, Ossó & Téodori |
Paleocene (Thanetian) |
A crab belonging to the group Raninoidea and the family Lyreididae. |
|||
|
Sandiegocalcinus[105] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Nyborg, Fraaije & Dunbar |
Pliocene (Piacenzian) |
A hermit crab belonging to the family Calcinidae. Genus includes new species S. calvanoi. |
|||
|
Somalis[106] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Barros & de Oliveira |
Early Cretaceous (Aptian-Albian) |
A member of Penaeoidea. The type species is S. piauiensis. |
|||
|
Soomicaris ordosensis[107] |
Sp. nov |
Liu et al. |
Ordovician |
Lashizhong Formation |
A member of Phyllocarida belonging to the group Archaeostraca and the family Caryocarididae. |
|||
|
Spinirostrimaia echinata[75] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Ferratges et al. |
Eocene |
Pamplona Marls Formation |
A crab belonging to the family Majidae. |
||
|
Squamipelta[43] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Yost, Feldmann & Schweitzer |
Paleocene |
Kambühel Formation |
A hermit crab belonging to the family Annuntidiogenidae. The type species is S. insecta. |
||
|
Tanaidaurum[108] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Pazinato, Müller & Haug |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A member of Tanaidacea. The type species is T. kachinensis. |
||
|
Tanidromites maerteni[109] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Fraaije et al. |
Middle Jurassic (Bajocian) |
A tanidromitid crab. Announced in 2013;[110] validated in 2023. |
|||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Smith, Charbonnier, Fara & Brayard in Smith et al. |
Early Triassic |
A mantis shrimp belonging to the group Unipeltata. The type species is T. ahyongi. |
||||
|
Trichopeltarion ryouheii[112] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Kato in Kato et al. |
Miocene |
Kosho Formation |
A member of the family Trichopeltariidae. |
||
|
Urda buechneri[73] |
Sp. nov |
Schädel, Nagler & Hyžný |
Middle Jurassic (Bajocian) |
An isopod belonging to the group Scutocoxifera. |
||||
|
Urda stemmerbergensis[73] |
Comb. nov |
(Malzahn) |
Early Cretaceous (Hauterivian) |
An isopod belonging to the group Scutocoxifera. Moved from "Palaega" stemmerbergensis Malzahn (1968). |
||||
|
Urda suevica[73] |
Comb. nov |
(Reiff) |
Early Jurassic (Pliensbachian) |
An isopod belonging to the group Scutocoxifera. Moved from "Palaega" suevica Reiff (1936). |
||||
|
Verrucarcinus marsae[84] |
Sp. nov |
In press |
Van Bakel & Guinot |
Middle Jurassic (Callovian) |
A crab belonging to the family Glaessneropsidae. |
|||
|
Viapagurus[61] |
Gen. et comb. nov |
Ferratges & Zamora in García-Penas et al. |
Early Cretaceous |
Maestrazgo Basin |
A hermit crab. The type species is "Pagurus" avellanedai Vía (1951). |
|||
|
Vilsercarcinus[84] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
In press |
Van Bakel & Guinot |
Jurassic (Toarcian-Callovian) |
Austria-Germany border area |
A crab belonging to the family Glaessneropsidae. The type species is V. keuppi. |
||
|
Xanthosia sakoi[74] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Karasawa, Ohara & Kato |
Early Cretaceous (Barremian) |
Arida Formation |
A member of the family Etyidae. Announced in 2008 in an online-only journal, prior to electronic-only publications being allowed under ICZN; validated in 2023.[74] |
||
Malacostracan research
- Chény, Charbonnier & Audo (2023) reexamine the fossil record of lobsters from the Middle Jurassic of Normandy (France), providing evidence of the presence of sexual dimorphism in Glyphea dressieri and proposing the first reconstruction of this lobster.[113]
- Klompmaker et al. (2023) report the discovery of a specimen of Secretanella sp. from a Campanian methane seep in South Dakota (United Kingdom) preserved with parts of its internal anatomy, including the first esophagus preserved in a fossil decapod reported to date.[114]
- New specimen of Eogeryon elegius, providing new information on the anatomy of this crab, is described from the Cenomanian Villa de Vés Formation (Spain) by Ossó (2023).[115]
- Putative hypothalassiid Lathahypossia aculeata is reinterpreted as a xanthid by Ossó & Ng (2023).[116]
- A specimen of Araripenaeus timidus with a swelling on its carapace which might be indicative of infestation by bopyrid isopods is described from the Lower Cretaceous Romualdo Formation (Brazil) by Lima et al. (2023), representing the oldest evidence of parasitism in marine dendrobranchiate shrimps reported to date.[117]
- New solenocerid, glypheid and mecochirid fossil material is reported from the upper Callovian sites of the Ryazan Region (Russia) by Dadykin & Shmakov (2023).[118]
- A study on the extinction and survival of the decapod crustacean groups during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event is published by Schweitzer & Feldmann (2023).[119]
Ostracods
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Type locality | Country | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Acratia xinjiangensis[120] |
Sp. nov |
Luo et al. |
Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) |
|||||
|
Aechmina iwatensis[121] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Tanaka |
Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) |
Nagaiwa Formation |
|||
|
Bairdia dukanensis[122] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Hawramy, Al-Obidee & Aziz |
Late Cretaceous |
Shiranish Formation |
A member of the family Bairdiidae. |
||
|
Bairdoppilata shiranishensis[122] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Hawramy, Al-Obidee & Aziz |
Late Cretaceous |
Shiranish Formation |
A member of the family Bairdiidae. |
||
|
Bungonibeyrichia treslata[123] |
Sp. nov |
In press |
Camilleri, Weldon & Warne |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Woori Yallock Formation |
A member of Palaeocopida belonging to the group Beyrichicopina and the family Craspedobolbinidae. |
||
|
Buntonia whittakerensis[124] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Khosla et al. |
Late Cretaceous-Paleocene transition |
||||
|
Calocaria callundosa[125] |
Sp. nov |
Perrier et al. |
Silurian (Přídolí) |
A myodocope ostracod. |
||||
|
Cutympanum[126] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
In press |
Williams et al. |
Si Ka Formation |
A glossomorphitine hollinoidean ostracod. Genus includes new species C. hagiangensis. |
|||
|
Cyprideis calchaquiensis[127] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Zamudio & Carignano |
Miocene |
A member of the family Cytherideidae. |
|||
|
Cyprideis qattaraensis[128] |
Sp. nov |
Shahin, El Khawagah & Shahin |
||||||
|
Cytherella indica[129] |
Sp. nov |
Kumari |
Middle Jurassic |
Jaisalmer Formation |
A species of Cytherella. The name is shared with Cytherella indica Neale & Singh (1986). |
|||
|
Cytheropteron tesakovae[130] |
Sp. nov |
Karpuk |
Early Cretaceous (Barremian–Aptian) |
Crimea |
A member of Podocopida belonging to the family Paradoxostomatidae. The specific name is shared with Cytheropteron tesakovae Kempf (2011). |
|||
|
Damonella medialtis[131] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Santos Filho et al. |
Early Cretaceous |
||||
|
Healdia ofunatensis[121] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Tanaka |
Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) |
Nagaiwa Formation |
|||
|
Healdia rikutyuensis[121] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Tanaka |
Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) |
Nagaiwa Formation |
|||
|
Healdianella shiqianensis[120] |
Sp. nov |
Luo et al. |
Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) |
|||||
|
Hornibrookella nudosa[122] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Hawramy, Al-Obidee & Aziz |
Late Cretaceous |
Shiranish Formation |
A member of the family Hemicytheridae. |
||
|
Ideluralia[132] |
Nom. nov |
Valid |
Antonietto & Brandão |
Devonian |
A member of the family Bairdiidae; a replacement name for Bairdiella Egorova (1960). |
|||
|
Jordanites michinokuensis[121] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Tanaka |
Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) |
Nagaiwa Formation |
|||
|
Judahella kangpla[133] |
Sp. nov |
Forel & Chitnarin |
Late Triassic (Carnian) |
Kang Pla Formation |
||||
|
Limnocythere martensi[124] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Khosla et al. |
Late Cretaceous-Paleocene transition |
Deccan Intertrappean Beds |
A species of Limnocythere. |
||
|
Liuzhinia phetchabunensis[134] |
Sp. nov |
Forel & Chitnarin |
Permian |
|||||
|
Looneyellopsis? sagittensis[131] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Santos Filho et al. |
Early Cretaceous |
||||
|
Microceratina andreui[135] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Cabral & Lord in Danielopol et al. |
São Gião Formation |
A member of the family Cytheruridae. |
|||
|
Micropneumatocythere joyanensis[129] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Kumari |
Middle Jurassic |
Jaisalmer Formation |
|||
|
Monspopulus[126] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
In press |
Williams et al. |
Silurian |
Si Ka Formation |
A sigmoopsine hollinoidean ostracod. Genus includes new species M. amicus. |
||
|
Neomonoceratina farasensis[128] |
Sp. nov |
Shahin, El Khawagah & Shahin |
||||||
|
Pattersoncypris trapezium[131] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Santos Filho et al. |
Early Cretaceous |
||||
|
Platyrhomboides japonica[121] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Tanaka |
Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) |
Nagaiwa Formation |
|||
|
Platyrhomboides tohokuensis[121] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Tanaka |
Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) |
Nagaiwa Formation |
|||
|
Progonocythere khoslai[129] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Kumari |
Middle Jurassic |
Jaisalmer Formation |
|||
|
Pseudobythocypris asiatica[121] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Tanaka |
Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) |
Nagaiwa Formation |
|||
|
Pseudobythocypris siveteri[121] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Tanaka |
Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) |
Nagaiwa Formation |
|||
|
Pseudobythocypris zipangu[121] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Tanaka |
Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) |
Nagaiwa Formation |
|||
|
Thuringobolbina ikeyai[121] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Tanaka |
Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) |
Nagaiwa Formation |
|||
|
Trichordis minuta[129] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Kumari |
Middle Jurassic |
Jaisalmer Formation |
|||
|
Zonocypris penchi[124] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Khosla et al. |
Late Cretaceous-Paleocene transition |
Deccan Intertrappean Beds |
|||
Ostracod research
Thecostracans
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Type locality | Country | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Calvatilepas[136] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Gale & Vidovic |
Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) |
Grey Chalk Subgroup |
A barnacle belonging to the group Balanomorpha and the family Brachylepadidae. The type species is C. recurvus. |
||
|
Crithmumlepas[136] |
Gen. et 2 sp. nov |
Valid |
Gale & Vidovic |
Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian to Coniacian) |
Grey Chalk Subgroup |
A barnacle belonging to the group Balanomorpha and the family Brachylepadidae. The type species is C. hoensis; genus also includes C. aycliffensis. |
||
|
Eolepas carniensis[137] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Gale et al. |
Late Triassic (Carnian) |
Grabfeld Formation |
A barnacle belonging to the family Eolepadidae. |
||
|
Eoverruca barringtonensis[136] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Gale & Vidovic |
Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) |
West Melbury Formation |
A barnacle belonging to the group Verrucomorpha and the family Eoverrucidae. |
||
|
Pedupycnolepas lamellatus[136] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Gale & Vidovic |
Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) |
West Melbury Formation |
A barnacle belonging to the group Verrucomorpha and the family Pycnolepadidae. |
||
|
Protochelonibia hermani[138] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Gale in De Schutter et al. |
Oligocene (Rupelian) |
Boom Formation |
A barnacle belonging to the family Chelonibiidae. |
||
|
Pycnolepas batchelorum[136] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Gale & Vidovic |
Early Cretaceous (Aptian) |
Bargate Formation |
A barnacle belonging to the group Verrucomorpha and the family Pycnolepadidae. |
||
Thecostracan research
Other crustaceans
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Type locality | Country | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Carapacestheria cangshanensis[139] |
Sp. nov |
In press |
Li |
Late Jurassic |
A clam shrimp. |
|||
|
Malayacyclus[140] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Tang et al. |
A member of Cyclida. Genus includes new species M. terengganuensis. Announced in 2021;[141] validated in 2023. |
||||
|
Triglypta jiyuanensis[142] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Liao & Huang in Liao et al. |
Late Jurassic |
Maao Formation |
A clam shrimp. |
||
Other crustacean research
- Li (2023) redescribes the type material of Anyuanestheria subquadrata and emends its diagnosis.[143]
General crustacean research
Insects
Megacheirians
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Type locality | Country | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Megacheirian research
Radiodonts
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Type locality | Country | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Paterson, García-Bellido & Edgecombe |
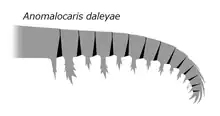 | |||||
|
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Paterson, García-Bellido & Edgecombe |
Cambrian Stage 4 |
A member of the family Tamisiocarididae. The type species is "Anomalocaris" briggsi Nedin (1995). |
 | |||
|
Gen. et comb. nov |
Zhang et al. |
Wulongqing Formation |
An amplectobeluid radiodont. The type species is "Anomalocaris" kunmingensis Wang, Huang & Hu (2013). |
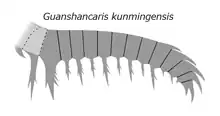 | ||||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Potin, Gueriau & Daley |
Ordovician (Tremadocian) |
A suspension feeding hurdiid radiodont within new subfamily Aegirocassisinae. |
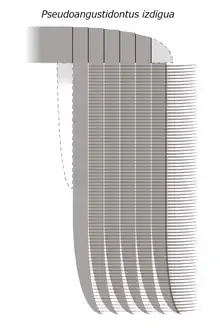 | |||
Radiodont research
- A study on molting patterns and ontogeny in Stanleycaris is published by Moysiuk & Caron (2023), who find evidence for two distinct fossil types of Stanleycaris (carcasses and molted exoskeletal remains), interpret their findings as confirming that radiodonts grew by periodic ecdysis, and consider the general pattern of molting in Stanleycaris to be likely shared with other radiodonts and possibly with other early arthropods.[147]
- A study on the functional capabilities and hydrodynamic performance of the frontal appendages of Anomalocaris canadensis is published by Bicknell et al. (2023), who interpret their findings as indicating that A. canadensis targeted soft-bodied prey.[148]
- A study on the development of the frontal appendage of Amplectobelua symbrachiata is published by Wu et al. (2023), who interpret their findings as indicative of rapid growth.[149]
Trilobites
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Type locality | Country | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Aaraecoryphe[150] |
Gen. et sp. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
A member of the family Tropidocoryphidae. The type species is A. hermanni; genus also includes "Wolayella" celox Šnajdr (1980). |
|||
|
Anderssonella undulata[151] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wernette & Hughes in Wernette et al. |
Cambrian (Furongian) |
Ao Mo Lae Formation |
A member of Asaphida belonging to the family Dikelocephalidae. |
||
|
Arisemolobes[152] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Ingham & Fortey |
Ordovician |
Charchaq Group |
A member of Asaphida belonging to the group Cyclopygoidea and the family Ellipsotaphridae. Genus includes new species A. zhouzhiyii. |
||
|
Asaphellus charoenmiti[151] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wernette & Hughes in Wernette et al. |
Ordovician (Tremadocian) |
Talo Wao Formation |
A member of the family Asaphidae. |
||
|
Asaphellus zheni[153] |
Sp. nov |
In press |
Smith & Allen |
Ordovician (Floian) |
Nambeet Formation |
A member of the family Asaphidae. |
||
|
Sp. nov |
Kerber et al. |
Devonian |
||||||
|
Branikarges[150] |
Nom. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian |
A member of the family Lichidae; a replacement name for Lobopyge Přibyl & Erben (1952). The type species is "Lichas" branikensis Barrande (1872). |
|||
|
Buttsia trema[155] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Westrop & Eoff |
Cambrian (Jiangshanian) |
Shallow Bay Formation |
|||
|
Carnicaspis[150] |
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Silurian |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. The type species is "Radiaspis" pecten Santel (2001). |
|||
|
Catinouyia heyunensis[156] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Sun et al. |
Burgasutay Formation |
||||
|
Caznaia imsamuti[151] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wernette & Hughes in Wernette et al. |
Cambrian (Furongian) |
Ao Mo Lae Formation |
A member of Asaphida belonging to the family Dikelocephalidae. |
||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian |
Greifenstein Limestone |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. |
|||
|
Ceratocephala hoerriana[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian |
Greifenstein Limestone |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. |
||
|
Ceratocephala martinii[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Shale |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. |
||
|
Ceratocephalina angustifurcata[157] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Feist & Clarkson |
Silurian |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. |
|||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Limestone |
A member of the family Phacopidae. |
|||
|
Chotecops braunfelsensis[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Limestone |
A member of the family Phacopidae. |
||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Ingham & Fortey |
Ordovician |
Myoch Formation |
||||
|
Corbinia perforata[151] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wernette & Hughes in Wernette et al. |
Ordovician (Tremadocian) |
Talo Wao Formation |
A member of the family Eurekiidae. |
||
|
Crassibole kore[158] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Müller & Hahn |
Carboniferous (Viséan) |
Hillershausen Formation |
|||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Flick & Flick |
Devonian (Eifelian) |
A member of Proetida belonging to the family Aulacopleuridae and the subfamily Otarioninae. |
||||
|
Devononeseuretus[160] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Alberti |
Devonian |
A member of Phacopida belonging to the family Calymenidae and the subfamily Reedocalymeninae. The type species is D. beichti. |
|||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Limestone |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
|||
|
Diademaproetus frankschmidti[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Shale |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
||
|
Diademaproetus holzapfeli ahrensi[150] |
Ssp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Limestone |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Lemke |
Devonian (Famennian) |
Wocklum Limestone |
||||
|
Eoleonaspis maeander[157] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Feist & Clarkson |
Silurian (Homerian) |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. |
|||
|
Funeralaspis[162] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Adrain & Pérez-Peris |
Ordovician (Dapingian) |
An odontopleurine trilobite. The type species is F. deathvalleyensis. |
|||
|
Ignoproetus bohatyi[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Limestone |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
||
|
Jiia talowaois[151] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wernette & Hughes in Wernette et al. |
Ordovician (Tremadocian) |
Talo Wao Formation |
A member of Asaphida belonging to the family Remopleurididae. |
||
|
Karslanus leishuae[163] |
Sp. nov |
Peng et al. |
Cambrian (Guzhangian) |
Longha Formation |
||||
|
Kettneraspis acanthifrons[157] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Feist & Clarkson |
Silurian (Homerian) |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. |
|||
|
Kettneraspis anteflexa[157] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Feist & Clarkson |
Silurian (Homerian) |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. |
|||
|
Kettneraspis loehnbergensis[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Shale |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. |
||
|
Kettneraspis rojanensis[157] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Feist & Clarkson |
Silurian (Homerian) |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. |
|||
|
Koneprusia morrisoni[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Shale |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. |
||
|
Koneprusites aarae[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Eifelian) |
Günterod Limestone |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
||
|
Koneprusites lahnae[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Limestone |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
||
|
Laethoprusia augur[157] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Feist & Clarkson |
Silurian (Homerian) |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. |
|||
|
Lahnops postmahrheckam[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Shale |
A member of the family Phacopidae. |
||
|
Leishuia[164] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
In press |
Peng et al. |
Longha Formation |
A dameselloid trilobite. Genus includes new species L. leishuae. |
|||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Shale |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. |
|||
|
Lophosaukia nuchanongi[151] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wernette & Hughes in Wernette et al. |
Cambrian (Furongian) |
Ao Mo Lae Formation |
A member of Asaphida belonging to the family Dikelocephalidae. |
||
|
Lorrettina waterhousei[165] |
Sp. nov |
Smith |
Cambrian (Jiangshanian) |
Goyder Formation |
A dokimocephalid trilobite. |
|||
|
Macroblepharum leunense[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Limestone |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
||
|
Madiganaspis lauriei[153] |
Sp. nov |
In press |
Smith & Allen |
Ordovician (Floian) |
Nambeet Formation |
A member of the family Asaphidae. |
||
|
Mitroplax[166] |
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Holloway |
Devonian (Pragian to Emsian) |
Norton Gully Sandstone |
A scutelluid trilobite. The type species is "Bronteus" enormis Etheridge (1894). |
||
|
Monocheilus reginae[167] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Blackwell & Westrop |
Cambrian (Jiangshanian) |
Honey Creek Formation |
A member of the family Eurekiidae. |
||
|
Monocheilus richardi[167] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Blackwell & Westrop |
Cambrian (Jiangshanian) |
Honey Creek Formation |
A member of the family Eurekiidae. |
||
|
Norasaphus (Norasaphus) jagoi[153] |
Sp. nov |
In press |
Smith & Allen |
Ordovician (Floian) |
Nambeet Formation |
A member of the family Asaphidae. |
||
|
Comb. nov |
(Rusconi) |
Cambrian (Guzhangian) |
Moved from Cancapolia proa Rusconi (1954). |
|||||
|
Omegops honggulelengensis[169] |
Sp. nov |
Junior synonym |
Zong |
Devonian (Famennian) |
A phacopid trilobite. Subsequently considered to be a junior synonym of Omegops mobilis (Xiang, 1981) by Zong (2023).[170] |
|||
|
Omegops xiangi[169] |
Sp. nov |
Junior synonym |
Zong |
Devonian (Famennian) |
A phacopid trilobite. Subsequently considered to be a junior synonym of Clarksonops junggariensis Crônier in Crônier and Waters (2022) by Zong (2023), resulting in a new combination Omegops junggariensis.[170] |
|||
|
Orbitoproetus ager[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Limestone |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Korovnikov |
Cambrian |
Kuonamka Formation |
||||
|
Oryctocephalus molodoensis[171] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Korovnikov |
Cambrian |
Kuonam formation |
|||
|
Otarion hetairos[159] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Flick & Flick |
Devonian (Eifelian) |
A member of Proetida belonging to the family Aulacopleuridae and the subfamily Otarioninae. |
|||
|
Pagodia? uhleini[151] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wernette & Hughes in Wernette et al. |
Cambrian (Furongian) |
Ao Mo Lae Formation |
A member of Corynexochida belonging to the group Leiostegiina and the family Leiostegiidae. |
||
|
Perunaspis mathesii[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Limestone |
A member of the family Lichidae. |
||
|
Phaetonellus naspae[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Limestone |
A member of the family Tropidocoryphidae. |
||
|
Plesiowensus erraticus[172] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Schöning |
Silurian |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
|||
|
Pseudokoldinioidia maneekuti[151] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wernette & Hughes in Wernette et al. |
Cambrian (Furongian) |
Ao Mo Lae Formation |
A member of Corynexochida belonging to the group Leiostegiina and the family Missisquoiidae. |
||
|
Ptychaspis matuszaki[167] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Blackwell & Westrop |
Cambrian (Jiangshanian) |
Fort Sill Formation |
A member of the family Ptychaspididae. |
||
|
Ptychaspis occulta[167] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Blackwell & Westrop |
Cambrian |
A member of the family Ptychaspididae. |
|||
|
Pulcherproetus brandenborchnova[172] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Schöning |
Silurian |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
|||
|
Pulcherproetus inexspectatus[172] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Schöning |
Silurian |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
|||
|
Pulcherproetus laerheidensis[172] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Schöning |
Silurian |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
|||
|
Pulcherproetus maennilae[172] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Schöning |
Silurian |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
|||
|
Pulcherproetus schranki[172] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Schöning |
Silurian |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
|||
|
Pulcherproetus sutherbergensis[172] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Schöning |
Silurian |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
|||
|
Pulcherproetus trachyglossus[172] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Schöning |
Silurian |
A member of the family Proetidae. |
|||
|
Rabienops borkewehrensis[161] |
Sp. nov |
Basse & Lemke |
Devonian (Famennian) |
Wocklum Limestone |
A member of the family Phacopidae. Basse & Lemke (2023) did not exclude the possibility of the synonymy with R. evae.[161] |
|||
|
Rabienops dxv[161] |
Sp. nov |
Basse & Lemke |
Devonian (Famennian) |
Wocklum Limestone |
A member of the family Phacopidae. Basse & Lemke (2023) did not exclude the possibility of the synonymy with R. evae.[161] |
|||
|
Radiaspis guenterodensis[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. |
|||
|
Radiaspis knoppi[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian |
Greifenstein Limestone |
A member of the family Odontopleuridae. |
||
|
Sp. nov |
Wei et al. |
Ordovician (Katian) |
Koumenzi Formation |
|||||
|
Rheicarges[150] |
Gen. et comb. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian |
A member of the family Lichidae. The type species is "Lichas" decheni Holzapfel (1895); genus also includes "Lobopyge" niobe Basse (1998) and a new species R. schneideri. |
|||
|
Rodingaia leggi[153] |
Sp. nov |
In press |
Smith & Allen |
Ordovician (Floian) |
Nambeet Formation |
A member of the family Asaphidae. |
||
|
Sanbernardaspis excalibur[153] |
Sp. nov |
In press |
Smith & Allen |
Ordovician (Tremadocian) |
Nambeet Formation |
A member of the family Asaphidae. |
||
|
Signatoproetus[172] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Schöning |
Silurian |
A member of the family Proetidae. Genus includes new species S. wiedae. |
|||
|
Spinicryphops wocklumeriae[161] |
Comb. nov |
Valid |
(Richter & Richter) |
Devonian (Famennian) |
Wocklum Limestone |
A member of the family Phacopidae. Moved from Phacops (Cryphops?) wocklumeriae Richter & Richter (1926). |
||
|
Struveaspis haigeriana[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian |
Wissenbach Shale |
A member of the family Phacopidae. |
||
|
Struveaspis liuunensis[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Limestone |
A member of the family Phacopidae. |
||
|
Synaptotaphrus[152] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Ingham & Fortey |
Ordovician |
Myoch Formation |
A member of Asaphida belonging to the group Cyclopygoidea and the family Ellipsotaphridae. Genus includes new species S. oarion. |
||
|
Tarutaoia[151] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wernette & Hughes in Wernette et al. |
Ordovician (Tremadocian) |
Talo Wao Formation |
A member of Asaphida belonging to the family Remopleurididae. The type species is T. techawani. |
||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Limestone |
A member of the family Scutelluidae. |
|||
|
Triorygma[155] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Westrop & Eoff |
Cambrian (Jiangshanian) |
Shallow Bay Formation |
Genus includes new species T. burkhalteri. |
||
|
Tropidocoryphe hesseniana[150] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Basse & Müller |
Devonian (Emsian) |
Leun Limestone |
A member of the family Tropidocoryphidae. |
||
|
Tsinania sirindhornae[151] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Wernette & Hughes in Wernette et al. |
Cambrian (Furongian) |
Ao Mo Lae Formation |
A member of Corynexochida belonging to the group Illaenina and the family Tsinaniidae. |
||
|
Vandergrachtia vandergrachtii carsteni[158] |
Ssp. nov |
Valid |
Müller & Hahn |
Carboniferous (Viséan) |
Hillershausen Formation |
|||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
In press |
Smith & Allen |
Ordovician (Tremadocian) |
Nambeet Formation |
A member of the family Bathyuridae. The type species is V. jelli. |
|||
|
Zhiyia[174] |
Gen. et comb. nov |
Valid |
Wei & Zhou |
Ordovician (Floian) |
Duoquanshan Formation |
A member of the family Asaphidae belonging to the subfamily Isotelinae. The type species is "Isotelus" tsinghaiensis Chang & Fan (1960); genus also includes "Niobe (Niobella)" obscura Zhou & Zhou (2019). |
||
Trilobite research
- Evidence indicating that a mechanism similar to the molecular activator/inhibitor mechanism present in vertebrates and known as the inhibitory cascade had controls on segment size development in trilobites is presented by Nikolic, Hopkins & Evans (2023).[175][176]
- A study on the timing of the appearance of trilobite planktic larvae is published Laibl, Saleh & Pérez-Peris (2023), who interpret their findings as indicating that Cambrian ecosystems were dominated by trilobites with exclusively benthic early post-embryonic stages, and that a progressive increase in the number of trilobite taxa that incorporated planktic stages in their development happened between the Miaolingian and the Middle Ordovician.[177]
- A study on the disparity of trilobite cephalic structures across Cambrian Series 2, providing evidence that the development of disparity of various cephalic structures was constrained in different ways, is published by Holmes (2023).[178]
- A study on the morphology and evolutionary relationships of Duyunaspis duyunensis, D. jianheensis and Balangia balangensis from the Cambrian Balang and Tsinghsutung formations (China) is published by Chen et al. (2023), who report evidence of gradual evolution indicative that Balangia was more likely to be an ancestor of Duyunaspis rather than its descendant.[179]
- Taxonomic revision of the species belonging to the genus Abadiella is published by Wang, Peng & Zhang (2023), who consider Parabadiella, Guangyuanaspis and Parabadiella (Danangouia) to be junior junior synonyms of Abadiella, and consider the species A. huoi and A. bourgini to have wide geographic distribution in Gondwana, making stratigraphical correlations between various Gondwana regions based on Cambrian trilobites possible.[180]
- A study on the morphology, ontogeny and systematics of Walcottaspis vanhornei is published by Srivastava & Hughes (2023).[181]
- Hou, Hughes & Hopkins (2023) report the presence of setae on the walking legs of the Cambrian Olenoides serratus and on the gill shaft of the Ordovician Triarthrus eatoni, and interpret these setae as likely used to groom the gills of the trilobites.[182]
- Evidence of the presence of countercurrent gaseous exchange mechanism in the gills of Triarthrus eatoni is presented by Hou et al. (2023).[183]
- A study on the taphonomy of the Ordovician trilobites from the Walcott–Rust quarry (New York, United States) is published by Losso, Thines & Ortega-Hernández (2023), who report evidence indicating that fine-grained sediment supported the preservation of delicate appendages and facilitated their fossilization.[184]
- A study on the morphology of the ventral part of the exoskeletons of trilobites from the Walcott–Rust quarry, providing evidence of adaptations facilitating complete enrolment convergent with those present in extant arthropods, is published by Losso et al. (2023).[185]
- Laibl et al. (2023) describe early developmental stages of at least nine trilobite species from the Fezouata Formation (Morocco), providing new information on the development of early Ordovician trilobites.[186]
- Schoenemann & Clarkson (2023) describe specimens of Aulacopleura koninckii and Cyclopyge sibilla preserved with structures interpreted as likely median eyes, and interpret this finding as indicating that early developmental stages of trilobites possessed median eyes (probably unlike adult specimens).[187]
- A study on the impact of changes of body shape and construction of Aulacopleura koninckii during its growth on changes of the style of its enrolment is published by Esteve & Hughes (2023), who find that the change in enrolment style happening at the onset of mature growth made it possible for A. koninckii to assume defensive posture regardless of the variation in the number of mature trunk segments of specimens belonging to the studied species.[188]
- A study on the hydrodynamics of Microparia speciosa, indicating that it had a high stability in the water column when it was enrolled, is published by Esteve & López-Pachón (2023).[189]
- Kraft et al. (2023) describe a specimen of Bohemolichas incola from the Darriwilian Šárka Formation (Czech Republic) preserved with fossilized gut contents, providing evidence of adaptation of the studied trilobite to feeding on organic remains including shells, and probably of digestive enzymes similar to those in modern crustaceans or chelicerates.[190]
- Gishlick & Fortey (2023) describe a specimen of Walliserops trifurcatus with a malformed cephalic trident showing four rather than three tines, and consider its anatomy to be consistent with the interpretation of the trident as a weapon used for intraspecific combat.[191]
- Fossil evidence confirming the survival of encrinurid trilobites into the earliest Devonian is reported from the Wutubulake and Mangeer formations (China) by Ma et al. (2023).[192]
- A study on the impact of the Late Devonian extinctions on the taxonomic and morphological diversity of trilobites, and on the trilobite recovery after the extinction events, is published by Bault (2023).[193]
- A study on the locomotion of trilobites, based on data from three-dimensional models, is published by Esteve & Rubio (2023), who find evidence for two main gait types reflecting burrowing and walking, as well as evidence indicating that the body structure constrained speed and lifestyles of trilobites.[194]
- A study on changes of the morphological diversity of phacopid trilobites throughout their evolutionary history is published by Bault et al. (2023).[195]
- Park (2023) examined trilobite specimens and shown that hypostome is fusion of anterior sclerite and labrum.[196]
Other arthropods
| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Type locality | Country | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Austriocaris secretanae[197] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Laville, Forel & Charbonnier |
Middle Jurassic (Callovian) |
||||
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Briggs et al. |
Silurian (Wenlock) |
A member of Artiopoda belonging to the group Vicissicaudata. The type species is C. neptuni. |
 | ||||
|
Cotalagnostus greilingi[199] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Weidner, Nielsen & Ebbestad |
Cambrian (Miaolingian) |
A member of Agnostoidea belonging to the family Spinagnostidae. |
|||
|
Cretojapyx[200] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Wang, Huang & Cai |
Cretaceous (Albian to Cenomanian) |
Burmese amber |
A member of Diplura belonging to the family Japygidae. The type species is C. huangi. |
||
|
Electroprojapyx[201] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Sánchez-García et al. |
Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) |
Burmese amber |
A member of Diplura belonging to the family Projapygidae. The type species is E. alchemicus. |
||
|
Lauravolsella[202] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Haug, Fraaije & Haug |
Carboniferous (Westphalian) |
A millipede, possibly belonging to the group Archipolypoda. The type species is L. willemeni. |
|||
|
Lepidocampa glaesi[203] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Sánchez-García, Sendra & Grimaldi in Sánchez-García et al. |
Miocene |
Dominican amber |
A member of Diplura belonging to the family Campodeidae. |
||
|
Lithopendra[204] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Haug, Haug & Haug |
Cretaceous |
Burmese amber |
A centipede belonging to the group Pleurostigmophora. The type species is L. anjafliessae. |
||
|
Litocampa eobaltica[203] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Sánchez-García, Sendra & Grimaldi in Sánchez-García et al. |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A member of Diplura belonging to the family Campodeidae, a species of Litocampa. |
|
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Zong et al. |
Silurian (Pridoli) |
|||||
|
Paraclausocaris[197] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Laville, Forel & Charbonnier |
Middle Jurassic (Callovian) |
La Voulte-sur-Rhône Lagerstätte |
A thylacocephalan. The type species is P. harpa. |
||
|
Propolydesmus cretaceus[206] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Su, Cai & Huang |
Cretaceous (Albian to Cenomanian) |
Burmese amber |
A millipede belonging to the family Polydesmidae. |
||
|
Rostricampa[203] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Sánchez-García, Sendra & Grimaldi in Sánchez-García et al. |
Miocene |
Dominican amber |
A member of Diplura belonging to the family Campodeidae. The type species is R. engeli. |
||
|
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Zhu et al. |
Yu'anshan Formation |
|||||
|
Sidneyia minor[208] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Du et al. |
Cambrian Stage 3 |
 | |||
|
Symphylurinopsis[201] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Sánchez-García et al. |
Miocene |
Dominican amber |
A member of Diplura belonging to the family Projapygidae. The type species is S. punctatus. |
||
|
Theatops groehni[209] |
Sp. nov |
Valid |
Edgecombe et al. |
Eocene |
Baltic amber |
Europe (Baltic Sea region) |
A centipede belonging to the family Plutoniumidae. |
|
|
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Berks et al. |
A member of Artiopoda. The type species is T. tholops. |
| ||||
|
Tonglaiia[207] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Zhu et al. |
Cambrian Stage 3 |
Yu'anshan Formation |
A member of Artiopoda of uncertain affinities. The type species is T. bispinosa. |
||
|
Zhugeia[207] |
Gen. et sp. nov |
Valid |
Zhu et al. |
Cambrian Stage 3 |
Yu'anshan Formation |
A member of Artiopoda belonging to the group Xandarellida. The type species is Z. acuticaudata. |
||
- New information on the anatomy of Kylinxia zhangi, indicating that its head was composed of six segments (as in extant mandibulates), is presented by O'Flynn et al. (2023), who interpret their findings as indicating that a six-segmented head was already present in the last common ancestor of Kylinxia and the euarthropod crown group.[211]
- Redescription of Isoxys curvirostratus, incorporating data from new fossil material from the Cambrian Chiungchussu Formation (China) and focusing on the biramous appendages of this arthropod, is published by Zhang et al. (2023), who report that the appendage differentiation in Isoxys was higher than previously considered, that the trunk of I. curvirostratus was not arthrodized, and that Isoxys was one of the earliest branching members of Deuteropoda.[212]
- A study on the ontogeny of Isoxys minor, based on data from specimens from the Cambrian Shuijingtuo formation (China), is published by Ma et al. (2023), who interpret the studied fossil material as indicative of only slight morphological differences between the specimens of I. minor which might have been caused by different environment, indicative of the presence of brood care in I. minor, and well as indicative of reproductive ability at the early life stages of this arthropod.[213]
- Pates & Zamora (2023) report the discovery of arthropod carapaces representing at least two taxa (including a tuzoiid) from the Cambrian (Drumian) Murero Formation (Spain), and interpret this finding as possibly indicating that Cambrian bivalved euarthropods living at higher latitudes were larger than those from low latitudes.[214]
- New fossil material of Acanthomeridion serratum, providing new information on the anatomy of members of this species, is described by Du et al. (2023), who interpret A. anacanthus as a junior synonym of A. serratum, and interpret dorsal cephalic sutures of trilobites as more likely to have multiple origins within Artiopoda rather than a single, deep origin.[215]
- Drage, Legg & Daley (2023) describe exuviae from a marrellid marrellomorph from the Ordovician Fezouata Formation (Morocco), providing evidence of moulting behaviour distinct from that described for Marrella splendens.[216]
- A study on the morphology of early developmental stages of marrellids from the Fezouata Formation is published by Laibl et al. (2023), who report that adults and immature individuals shares the same general appendage differentiation, and avoided direct competition for food resources only by feeding on particles of different size.[217]
- New information on the anatomy of Concavicaris woodfordi, including the structure of the shield, the circulatory, digestive and reproductive systems, and the appendages, is presented by Laville et al. (2023).[218]
- Wellman et al. (2023) present data supporting a Silurian (late Wenlock) age of the "Lower Old Red Sandstone" deposits of the Midland Valley (Scotland, United Kingdom) preserving the fossil material of Pneumodesmus newmani, supporting the interpretation of this myriapod as the oldest known air-breathing land animal.[219]
- New information on the morphology of the Carboniferous millipedes Amynilyspes fatimae and Blanziulus parriati from the Montceau-les-Mines Lagerstätte (France) is presented by Lheritier et al. (2023).[220]
General research
- New, diverse fossil material of radiodonts (including indeterminate hurdiids) and euarthropods (including Thelxiope cf. T. palaeothalassia, Perspicaris? dilatus, Branchiocaris pretiosa, Tuzoia retifera, T. guntheri, Dioxycaris argenta, bradoriids and a possible indeterminate species of Naraoia) is described from the Cambrian (Wuliuan) Spence Shale (Idaho and Utah, United States) by Kimmig et al. (2023).[221]
- Naimark, Sizov & Khubanov (2023) report the discovery of a new assemblage of Cambrian arthropods from the Kimiltei site (Irkutsk Oblast, Russia), including the first records of members of Euthycarcinoidea and Synziphosurina from the Siberian platform and the first Cambrian record of Chasmataspidida from this platform.[222]
- Braddy (2023) describes a resting trace of a phyllocarid crustacean from the Miaolingian Hickory Sandstone Member of the Riley Formation (Texas, United States), names a new ichnotaxon Minterichnus shieldi, and reinterprets the arthropod body fossil associated with the resting trace as a phyllocarid rather than the oldest known chasmataspidid.[223]
References
- ↑ Novák, J.; Harvey, M. S.; Szabó, M.; Hammel, J. U.; Harms, D.; Kotthoff, U.; Hörweg, C.; Brazidec, M.; Ősi, A. (2023). "A new Mesozoic record of the pseudoscorpion family Garypinidae from Upper Cretaceous (Santonian) Ajkaite amber, Ajka area, Hungary". Cretaceous Research. 105709. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2023.105709.
- 1 2 Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Dunlop, J. A.; Pfeffer, T.; Würzinger, F.; Handschuh, S.; Mans, B. (2022). "Hard ticks in Burmese amber with Australasian affinities". Parasitology. 150 (2): 157–171. doi:10.1017/S0031182022001585. PMC 10090639. PMID 36341553. S2CID 253382440.
- ↑ Lourenço, W. R.; Velten, J. (2023). "A second species of Archaeoscorpiops Lourenço, 2015 from Cretaceous Burmese amber (Scorpiones: Palaeoeuscorpiidae)". Faunitaxys. 11 (57): 1–4. doi:10.57800/faunitaxys-11(57).
- ↑ Dunlop, J. A. (2023). "The first Palaeozoic spider (Arachnida: Araneae) from Germany". PalZ. 97 (3): 497–504. doi:10.1007/s12542-023-00657-7. S2CID 259941358.
- ↑ Stanczak, N.; Harvey, M. S.; Harms, D.; Hammel, J. U.; Kotthoff, U.; Loria, S. F. (2023). "A new pseudoscorpion genus (Garypinoidea: Garypinidae) from the Eocene supports extinction and range contraction in the European paleobiota". PeerJ. 11. e15989. doi:10.7717/peerj.15989. PMC 10637241.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Wunderlich, J. (2023). "Contribution to the fossil spider (Araneida) fauna in Eocene Baltic and Rovno amber" (PDF). In Jörg Wunderlich (ed.). Beiträge zur Araneologie, 16. Joerg Wunderlich. pp. 113–161.
- 1 2 Xuan, Q.; Cai, C.Y.; Huang, D.Y. (2023). "Revision of palaeoburmesebuthid scorpions in mid-Cretaceous amber from northern Myanmar (Scorpiones: Buthoidea)". Palaeoentomology. 6 (1): 64–101. doi:10.11646/palaeoentomology.6.1.10. S2CID 257247707.
- ↑ Arillo, A.; Subías, L. S.; Huang, D.Y. (2023). "Oribatid mites in Burmese amber I. First record of the family Achipteriidae (Acariformes, Oribatida) in Cretaceous amber, with the description of a new species of Cerachipteria Grandjean, 1935". Palaeoentomology. 6 (5): 443–446. doi:10.11646/palaeoentomology.6.5.1.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Wunderlich, J. (2023). "Contribution to the spider (Araneida: Araneae and Chimerarachnida) fauna in Upper (Mid) Cretaceous Burmese (Kachin) amber" (PDF). In Jörg Wunderlich (ed.). Beiträge zur Araneologie, 16. Joerg Wunderlich. pp. 162–215.
- ↑ Turbanov, I. S.; Kolesnikov, V. B.; Vorontsov, D. D.; Vasilenko, D. V.; Perkovsky, E. E. (2023). "Chthonius marusiki sp. nov. – the first pseudoscorpion of the family Chthoniidae Daday, 1889 (Arachnida, Pseudoscorpiones) from the late Eocene Rovno amber". Historical Biology: An International Journal of Paleobiology. doi:10.1080/08912963.2023.2266821.
- ↑ Kolesnikov, V. B.; Vorontsov, D. D.; Perkovsky, E. E.; Vasilenko, D. V.; Klimov, P. B. (2023). "Confocal autofluorescence microscopy revealed the fine morphology of the amber preserved mite Congovidia glesoconomorphi sp. nov. (Acari: Hemisarcoptidae) phoretic on a mycterid beetle". Palaeoentomology. 6 (6): 665–678. doi:10.11646/palaeoentomology.6.6.8.
- ↑ Lourenço, W. R.; Velten, J. (2023). "Confirmation of the validity of the genus Cretaceousbuthus Lourenço, 2022 and description of a new species from Burmite (Scorpiones: Buthoidea: Buthidae)". Faunitaxys. 11 (35): 1–6. doi:10.57800/faunitaxys-11(35).
- ↑ Xuan, Q.; Cai, C.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, D. (2023). "A new species of Cretaceoushormiops from the mid-Cretaceous amber of northern Myanmar (Arachnida: Scorpiones: Protoischnuridae)". PalZ. doi:10.1007/s12542-023-00673-7.
- ↑ Zhou, L.-J.; Wang, H.; Jarzembowski, E. A.; Xiao, C. (2023). "A new genus of whip scorpion (Arachnida: Thelyphonida: Thelyphonidae) from mid-Cretaceous Kachin amber of northern Myanmar". Cretaceous Research. 105702. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2023.105702.
- ↑ Dunlop, J. A.; Erdek, M.; Bartel, C. (2023). "A new species of camel spider (Arachnida: Solifugae) in Baltic amber". Arachnology. 19 (4): 772–776. doi:10.13156/arac.2023.19.4.772. S2CID 257632799.
- ↑ Peng, Y.; Shi, C.; Long, X.; Engel, M. S.; Wang, S. (2023). "Discovery of a new species of Eomysmauchenius from mid-Cretaceous Kachin amber (Araneae: Archaeidae)". Cretaceous Research. 105703. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2023.105703.
- 1 2 3 4 Bartel, C.; Dunlop, J. A.; Giribet, G. (2023). "An unexpected diversity of Cyphophthalmi (Arachnida: Opiliones) in Upper Cretaceous Burmese amber". Zootaxa. 5296 (3): 421–445. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5296.3.6. PMID 37518436. S2CID 258964248.
- ↑ McCurry, M. R.; Frese, M.; Raven, R. (2023). "A large brush-footed trapdoor spider (Mygalomorphae: Barychelidae) from the Miocene of Australia". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlad100.
- ↑ Knecht, R. J.; Benner, J. S.; Dunlop, J. A.; Renczkowski, M. D. (2022). "The largest Palaeozoic whip scorpion and the smallest (Arachnida: Uropygi: Thelyphonida); a new species and a new ichnospecies from the Carboniferous of New England, USA". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlad088.
- ↑ Tang, Y.-N.; Peng, A.-C.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Engel, M. S.; Yang, Z.-Z.; Liu, Y. (2023). "Mygalomorph spiders in mid-Cretaceous Kachin amber (Araneae: Mygalomorphae), northern Myanmar: a new genus and species of the family Macrothelidae". Cretaceous Research. 147. 105514. Bibcode:2023CrRes.14705514T. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2023.105514. S2CID 257306643.
- ↑ Viaretti, M.; Bindellini, G.; Dal Sasso, C. (2023). "A new Mesozoic scorpion from the Besano Formation (Middle Triassic, Monte San Giorgio UNESCO WHL), Italy". PalZ. 97 (3): 505–517. doi:10.1007/s12542-023-00659-5. S2CID 259917687.
- ↑ Agnihotri, P.; Singh, H.; Subramanian, K. A.; Acharya, S. (2023). "Scanning electron microscopy of Sarcoptes kutchensis, a new species of a Middle Eocene sarcoptid mite in amber from the Umarsar Lignite Mine of Kutch, Western India". Historical Biology: An International Journal of Paleobiology. doi:10.1080/08912963.2023.2281579.
- ↑ Bartel, C.; Dunlop, J. A. (2023). "First eupnoid harvestmen (Arachnida: Opiliones: Eupnoi) from mid-Cretaceous Kachin amber, with notes on sexual dimorphism in Halitherses grimaldii (Arachnida: Opiliones: Dyspnoi)". Palaeoentomology. 6 (3): 278–291. doi:10.11646/palaeoentomology.6.3.11. S2CID 259732838.
- ↑ Khaustov, A. A.; Vorontsov, D. D.; Lindquist, E. E. (2023). "Unguicheylidae fam. nov., a new fossil family of prostigmatic mites (Acari: Prostigmata) from the Cretaceous Taimyr amber". Systematic and Applied Acarology. 28 (4): 766–776. doi:10.11158/saa.28.4.12. S2CID 258377428.
- ↑ Lindquist, E. E.; Vorontsov, D. D. (2023). "Uropodella (Acari: Mesostigmata: Sejidae), mites unchanged from Eocene past to Holocene present". Acarologia. 63 (2): 346–355. doi:10.24349/y1ey-edzd. S2CID 257800454.
- ↑ Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Pfeffer, T.; Würzinger, F.; Handschuh, S.; Dunlop, J. A. (2023). "New larval records of the extinct hard tick Compluriscutula vetulum (Arachnida: Ixodida) from Burmese amber, with notes on its morphology". Palaeoworld. doi:10.1016/j.palwor.2023.10.002.
- ↑ Dunlop, J. A.; Garwood, R. J. (2023). "The status of two fossils assigned to the scorpion genus Palaeophonus and its interpretation as a senior synonym of Allopalaeophonus". Arachnology. 19 (6): 940–943. doi:10.13156/arac.2023.19.6.940.
- ↑ Dunlop, J. A.; Dernov, V. S. (2023). "The first trigonotarbid arachnid from Ukraine". Acta Geologica Polonica. 73 (2): 181–187. doi:10.24425/agp.2022.143600. S2CID 259699027.
- ↑ Garwood, R. J.; Dunlop, J. A. (2023). "X-ray microtomography of the late Carboniferous whip scorpions (Arachnida, Thelyphonida) Geralinura britannica and Proschizomus petrunkevitchi". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 21 (1). 2180450. doi:10.1080/14772019.2023.2180450. S2CID 257976364.
- ↑ Alberto, G. M.; Bezerra, F. I.; Giupponi, A. P. L.; Mendes, M. (2023). "A new specimen of whip scorpion (Arachnida; Thelyphonida) from the Crato Formation, Lower Cretaceous of Brazil". Revista Brasileira de Paleontologia. 26 (3): 147–155. doi:10.4072/rbp.2023.3.01.
- ↑ García-Villafuerte, M. Á.; Ibarra-Núñez, G. (2023). "The male of Strotarchus paradoxus (Petrunkevitch, 1963) (Araneae: Cheiracanthiidae), a fossil spider from Chiapas, Mexico". Acta Zoológica Mexicana. nueva serie. 39. e3912588. doi:10.21829/azm.2023.3912588. S2CID 258453853.
- ↑ Wood, H. M.; Wunderlich, J. (2023). "Burma Terrane Amber Fauna Shows Connections to Gondwana and Transported Gondwanan Lineages to the Northern Hemisphere (Araneae: Palpimanoidea)". Systematic Biology. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syad047. PMID 37527553.
- ↑ Richardson, B. J.; McCurry, M. R.; Frese, M. (2023). "Description and evolutionary biogeography of the first Miocene jumping spider (Aranaea: Salticidae) from a southern continent". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlad105.
- ↑ Wang, H.; Braddy, S. J.; Botting, J.; Zhang, Y. (2023). "The first documentation of an Ordovician eurypterid (Chelicerata) from China". Journal of Paleontology. 97 (3): 606–611. doi:10.1017/jpa.2023.21. S2CID 258623960.
- ↑ Braddy, S. J. (2023). "Pterygotid eurypterid palaeoecology: praedichnia and palaeocommunities". Bulletin of Geosciences. 98 (4): 289–302. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1891.
- ↑ Bicknell, R. D. C.; Kenny, K.; Plotnick, R. E. (2023). "Ex vivo three-dimensional reconstruction of Acutiramus: a giant pterygotid sea scorpion". American Museum Novitates. 4004: 1–20. doi:10.1206/4004.1. hdl:2246/7335.
- ↑ Lustri, L.; Antcliffe, J. B.; Saleh, F.; Haug, C.; Laibl, L.; Garwood, R. J.; Haug, J. T.; Daley, A. C. (2023). "New perspectives on the evolutionary history of xiphosuran development through comparison with other fossil euchelicerates". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. 11. 1270429. doi:10.3389/fevo.2023.1270429.
- ↑ Klompmaker, A. A.; van Eldijk, T. J. B.; Winkelhorst, H.; Reumer, J. W. F. (2023). "A non-marine horseshoe crab from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) of the Netherlands". Netherlands Journal of Geosciences. 102. e1. doi:10.1017/njg.2022.16. S2CID 255547401.
- ↑ Siveter, D. J.; Sabroux, R.; Briggs, D. E. G.; Siveter, D. J.; Sutton, M. D. (2023). "Newly discovered morphology of the Silurian sea spider Haliestes and its implications". Papers in Palaeontology. 9 (5). e1528. doi:10.1002/spp2.1528.
- ↑ Sabroux, R.; Edgecombe, G. D.; Pisani, D.; Garwood, R. J. (2023). "New insights into the sea spider fauna (Arthropoda, Pycnogonida) of La Voulte-sur-Rhône, France (Jurassic, Callovian)". Papers in Palaeontology. 9 (4). e1515. doi:10.1002/spp2.1515. S2CID 260180232.
- ↑ Garassino, A.; Pasini, G.; Castro, P. (2023). "Validation of Albaidaplax ispalensis Garassino, Pasini & Castro, a fossil goneplacid crab from Spain and Italy (Crustacea: Decapoda: Goneplacidae)". Zootaxa. 5318 (2): 297–298. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5318.2.12. PMID 37518380. S2CID 260013794.
- ↑ Garassino, A.; Pasini, G.; Castro, P. (2013). "Revision of the fossil species of Goneplax Leach, 1814 (Crustacea, Decapoda, Brachyura, Goneplacidae)". Boletín de la Sociedad Geológica Mexicana. 65 (2): 355–368. doi:10.18268/BSGM2013v65n2a16.
- 1 2 3 Yost, S. L.; Feldmann, R. M.; Schweitzer, C. E. (2023). "New Decapoda (Anomura) from the Paleocene Kambühel Formation, Austria" (PDF). Annalen des Naturhistorischen Museums in Wien, Serie A. 124: 149–166. JSTOR 27213513.
- ↑ Vohs, A.; Feldmann, R. M.; Schweitzer, C. E. (2023). "A new Late Carboniferous shrimp-like crustacean from the Gwin Coal Seam, Alabama, U.S.A.". Bulletin of the Mizunami Fossil Museum. 50 (1): 69–75. doi:10.50897/bmfm.50.1_69.
- ↑ Gašparič, R.; Audo, D.; Kawai, T.; Kolar-Jurkovšek, T.; Marinšek, M.; Jurkovšek, B. (2023). "A new species of Austropotamobius Skorikov, 1907 (Decapoda: Astacidae: Astacidae) from the late Miocene (Messinian) of Slovenia, with remarks on the evolution of European crayfishes". Journal of Crustacean Biology. 43 (4). ruad058. doi:10.1093/jcbiol/ruad058.
- ↑ Schweitzer, C. E.; Santana, W.; Pinheiro, A.; Feldmann, R. M. (2023). "Validation of Bahiacaris Schweitzer, Santana, Pinheiro & Feldmann (Crustacea, Decapoda, Caridea) from the Cretaceous (Aptian) of Brazil". Zootaxa. 5318 (2): 299–300. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5318.2.13. PMID 37518379. S2CID 260020820.
- ↑ Schweitzer, C. E.; Santana, W.; Pinheiro, A.; Feldmann, R. M. (2019). "Redescription and illustration of caridean shrimp from the Cretaceous (Aptian) of Brazil". Journal of South American Earth Sciences. 90: 70–75. Bibcode:2019JSAES..90...70S. doi:10.1016/j.jsames.2018.12.001. S2CID 133909136.
- ↑ de Mazancourt, V.; Wappler, T.; Wedmann, S. (2022). "Exceptional preservation of internal organs in a new fossil species of freshwater shrimp (Caridea: Palaemonoidea) from the Eocene of Messel (Germany)". Scientific Reports. 12 (1). 18114. Bibcode:2022NatSR..1218114D. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-23125-9. PMC 9613706. PMID 36302944.
- ↑ de Mazancourt, V.; Wappler, T.; Wedmann, S. (2023). "Author Correction: Exceptional preservation of internal organs in a new fossil species of freshwater shrimp (Caridea: Palaemonoidea) from the Eocene of Messel (Germany)". Scientific Reports. 13 (1). 5943. Bibcode:2023NatSR..13.5943D. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-32986-7. PMC 10097716. PMID 37046034.
- 1 2 3 4 5 De Angeli, A. (2023). "Nuovi crostacei decapodi dell'Eocene superiore dei Monti Berici (Vicenza, Italia nordorientale)". Lavori – Società Veneziana di Scienze Naturali. 48: 169–186.
- 1 2 Vega, F. J.; Nyborg, T.; Garassino, A. (2023). "New frog crabs (Brachyura, Raninoidea) from the early Maastrichtian of Paredón (Coahuila, NE Mexico)". Journal of South American Earth Sciences. 104746. doi:10.1016/j.jsames.2023.104746.
- 1 2 3 Miller, J. B.; Schweitzer, C. E.; Feldmann, R. M. (2023). "New Decapoda (Brachyura) from the Paleocene Kambühel Formation, Austria" (PDF). Annalen des Naturhistorischen Museums in Wien, Serie A. 124: 125–148. JSTOR 27213512.
- ↑ Hyžný, M.; Vega, F. J.; Coutiño, M. A. (2023). "Validation of Callianassa ocozocoautlaensis Hyžný, Vega & Coutiño, a fossil ghost shrimp (Malacostraca: Decapoda: Axiidea) from the Upper Cretaceous of Chiapas, Mexico". Zootaxa. 5318 (2): 295–296. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5318.2.11. PMID 37518381. S2CID 260032805.
- ↑ Hyžný, M.; Vega, F. J.; Coutiño, M. A. (2013). "Ghost shrimps (Decapoda: Axiidea: Callianassidae) of the Maastrichtian (Late Cretaceous) Ocozocoautla Formation, Chiapas (Mexico)". Boletín de la Sociedad Geológica Mexicana. 65 (2): 255–264. doi:10.18268/BSGM2013v65n2a7.
- ↑ Nyborg, T.; Hyžný, M.; Haggart, J. W. (2023). "On the occurrence of a burrowing lobster (Malacostraca: Decapoda: Axiidea) from the Upper Cretaceous Cedar District Formation, Little Sucia Island, Washington State, with a description of a new genus". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 309 (2): 153–159. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2023/1156.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Feldmann, R. M.; Schweitzer, C. E.; Casadío, S. (2023). "Oligocene and Miocene Decapoda (Crustacea: Axiidea, Anomura, Brachyura) from Southern Argentina". Annals of Carnegie Museum. 88 (2): 91–114. doi:10.2992/007.088.0201.
- ↑ Santana, W.; Tavares, M.; Martins, C. A. M.; Melo, J. P. P.; Pinheiro, A. P. (2023). "Validation of Chronocancer camilosantanai† Santana, Tavares, Martins, Melo & Pinheiro (Crustacea, Decapoda, Brachyura) from the Romualdo Formation, Araripe Sedimentary Basin, Brazil". Papéis Avulsos de Zoologia. 63. e202363014. doi:10.11606/1807-0205/2023.63.014. S2CID 258596942.
- ↑ Santana, W.; Tavares, M.; Martins, C. A. M.; Melo, J. P. P.; Pinheiro, A. P. (2022). "A new genus and species of brachyuran crab (Crustacea, Decapoda) from the Aptian-Albian (Cretaceous) of the Araripe Sedimentary Basin, Brazil". Journal of South American Earth Sciences. 116. 103848. Bibcode:2022JSAES.11603848S. doi:10.1016/j.jsames.2022.103848. S2CID 249005503.
- ↑ Nyborg, T.; Vega, F. J.; Filkorn, H. F. (2023). "Validation of Costacopluma squiresi Nyborg, Vega & Filkorn (Crustacea: Brachyura: Retroplumidae) from the Pacific Slope, Paleocene of California, USA". Zootaxa. 5315 (5): 492–494. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5315.5.7. PMID 37518412. S2CID 259896337.
- ↑ Nyborg, T.; Vega, F. J.; Filkorn, H. F. (2009). "First described species of Costacopluma (Crustacea: Brachyura: Retroplumidae) from the Pacific slope, Paleocene of California, USA". Boletín de la Sociedad Geológica Mexicana. 61 (2): 203–209. doi:10.18268/BSGM2009v61n2a7.
- 1 2 3 García-Penas, Á.; Ferratges, F. A.; Moreno-Bedmar, J. A.; Bover-Arnal, T.; Gasca, J. M.; Aurell, M.; Zamora, S. (2023). "Decapod crustaceans from the Lower Cretaceous of Spain, with an account of new occurrences in Barremian-Aptian strata of the Maestrazgo Basin". Cretaceous Research. 150. 105576. Bibcode:2023CrRes.15005576G. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2023.105576. S2CID 258754780.
- ↑ Nyborg, T.; Garassino, A.; Vega, F. J. (2023). "Validation of Cretalamoha boweni Nyborg & Garassino (Brachyura: Homolidae) from the early Campanian, Upper Cretaceous of British Columbia, Canada". Zootaxa. 5318 (1): 148–150. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5318.1.8. PMID 37518392. S2CID 260028035.
- 1 2 Nyborg, T.; Garassino, A. (2017). "New Occurrences of Fossil Homolidae from the Eastern Pacific". Boletín de la Sociedad Geológica Mexicana. 69 (1): 135–148. doi:10.18268/BSGM2017v69n1a6.
- 1 2 Liu, Y.; Poschmann, M. J.; Fan, R.; Zong, R.; Gong, Y. (2023). "Silurian phyllocarid crustaceans (Phyllocarida, Archaeostraca) from South China". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 21 (1). 2187718. doi:10.1080/14772019.2023.2187718. S2CID 257971372.
- 1 2 3 Wallaard, J. J. W.; Fraaije, R. H. B.; Van Bakel, B. W. M.; Jagt, J. W. M.; Müller, P. M. (2023). "Miocene decapod crustacean faunas from Cyprus – Part 1. Geographical-stratigraphical setting and Anomura". Palaeontologia Electronica. 26 (3). 26.3.a38. doi:10.26879/1258.
- ↑ Gómez-Cruz, A. de J.; Bermúdez, H. D.; Vega, F. J. (2023). "Validation of Diaulax rosablanca Gómez-Cruz, Bermúdez & Vega (Brachyura: Dialucidae) from the Lower Cretaceous Rosablanca Formation, Colombia". Zootaxa. 5315 (4): 396–398. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5315.4.7. PMID 37518592. S2CID 259838457.
- ↑ Gómez-Cruz, A. de J.; Bermúdez, H. D.; Vega, F. J. (2015). "A new species of Diaulax Bell, 1863 (Brachyura: Dialucidae) in the Early Cretaceous of the Rosablanca Formation, Colombia". Boletín de la Sociedad Geológica Mexicana. 67 (1): 103–112. doi:10.18268/BSGM2015v67n1a8.
- ↑ Van Bakel, B. W. M.; Hyžný, M.; Valentin, X.; N., Robin (2023). "Validation of Dinocarcinus velauciensis Van Bakel, Hyžný, Valentin & Robin, a fossil crab (Crustacea, Decapoda, Brachyura) from Upper Cretaceous (Campanian) continental deposits of Velaux and vicinity, southern France". Zootaxa. 5315 (5): 483–484. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5315.5.5. PMID 37518414. S2CID 259879589.
- ↑ N., Robin; Van Bakel, B. W. M.; Hyžný, M.; A., Cincotta; G., Garcia; S., Charbonnier; P., Godefroit; Valentin, X. (2019). "The oldest freshwater crabs: claws on dinosaur bones". Scientific Reports. 9 (1). 20220. Bibcode:2019NatSR...920220R. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-56180-w. PMC 6934782. PMID 31882600.
- ↑ Alencar, D. R.; Santana, W.; Pinheiro, A. P.; Lima, D.; Feitosa Saraiva, A. Á.; de Oliveira, G. R. (2023). "New Cretaceous (Aptian/Albian) boxer shrimp (Crustacea, Decapoda, Stenopodidea) from the Araripe Sedimentary Basin, NE, Brazil". PLOS ONE. 18 (3). e0281334. Bibcode:2023PLoSO..1881334A. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0281334. PMC 10032536. PMID 36947562.
- ↑ Vega, F. J.; Garassino, A.; Zapata-Jaime, R. (2023). "Validation of Enoploclytia tepeyacensis Vega, Garassino, & Zapata-Jaime (Crustacea: Decapoda: Erymidae) from the Cretaceous (Campanian) of Mexico". Zootaxa. 5315 (5): 498–500. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5315.5.9. PMID 37518410. S2CID 259898664.
- ↑ Vega, F. J.; Garassino, A.; Zapata-Jaime, R. (2013). "Enoploclytia tepeyacensis n. sp. (Crustacea, Decapoda, Erymidae) from the Cretaceous (Campanian) of Coahuila, NE Mexico". Boletín de la Sociedad Geológica Mexicana. 65 (2): 207–211. doi:10.18268/BSGM2013v65n2a1.
- 1 2 3 4 Schädel, M.; Nagler, C.; Hyžný, M. (2023). "Fossil relatives of extant parasitic crustaceans from the Mesozoic of Europe" (PDF). Boletín de la Sociedad Geológica Mexicana. 75 (2). A220323. doi:10.18268/BSGM2023v75n2a220323. S2CID 259579171.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Karasawa, H.; Ohara, M.; Kato, H. (2023). "Validation of the names of four species of Decapoda and one species of Isopoda from the Lower Cretaceous (Barremian) Arida Formation of central Japan". Zootaxa. 5277 (1): 198–200. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5277.1.12. PMID 37518321. S2CID 258447077.
- 1 2 3 Ferratges, F. A.; Domínguez, J. L.; Ossó, À.; Zamora, S. (2023). "Spider crabs (Decapoda: Brachyura: Majoidea) from the upper Eocene of south Pyrenees (Huesca, Spain)". Palaeontologia Electronica. 26 (2). 26.2.a27. doi:10.26879/1270.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Ossó, À.; van Bakel, B. W. M.; Artal, P.; Moreno-Bedmar, J. A.; Sánchez-Beristain, F.; Bover-Arnal, T. (2023). "An Aptian sponge-associated decapod crustacean assemblage from Cal Cassanyes (Catalonia, north-east Iberian Peninsula): taxonomy and palaeoecological implications". Cretaceous Research. 105750. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2023.105750.
- ↑ Garassino, A.; Pasini, G.; Schweigert, G.; Charbonnier, S. (2023). "An updated reassessment of Antrimpos Münster, 1839 (Dendrobranchiata, Penaeidae)". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 307 (1): 1–15. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2023/1107. S2CID 256748593.
- ↑ Charbonnier, S.; Garassino, A.; López-Horgue, M. A. (2023). "A new species of glypheid lobster, Glyphea pisuergae (Crustacea, Glypheoidea), from the Early Jurassic of Palencia, Basque-Cantabrian Basin, Spain". Annales de Paléontologie. 109 (1). 102596. Bibcode:2023AnPal.10902596C. doi:10.1016/j.annpal.2023.102596. S2CID 257862576.
- 1 2 Lima, D.; Silva, R. C.; Aguilera, O.; Pinheiro, A. P.; Santana, W. (2023). "Brazilian Miocene crabs I. Taxonomic review of Cyclocancer tuberculatus Beurlen, 1958 and Hepatella amazonica Beurlen, 1958 (Pancrustacea, Decapoda, Brachyura)". Papéis Avulsos de Zoologia. 63: e202363012. doi:10.11606/1807-0205/2023.63.012. S2CID 258096809.
- ↑ García-Vázquez, L.; Alvarado-Ortega, J.; Vega, F. J. (2023). "Pliocene freshwater isopods (Crustacea: Peracarida: Isopoda) from Jalisco, Mexico" (PDF). Boletín de la Sociedad Geológica Mexicana. 75 (1). A271122. doi:10.18268/BSGM2023v75n1a271122. S2CID 258184899.
- 1 2 3 Starzyk, N.; Van Bakel, B. W. M.; Klompmaker, A. A.; Schweigert, G.; Fraaije, R. H. B. (2023). "A new approach to the systematics of Laeviprosopon (Brachyura: Homolidae), with remarks on molting process of the early brachyurans". Palaeontologia Electronica. 26 (1). 26.1.a10. doi:10.26879/1204.
- ↑ Fraaije, R. H. B.; van Bakel, B. W. M.; Jagt, J. W. M.; Wallaard, J. J. W.; De Coninck, L. (2023). "A new hermit crab (Anomura, Paguroidea) from the middle Albian of Wissant, Pas-de-Calais (northern France)". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 307 (2): 107–111. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2023/1117. S2CID 257561920.
- ↑ Charbonnier, S.; Gilardet, R.; Garassino, A.; Odin, G. P. (2023). "A new species of mecochirid lobster from the Late Cretaceous of France, preserved with its eggs". Geodiversitas. 45 (23): 681–688. doi:10.5252/geodiversitas2023v45a23.
- 1 2 3 van Bakel, B. W. M.; Guinot, D. (2023). "New genera and species of glaessneropsid crabs from the Lower and Middle Jurassic of France and Germany-Austria, and reconsolidation of Charassocarcinus Van Straelen, 1925". Geobios. doi:10.1016/j.geobios.2023.05.007. S2CID 259916458.
- ↑ Bruce, N. L.; Rodcharoen, E. (2023). "Electrolana Schädel, Hyžný & Haug, 2021 (Crustacea: Isopoda: Cirolanidae), a junior synonym of Cirolana Leach, 1818 and a new species of Metacirolana Kussakin, 1978 from Cretaceous amber of Myanmar". Records of the Australian Museum. 75 (4): 405–412. doi:10.3853/j.2201-4349.75.2023.1880.
- ↑ Gašparič, R.; Tshudy, D.; Chan, T.-Y.; Ćorić, S. (2023). "Validation of Metanephrops serendipitus (Crustacea, Decapoda, Nephropidae), a deep-water lobster from lower Miocene of Meljski hrib (Maribor, Slovenia)". Zootaxa. 5323 (3): 440–442. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5323.3.9. S2CID 260528714.
- ↑ Gašparič, R.; Tshudy, D.; Chan, T.-Y.; Ćorić, S. (2021). "A new deep-water lobster, Metanephrops serendipitus sp. nov. (Crustacea, Decapoda, Nephropidae), from lower Miocene of Meljski hrib (Maribor, Slovenia)". Boletín de la Sociedad Geológica Mexicana. 73 (3). A240521. doi:10.18268/BSGM2021v73n3a240521. S2CID 245028447.
- ↑ Charbonnier, S.; Garassino, A.; Gendry, D.; Devillez, J.; Picot, L. (2023). "The decapod crustacean fauna from the Late Jurassic of Cricqueboeuf, Normandy (France)". Geodiversitas. 45 (19): 573–588. doi:10.5252/geodiversitas2023v45a19.
- ↑ Fraaije, R. H. B.; Mychko, E. V.; Barsukov, L. S.; Jagt, J. W. M. (2023). "A new mid-Cretaceous hermit crab (Crustacea, Anomura) from Central Russia sheds new light on paguroid evolution". Cretaceous Research. 105749. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2023.105749.
- ↑ Mychko, E. V.; Schweitzer, C. E.; Feldmann, R. M.; Shmakov, A. S. (2023). "The first report of Necrocarcinus (Crustacea: Brachyura: Raninoida) from the Cenomanian of Central Russia". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 309 (1): 31–42. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2023/1146. S2CID 260661087.
- ↑ Guzmán, W.; Bermúdez, H. D.; Gómez-Cruz, A. de J.; F. J., Vega (2023). "Validation of Ophthalmoplax andina Guzmán, Bermúdez, Gómez-Cruz, & Vega (Decapoda: Brachyura: Portunoidea) from the late Campanian, Upper Cretaceous of Colombia". Zootaxa. 5315 (5): 495–497. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5315.5.8. PMID 37518411. S2CID 259888756.
- ↑ Guzmán, W.; Bermúdez, H. D.; Gómez-Cruz, A. de J.; F. J., Vega (2016). "Ophthalmoplax (Decapoda: Brachyura: Portunoidea) from the late Campanian, Upper Cretaceous, of Colombia". Boletín de la Sociedad Geológica Mexicana. 68 (1): 93–103. doi:10.18268/BSGM2016v68n1a11.
- ↑ Nyborg, T.; Garassino, A.; Nyborg, B. (2023). "A new fossil frog crab (Brachyura, Lyreididae) from the Eocene of northeastern Pacific". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 307 (1): 29–39. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2023/1110. S2CID 256754390.
- ↑ Artal, P.; Onetti, A.; Ossó, À. (2023). "New pseudoziid crab (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura) from the Lutetian outcrops of Girona and Barcelona (Catalonia, NE Iberian Peninsula)". Bulletin of the Mizunami Fossil Museum. 50 (1): 77–88. doi:10.50897/bmfm.50.1_77.
- ↑ Braig, F.; Haug, J. T.; Ahyong, S. T.; Garassino, A.; Schädel, M.; Haug, C. (2023). "Another piece in the puzzle of mantis shrimp evolution – fossils from the Early Jurassic Osteno Lagerstätte of Northern Italy". Comptes Rendus Palevol. 22 (2): 17–31. doi:10.5852/cr-palevol2023v22a2. S2CID 256217869.
- 1 2 Wallaard, J. J. W.; Fraaije, R. H. B.; Van Bakel, B. W. M.; Nance, J. R.; Lindholm, A.; Jagt, J. W. M. (2023). "New hermit crab species (Anomura, Paguroidea) from the upper Miocene St. Marys Formation of Maryland (USA), preserved in their host shells". Zootaxa. 5227 (3): 389–397. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5227.3.7. PMID 37044682. S2CID 255668962.
- ↑ Fraaije, R. H. B.; Van Bakel, B. W. M.; Jagt, J. W. M.; Krobicki, M.; Ossó, À.; Palero, F.; Wallaard, J. J. W. (2023). "A reconsideration of the palinuroid family Synaxidae (Crustacea, Decapoda), with a new member from the Upper Jurassic of southern Poland". Palaeontologia Electronica. 26 (2). 26.2.19. doi:10.26879/1252.
- ↑ Nyborg, T.; Garassino, A.; Vega, F. J. (2023). "Validation of Paromola roseburgensis Nyborg & Garassino (Brachyura: Homolidae) from the early Eocene of Oregon, USA". Zootaxa. 5318 (3): 441–442. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5318.3.11. PMID 37518368. S2CID 260008133.
- 1 2 Schweigert, G. (2023). "Validation of Petersbuchia Schweigert, a prosopid crab from the Upper Jurassic of Germany". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 308 (3): 289–290. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2023/1144. S2CID 259588399.
- ↑ Schweigert, G. (2021). "A new genus of prosopid crabs (Decapoda: Brachyura: Dromiacea) from the Upper Jurassic of southern Germany". Boletín de la Sociedad Geológica Mexicana. 73 (3): A030121. doi:10.18268/BSGM2021v73n3a030121. S2CID 245103649.
- ↑ Ferratges, F. A.; Luque, J.; Domínguez, J. L.; Ossó, À.; Aurell, M.; Zamora, S. (2023). "The oldest dairoidid crab (Decapoda, Brachyura, Parthenopoidea) from the Eocene of Spain". Papers in Palaeontology. 9 (3). e1494. doi:10.1002/spp2.1494. S2CID 259124402.
- ↑ Lima, D.; Pinheiro, A. P.; Silva, R. C.; Aguilera, O.; Santana, W. (2023). "Brazilian Miocene crabs II. A new genus and species (crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura) from Pirabas Formation, northern Brazil". Journal of South American Earth Sciences. 104723. doi:10.1016/j.jsames.2023.104723.
- ↑ Pasini, G.; Garassino, A.; Charbonnier, S. (2023). "A new litogastrid lobster (Decapoda, Glypheoidea) from the Anisian (Middle Triassic) of the Dolomiti del Cadore (Belluno, Veneto, NE Italy)". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 307 (2): 101–105. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2023/1116. S2CID 257578672.
- ↑ van Bakel, B. W. M.; Ossó, À.; Téodori, D. (2023). "Rogueus belgodereae, a new raninoid crab (Crustacea: Brachyura: Raninoidea) from the Upper Palaeocene (Thanetian) of Southern France, with comments on early palaeocene decapod crustacean faunules". Palaeontologia Electronica. 26 (3). 26.3.a45. doi:10.26879/1269.
- ↑ Nyborg, T.; Fraaije, R. H. B.; Dunbar, S. G. (2023). "Pliocene hermit crabs (Decapoda, Anomura, Paguroidea) preserved in situ in host gastropod shells from the San Diego Formation near San Diego (southern California, USA)". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 310 (1): 71–81. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2023/1169.
- ↑ Barros, O. A.; de Oliveira, P. V. (2023). "New Dendrobranchiata fossil preserved in the Brazilian Cretaceous (Aptian/Albian) from the Araripe Basin, Piauí State". Zootaxa. 5264 (4): 545–563. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5264.4.5. PMID 37518032. S2CID 258205413.
- ↑ Liu, Y.; Fan, R.; Zong, R.; Gong, Y. (2023). "First occurrence of caryocaridids (Crustacea, Phyllocarida) in the Ordovician of North China". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 623. 111638. Bibcode:2023PPP...623k1638L. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2023.111638. S2CID 258727455.
- ↑ Pazinato, P. G.; Müller, P.; Haug, J. T. (2023). "New species of Tanaidacea from Cretaceous Kachin amber, with a brief review of the fossil record of tanaidacean crustaceans". Fossil Record. 26 (1): 39–50. doi:10.3897/fr.26.99995. S2CID 256482676.
- ↑ Fraaije, R. H. B.; van Bakel, B. W. M.; Guinot, D.; Jagt, J. W. M. (2023). "Validation of Tanidromites maerteni Fraaije, Van Bakel, Guinot & Jagt, a species of crab (Crustacea, Decapoda, Brachyura) from Middle Jurassic (Bajocian) deposits of Maizet, Calvados, northwest France". Zootaxa. 5318 (3): 437–438. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5318.3.9. PMID 37518370. S2CID 260017811.
- ↑ Fraaije, R. H. B.; van Bakel, B. W. M.; Guinot, D.; Jagt, J. W. M. (2013). "A new Middle Jurassic (Bajocian) homolodromioid crab from northwest France; the earliest record of the Tanidromitidae". Boletín de la Sociedad Geológica Mexicana. 65 (2): 249–254. doi:10.18268/BSGM2013v65n2a6.
- ↑ Smith, C. P. A.; Aubier, P.; Charbonnier, S.; Laville, T.; Olivier, N.; Escarguel, G.; Jenks, J. F.; Bylund, K. G.; Fara, E.; Brayard, A. (2023). "Closing a major gap in mantis shrimp evolution - first fossils of Stomatopoda from the Triassic". Bulletin of Geosciences. 98 (1): 95–110. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1864. S2CID 258089800.
- ↑ Kato, H.; Taru, H.; Haga, T.; Sugita, Y. (2023). "Decapod crustaceans from the Miocene Itsukaichi Basin, western Tokyo, Japan, including a new species of Trichopeltarion (Brachyura: Trichopeltariidae)". Bulletin of the Mizunami Fossil Museum. 50 (1): 21–35. doi:10.50897/bmfm.50.1_21.
- ↑ Chény, C.; Charbonnier, S.; Audo, D. (2023). "Middle Jurassic lobsters (Crustacea, Decapoda) from Normandy, France". Geodiversitas. 45 (4): 139–161. doi:10.5252/geodiversitas2023v45a4. S2CID 257696140.
- ↑ Klompmaker, A. A.; Kloess, P. A.; Jauvion, C.; Brezina, J.; Landman, N. H. (2023). "Internal anatomy of a brachyuran crab from a Late Cretaceous methane seep and an overview of internal soft tissues in fossil decapod crustaceans". Palaeontologia Electronica. 26 (3). 26.3.a44. doi:10.26879/1277.
- ↑ Ossó, À. (2023). "New data on Eogeryon elegius Ossó, 2021 (Decapoda: Eubrachyura: Portunoidea), one of the oldest modern-looking crabs, from the mid-Cretaceous of Iberia". Bulletin of the Mizunami Fossil Museum. 50 (1): 89–96. doi:10.50897/bmfm.50.1_89.
- ↑ Ossó, À.; Ng, P. K. L. (2023). "On the systematic placement of the fossil crab Lathahypossia aculeata (Busulini, Tessier & Visentin, 1984) (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura)". Zootaxa. 5351 (2): 265–275. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5351.2.4.
- ↑ Lima, D.; Alencar, D. R.; Santana, W.; Oliveira, N. C.; Saraiva, A. Á. F.; Oliveira, G. R.; Boyko, C. B.; Pinheiro, A. P. (2023). "110-million-years-old fossil suggests early parasitism in shrimps". Scientific Reports. 13 (1). 14549. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-40554-2. PMC 10477257. PMID 37666850.
- ↑ Dadykin, I. A.; Shmakov, A. S. (2023). "New findings of Decapoda (Crustacea) in the Callovian of the Ryazan region (Central European Russia)". Journal of Paleontology. 97 (5): 1049–1069. doi:10.1017/jpa.2023.73.
- ↑ Schweitzer, C. E.; Feldmann, R. M. (2023). "Selective extinction at the end-Cretaceous and appearance of the modern Decapoda". Journal of Crustacean Biology. 43 (2). ruad018. doi:10.1093/jcbiol/ruad018.
- 1 2 Luo, Z.; Wang, R.; Amuti, A.; Deng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Qie, W.; Song, J. (2023). "Late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) ostracods from East Junggar in Xinjiang, northwestern China". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 47: 31–44. doi:10.1080/03115518.2022.2157047. S2CID 256215419.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Tanaka, G. (2023). "Paleogeographical and paleoenvironmental significance of ostracodes from the Pennsylvanian Nagaiwa Formation, northeast Japan". Journal of Paleontology. 97 (Supplement S92): 1–33. Bibcode:2023JPal...97S...1T. doi:10.1017/jpa.2022.108. S2CID 257666299.
- 1 2 3 Hawramy, O. A.; Al-Obidee, W. Y.; Aziz, N. M.; Zhang, X. (2023). "Campanian-Maastrichtian Ostracods (Crustacea) From the Shiranish Formation, Dukan Area, Kurdistan Province, Northern Iraq". Iraqi Geological Journal. 56 (1C): 74–93. doi:10.46717/igj.56.1C.6ms-2023-3-17. S2CID 257908690.
- ↑ Camilleri, T. T. A.; Weldon, E. A.; Warne, M. T. (2023). "Early Devonian Ostracoda from the Norton Gully Sandstone, southeastern Australia". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology: 1–13. doi:10.1080/03115518.2023.2223658. S2CID 260363168.
- 1 2 3 Khosla, A.; Verma, O.; Kania, S.; Lucas, S. (2023). "Indian Late Cretaceous-Early Palaeocene Deccan Microbiota from the Intertrappean Beds of the Chhindwara District, Madhya Pradesh and Their Systematic Palaeontology". In A. Khosla; O. Verma; S. Kania; S. Lucas (eds.). Microbiota from the Late Cretaceous-Early Palaeocene Boundary Transition in the Deccan Intertrappean Beds of Central India. Systematics and Palaeoecological, Palaeoenvironmental and Palaeobiogeographical Implications. Topics in Geobiology. Vol. 54. Springer. pp. 77–205. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-28855-5_4. ISBN 978-3-031-28854-8.
- ↑ Perrier, V.; Perrichon, G.; Nesme, F.; Groos-Uffenorde, H.; Lorenzo, S.; Gutiérrez-Marco, J. C. (2023). "Ecologically distinct myodocope ostracod faunas from a single horizon in the late Silurian of Spain". Revue de Micropaléontologie. 80. 100729. doi:10.1016/j.revmic.2023.100729. S2CID 259584606.
- 1 2 Williams, M.; Komatsu, T.; Nguyen, P. D.; Siveter, D. J.; McGairy, A.; Bush, H.; Goodall, R. H.; Harvey, T. H. P.; Stocker, C. P.; Legrand, J.; Yamada, T.; Miller, C. G. (2023). "Ostracods from the Upper Silurian Si Ka Formation, Northern Vietnam, and Their Paleobiogeographical Significance". Paleontological Research. 27 (3): 261–276. doi:10.2517/PR210032. S2CID 255441183.
- ↑ Zamudio, M. B.; Carignano, A. P. (2023). "Upper Miocene calcareous microfossils (Foraminifera and Ostracoda) from northwestern Argentina". Publicación Electrónica de la Asociación Paleontológica Argentina. 23 (2): 27–44. doi:10.5710/PEAPA.12.04.2023.455. S2CID 259866665.
- 1 2 Shahin, A.; El Khawagah, S.; Shahin, B. (2023). "Implication of middle Eocene to early Miocene ostracodes from the N. El Faras-1X Well, Qattara Depression, Egypt, for paleobathymetry and paleobiogeographic reconstruction". Marine Micropaleontology. 181. 102244. Bibcode:2023MarMP.181j2244S. doi:10.1016/j.marmicro.2023.102244. S2CID 258158689.
- 1 2 3 4 Kumari, M. (2023). "Middle Jurassic Ostracodes from Joyan Member, Jaisalmer Formation, Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, India". Paleontological Journal. 57 (7): 775–783. doi:10.1134/S0031030123070055.
- ↑ Karpuk, M. S. (2023). "New Data on Planktonic Foraminifera and Ostracods from the Barremian(?)–Aptian of the Eastern Crimea: Stratigraphy and Paleoecology". Stratigraphy and Geological Correlation. 31 (2): 89–108. Bibcode:2023SGC....31...89K. doi:10.1134/S0869593823020028. S2CID 258336679.
- 1 2 3 Santos Filho, M. A. B.; Ceolin, D.; Fauth, G.; Lima, F. H. O. (2023). "Ostracods from the Barbalha and Crato formations, Aptian of the Araripe Basin, northeast Brazil". Zootaxa. 5319 (3): 332–350. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5319.3.2. PMID 37518227. S2CID 260213787.
- ↑ Antonietto, L. S.; Brandão, S. N. (2023). "Ideluralia nom. nov., a new name for the ostracode genus Bairdiella Egorova, 1960". Revista Brasileira de Paleontologia. 26 (2): 144. doi:10.4072/rbp.2023.2.06. S2CID 259941046.
- ↑ Forel, M.-B.; Chitnarin, A. (2023). "Judahella kangpla: a new marine ostracod from the Upper Triassic of Thailand". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. doi:10.1080/03115518.2023.2283470.
- ↑ Forel, M.-B.; Chitnarin, A. (2023). "The Permian and Triassic history of the ostracod genus Liuzhinia". Revue de Micropaléontologie. 78. 100714. doi:10.1016/j.revmic.2023.100714. S2CID 257801019.
- ↑ Danielopol, D. L.; Cabral, M. C.; Horne, D. J.; Namiotko, T.; Lord, A. R. (2023). "Reconciling diagnostic traits in living and fossil taxa: The taxonomy and evolution of the genus Microceratina (Crustacea, Ostracoda, Cytheruridae)". Zootaxa. 5244 (4): 301–340. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5244.4.1. PMID 37044458. S2CID 257061609.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Gale, A. S.; Vidovic, S. U. (2023). "The origins of major sessile cirripede groups; a revision of Cretaceous Brachylepadomorpha and Verrucomorpha". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 21 (1). 2258370. doi:10.1080/14772019.2023.2258370.
- ↑ Gale, A.; Keupp, H.; Schweigert, G.; Sell, J. (2023). "A new phosphatic cirripede from the Carnian (Upper Triassic) of Bavaria, Germany". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 309 (1): 19–29. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2023/1145. S2CID 260656539.
- ↑ De Schutter, P. J.; Everaert, S.; Gale, A.; Van Remoortel, W.; De Borger, G.; Sakala, J.; Koutecký, V.; Hoedemakers, K. (2023). "An exceptional concentration of marine fossils associated with wood-fall in the Terhagen Member (Boom Formation; Schelle, Belgium), Rupelian of the southern North Sea Basin". Geologica Belgica. 26 (1–2): 41–78. doi:10.20341/gb.2023.003. S2CID 260401823.
- ↑ Li, G. (2023). "First Discovery of the Spinicaudatan Genus Carapacestheria Shen, 1994 in Asia". Paleontological Research. 28 (1): 71–82. doi:10.2517/PR220025. S2CID 257962700.
- ↑ Tang, H. Y.; Mychko, E. V.; Feldmann, R. M.; Schweitzer, C. E.; Shaari, H.; Sone, M. (2023). "Validation of Malayacyclus Tang, Mychko, Feldmann, Schweitzer, Shaari & Sone, a cyclidan crustacean from the Early Carboniferous of Terengganu, Malaysia". Zootaxa. 5318 (3): 439–440. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5318.3.10. PMID 37518369. S2CID 260026897.
- ↑ Tang, H. Y.; Mychko, E. V.; Feldmann, R. M.; Schweitzer, C. E.; Shaari, H.; Sone, M. (2021). "Malayacyclus gen. nov., the first Southeast Asian Cyclida (Crustacea) from the Early Carboniferous of Terengganu, Malaysia". Geological Journal. 56 (12): 6022–6030. doi:10.1002/gj.4128. S2CID 233522378.
- ↑ Liao, H.Y.; Fang, S.H.; Feng, Z.; Gao, J.; Huang, D.Y. (2023). "A new clam shrimp (Branchiopoda: Diplostraca: Spinicaudata) from the Upper Jurassic in the Jiyuan Basin, China and its biostratigraphic significance". Zootaxa. 5396 (1): 50–57. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5396.1.10.
- ↑ Li, G. (2023). "Discovery of important taxonomic characters of the type species of the Late Triassic clam shrimp Anyuanestheria (Crustacea: Spinicaudata) from Jiangxi". Acta Palaeontologica Sinica. 62 (3): 390–397. doi:10.19800/j.cnki.aps.2022031.
- 1 2 Paterson, J. R.; García-Bellido, D. C.; Edgecombe, G. D. (2023). "The early Cambrian Emu Bay Shale radiodonts revisited: morphology and systematics". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 21 (1). 2225066. doi:10.1080/14772019.2023.2225066. S2CID 259719252.
- ↑ Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Lin, W.; Ma, J.; Wu, Y.; Fu, D. (2023). "Amplectobeluid Radiodont Guanshancaris gen. nov. from the Lower Cambrian (Stage 4) Guanshan Lagerstätte of South China: Biostratigraphic and Paleobiogeographic Implications". Biology. 12 (4). 583. doi:10.3390/biology12040583. PMC 10136193. PMID 37106783.
- ↑ Potin, G. J.-M.; Gueriau, P.; Daley, A. C. (2023). "Radiodont frontal appendages from the Fezouata Biota (Morocco) reveal high diversity and ecological adaptations to suspension-feeding during the Early Ordovician". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. 11. 1214109. doi:10.3389/fevo.2023.1214109.
- ↑ Moysiuk, J.; Caron, J.-B. (2023). "A quantitative assessment of ontogeny and molting in a Cambrian radiodont and the evolution of arthropod development". Paleobiology: 1–16. doi:10.1017/pab.2023.18. S2CID 260850034.
- ↑ Bicknell, R. D. C.; Schmidt, M.; Rahman, I. A.; Edgecombe, G. D.; Gutarra, S.; Daley, A. C.; Melzer, R. R.; Wroe, S.; Paterson, J. R. (2023). "Raptorial appendages of the Cambrian apex predator Anomalocaris canadensis are built for soft prey and speed". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 290 (2002). 20230638. doi:10.1098/rspb.2023.0638. PMC 10320336. PMID 37403497.
- ↑ Wu, Y.; Pates, S.; Pauly, D.; Zhang, X.L.; Fu, D.J. (2023). "Rapid growth in a large Cambrian apex predator". National Science Review. nwad284. doi:10.1093/nsr/nwad284.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 Basse, M.; Müller, P. (2023). "Trilobiten aus dem Leun-Schiefer und Leun-Kalk von Löhnberg und Leun in der zentralen Lahn-Mulde in Hessen (Grenzbereich Unter-/Mitteldevon, Rheinisches Massiv, Varisziden)". Mainzer Naturwissenschaftliches Archiv. Beiheft 37: 1–211.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Wernette, S. J.; Hughes, N. C.; Myrow, P. M.; Sardsud, A. (2023). "Trilobites of Thailand's Cambrian–Ordovician Tarutao Group and their geological setting". Papers in Palaeontology. 9 (5). e1516. doi:10.1002/spp2.1516.
- 1 2 3 Ingham, J. K.; Fortey, R. A. (2023). "Review of the Ordovician pelagic trilobite Ellipsotaphrus (Cyclopygoidea, Ellipsotaphridae) and its allies, with new discoveries from Girvan, Ayrshire". Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 113 (4): 313–336. doi:10.1017/S1755691022000263. S2CID 256292161.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Smith, P. M.; Allen, H. J. (2023). "Early Ordovician trilobites from Barnicarndy 1 stratigraphic well of the southern Canning Basin, Western Australia". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology: 1–58. doi:10.1080/03115518.2023.2226194. S2CID 260724589.
- ↑ Kerber, G.; Pacheco, M. L. A. F.; Horodyski, R. S.; Graciolli, G. (2023). "Revealing new trilobites from the early Devonian Alto Garças Sub-basin, Brazil". Historical Biology: An International Journal of Paleobiology: 1–17. doi:10.1080/08912963.2023.2209098. S2CID 258593725.
- 1 2 Westrop, S. R.; Eoff, J. D. (2023). "A Jiangshanian (Cambrian; Furongian) trilobite fauna from the Cow Head Group, western Newfoundland". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences. 60 (8): 1244–1264. doi:10.1139/cjes-2023-0036. S2CID 260397862.
- ↑ Sun, Z.; Yang, A.; Zhao, F.; Zhuravlev, A. Yu.; Pan, B.; Hu, C.; Feng, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhu, M. (2023). "New trilobite assemblage from the lower Cambrian (upper Stage 4) of the Lake Zone, western Mongolia". Journal of Paleontology. 97 (3): 577–590. doi:10.1017/jpa.2023.23. S2CID 259770938.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Feist, J.; Clarkson, E. N. K. (2023). "Mid-Silurian odontopleurid trilobites from Roquemaillere, Montagne Noire, Southern France". Bulletin of Geosciences. 98 (3): 247–263. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1885.
- 1 2 Müller, P.; Hahn, G. (2023). "New data on trilobites of the Hillershausen Formation (Viséan, Rhenish Massif, Germany)". Dortmunder Beiträge zur Landeskunde - naturwissenschaftliche Mitteilungen. 52: 71–131.
- 1 2 Flick, U.; Flick, H. (2023). "Trilobitenfunde am Lagergang vom Wasenbachtal (südwestliche Lahnmulde) – Neue Vertreter der Otarioninae Richter & Richter, 1926 aus den Rupbach-Schiefern des Nordbruchs". Mainzer geowissenschaftliche Mitteilungen. 51: 21–38. doi:10.23689/fidgeo-5821.
- ↑ Alberti, M. (2023). "Devononeseuretus beichti n. gen., n. sp., der Erstnachweis eines Calymeniden (Trilobita) aus dem Hunsrückschiefer". Mainzer geowissenschaftliche Mitteilungen. 51: 7–20. doi:10.23689/fidgeo-5820.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Basse, M.; Lemke, U. (2023). "Class Trilobita in the Wocklum Limestone of the northern Rhenish Massif east of the Rhine (late Famennian, late Devonian) – Part 2. Phacopinae (Dianops, Rabienops, Spinicryphops, and Weyerites), with new species of Dianops and Rabienops". Dortmunder Beiträge zur Landeskunde - naturwissenschaftliche Mitteilungen. 52: 133–181.
- ↑ Adrain, J. M.; Pérez-Peris, F. (2023). "Funeralaspis n. gen.: a new odontopleurine trilobite from the early Middle Ordovician (Dapingian) of Death Valley, eastern California, USA, and the classification of Ordovician odontopleurines". Zootaxa. 5336 (4): 509–529. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5336.4.3.
- ↑ Peng, S.-C.; Babcock, L. E.; Yang, X.-F.; Zhu, X.-J. (2023). "First complete specimens of Karslanus (Trilobita, Dameselloidea) from Longha Formation (Cambrian: Guzhangian), Yunnan, South China". Palaeoworld. doi:10.1016/j.palwor.2023.05.004. S2CID 258950129.
- ↑ Peng, S.-C.; Babcock, L. E.; Yang, X.-F.; Zhu, X.-J.; Liu, Y. (2023). "A new dameselloid trilobite from the Fulu Biota, Longha Formation (Cambrian: Guzhangian), Yunnan, South China, and revised classification of dameselloids". Palaeoworld. doi:10.1016/j.palwor.2023.01.006. S2CID 255934538.
- ↑ Smith, P. M. (2023). "A new species of Lorrettina (dokimocephalid trilobite) from the Iverian (Cambrian, Jiangshanian) of the Amadeus Basin, Northern Territory, Australia". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. doi:10.1080/03115518.2023.2284196.
- ↑ Holloway, D. J. (2023). "The trilobites Mitroplax gen. nov. and Spiniscutellum (Scutelluidae) from the Lower Devonian of Victoria, Australia". Bulletin of Geosciences. 98 (2): 181–198. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1879. S2CID 259614186.
- 1 2 3 4 Blackwell, S. R.; Westrop, S. R. (2023). "A new Cambrian (Jiangshanian, Sunwaptan) trilobite fauna from Oklahoma and its biostratigraphic significance". Journal of Paleontology. 97 (4): 865–890. doi:10.1017/jpa.2023.40. S2CID 259872800.
- ↑ Tortello, M. F. (2023). "Trilobites from the Cedaria prolifica Zone (Cambrian, upper Guzhangian) of the Precordillera of Mendoza, western Argentina". Journal of Paleontology. 97 (3): 591–605. doi:10.1017/jpa.2023.34. S2CID 259384662.
- 1 2 Zong, R.-W. (2023). "Variation in eye lenses of two new Late Devonian phacopid trilobites from western Junggar, NW China". Journal of Paleontology. 97 (4): 891–905. doi:10.1017/jpa.2023.31. S2CID 258981236.
- 1 2 Zong, R.-W. (2023). "Variation in eye lenses of two new Late Devonian phacopid trilobites from western Junggar, NW China – CORRIGENDUM". Journal of Paleontology. 97 (4): 958. doi:10.1017/jpa.2023.42.
- 1 2 Korovnikov, I. V. (2023). "New species of the genus Oryctocephalus Walcott from the Middle Cambrian of the Siberian Platform". Paleontological Journal. 57 (4): 410–416. doi:10.1134/S0031030123040068. S2CID 261104180.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Basse, M.; Schöning, H. (2023). "The Proetinae (Trilobita) of the German Silurian. 1. Plesiowensus, Signatoproetus n.g., and Pulcherproetus". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 309 (3): 209–254. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2023/1160.
- ↑ Wei, X.; Luan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, G.; Zhan, R. (2023). "Katian (Late Ordovician) trilobites of the North Qilian Mountains and their palaeogeographical implications for the Proto-Tethys Archipelagic Ocean". Papers in Palaeontology. 9 (6). e1532. doi:10.1002/spp2.1532.
- ↑ Wei, X.; Zhou, Z.Q. (2023). "Floian, Early Ordovician, trilobites from the Olongbluk Terrane, northwest China". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 68 (4): 683–693. doi:10.4202/app.01102.2023.
- ↑ Nikolic, M. C.; Hopkins, M. J.; Evans, A. R. (2023). "Shared patterns of segment size development in trilobites and vertebrates". Evolution. 77 (6): 1479–1487. doi:10.1093/evolut/qpad057. PMID 37074198.
- ↑ Verma, N. (2023). "Digest: Trilobites to vertebrates: how development influences the evolution of segmental patterning". Evolution. 77 (9): 2109–2110. doi:10.1093/evolut/qpad123. PMID 37407222.
- ↑ Laibl, L.; Saleh, F.; Pérez-Peris, F. (2023). "Drifting with trilobites: The invasion of early post-embryonic trilobite stages to the pelagic realm". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 613. 111403. Bibcode:2023PPP...613k1403L. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2023.111403. S2CID 255913893.
- ↑ Holmes, J. D. (2023). "Contrasting patterns of disparity suggest differing constraints on the evolution of trilobite cephalic structures during the Cambrian 'explosion'". Palaeontology. 66 (2). e12647. Bibcode:2023Palgy..6612647H. doi:10.1111/pala.12647. S2CID 258071940.
- ↑ Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Esteve, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, S. (2023). "Life cycle evolution in the trilobites Balangia and Duyunaspis from the Cambrian Series 2 (Stage 4) of South China". PeerJ. 11. e15068. doi:10.7717/peerj.15068. PMC 10100804. PMID 37065692.
- ↑ Wang, M.; Peng, S.; Zhang, X. (2023). "Taxonomic revision of the Cambrian trilobite Abadiella and its stratigraphic significance in Gondwana". Journal of Asian Earth Sciences. 105855. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2023.105855.
- ↑ Srivastava, S.; Hughes, N. C. (2023). "Morphology, variation, and systematics of the late Cambrian Laurentian dikelocephalid trilobite Walcottaspis vanhornei (Walcott, 1914)". Journal of Paleontology: 1–22. doi:10.1017/jpa.2023.29. S2CID 259391991.
- ↑ Hou, J.-B.; Hughes, N. C.; Hopkins, M. J. (2023). "Gill grooming in middle Cambrian and Late Ordovician trilobites". Geological Magazine. 160 (5): 905–910. Bibcode:2023GeoM..160..905H. doi:10.1017/S001675682300002X. S2CID 256917018.
- ↑ Hou, J.-B.; Hughes, N. C.; Hopkins, M. J.; Shu, D. (2023). "Gill function in an early arthropod and the widespread adoption of the countercurrent exchange mechanism". Royal Society Open Science. 10 (8). 230341. doi:10.1098/rsos.230341. PMC 10427831. PMID 37593708.
- ↑ Losso, S. R.; Thines, J. E.; Ortega-Hernández, J. (2023). "Taphonomy of non-biomineralized trilobite tissues preserved as calcite casts from the Ordovician Walcott-Rust Quarry, USA". Communications Earth & Environment. 4. 330. doi:10.1038/s43247-023-00981-5.
- ↑ Losso, S. R.; Affatato, P.; Nanglu, K.; Ortega-Hernández, J. (2023). "Convergent evolution of ventral adaptations for enrolment in trilobites and extant euarthropods". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 290 (2013). 20232212. doi:10.1098/rspb.2023.2212. PMC 10730288. PMID 38113938.
- ↑ Laibl, L.; Drage, H. B.; Pérez-Peris, F.; Schöder, S.; Saleh, F.; Daley, A. C. (2023). "Babies from the Fezouata Biota: Early developmental trilobite stages and their adaptation to high latitudes". Geobios. doi:10.1016/j.geobios.2023.06.005. S2CID 260694824.
- ↑ Schoenemann, B.; Clarkson, E. N. K. (2023). "The median eyes of trilobites". Scientific Reports. 13 (1). 3917. Bibcode:2023NatSR..13.3917S. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-31089-7. PMC 9995485. PMID 36890176.
- ↑ Esteve, J.; Hughes, N. C. (2023). "Developmental and functional controls on enrolment in an ancient, extinct arthropod". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 290 (2000). 20230871. doi:10.1098/rspb.2023.0871. PMC 10265026. PMID 37312547.
- ↑ Esteve, J.; López-Pachón, M. (2023). "Swimming and feeding in the Ordovician trilobite Microparia speciosa shed light on the early history of nektonic life habits". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 625. 111691. Bibcode:2023PPP...625k1691E. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2023.111691. S2CID 259788614.
- ↑ Kraft, P.; Vaškaninová, V.; Mergl, M.; Budil, P.; Fatka, O.; Ahlberg, P. E. (2023). "Uniquely preserved gut contents illuminate trilobite palaeophysiology". Nature. 622 (7983): 545–551. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06567-7. PMC 10584673. PMID 37758946.
- ↑ Gishlick, A. D.; Fortey, R. A. (2023). "Trilobite tridents demonstrate sexual combat at 400 Mya". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 120 (4). e2119970120. Bibcode:2023PNAS..12019970G. doi:10.1073/pnas.2119970120. PMC 9942788. PMID 36649420.
- ↑ Ma, J.; Yin, J.; Liu, Y.; Du, X.; Liu, S.; Zong, R. (2023). "The latest encrinurid trilobites from the Lower Devonian of Xinjiang, Northwest China". Geological Magazine: 1–8. doi:10.1017/S0016756823000596.
- ↑ Bault, V. (2023). "Trilobites showed strong resilience capacity through the Late Devonian events despite an inexorable decline". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 630. 111807. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2023.111807.
- ↑ Esteve, J.; Rubio, P. (2023). "Understanding locomotion in trilobites by means of three-dimensional models". iScience. 26 (9). 107512. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107512. PMC 10460995. PMID 37646017. S2CID 260412390.
- ↑ Bault, V.; Crônier, C.; Monnet, C.; Balseiro, D.; Serra, F.; Waisfeld, B.; Bignon, A.; Rustán, J. J. (2023). "Rise and fall of the phacopids: the morphological history of a successful trilobite family". Palaeontology. 66 (5). e12673. doi:10.1111/pala.12673.
- ↑ Park, Tae-Yoon S. (2023-11-01). "Trilobite hypostome as a fusion of anterior sclerite and labrum". Arthropod Structure & Development. 77: 101308. doi:10.1016/j.asd.2023.101308. ISSN 1467-8039.
- 1 2 Laville, T.; Forel, M.-B.; Charbonnier, S. (2023). "Re-appraisal of thylacocephalans (Euarthropoda, Thylacocephala) from the Jurassic La Voulte-sur-Rhône Lagerstätte". European Journal of Taxonomy (898): 1–61. doi:10.5852/ejt.2023.898.2295.
- ↑ Briggs, Derek E. G.; Siveter, David J.; Siveter, Derek J.; Sutton, Mark D.; Legg, David; Lamsdell, James C. (2023). "A vicissicaudatan arthropod from the Silurian Herefordshire Lagerstätte, UK". Royal Society Open Science. 10 (8). 230661. doi:10.1098/rsos.230661. PMC 10394423. PMID 37538743.
- ↑ Weidner, T.; Nielsen, A. T.; Ebbestad, J. O. R. (2023). Middle Cambrian agnostoids and trilobites from the Lower Allochthon, Swedish Caledonides. Fossils and Strata Series. Vol. 68. pp. 1–121. doi:10.18261/9788215068022-2023. ISBN 978-8-215-06801-5. S2CID 259227386.
- ↑ Wang, Y.H.; Huang, D.Y.; Cai, C.Y. (2023). "A new genus of japygids (Diplura: Japygidae) in mid-Cretaceous amber from northern Myanmar". Zootaxa. 5396 (1): 64–73. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5396.1.12.
- 1 2 Sánchez-García, A.; Sendra, A.; Davis, S.; Grimaldi, D. A. (2023). "Fossil diversity in 'dawn' hexapods (Diplura: Projapygoidea), with direct evidence for being chemically predaceous in the Cretaceous". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 198 (3): 847–870. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlac101.
- ↑ Haug, J. T.; Fraaije, R. H. B.; Haug, C. (2023). "A new species of possible archipolypodan millipede from the Carboniferous of the Netherlands with unusually long tergites". Comptes Rendus Palevol. 22 (29): 595–604. doi:10.5852/cr-palevol2023v22a29.
- 1 2 3 Sánchez-García, A.; Sendra, A.; Davis, S. R.; Grimaldi, D. A. (2023). "'Dawn' hexapods in Cenozoic ambers (Diplura: Campodeoidea)". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlad118.
- ↑ Haug, G. T.; Haug, J. T.; Haug, C. (2023). "Convergent evolution of defensive appendages – a lithobiomorph-like centipede with a scolopendromorph-type ultimate leg from about 100 million-year-old amber". Palaeobiodiversity and Palaeoenvironments. doi:10.1007/s12549-023-00581-3. S2CID 259349020.
- ↑ Zong, R.; Edgecombe, G. D.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Yin, J.; Ma, J.; Xu, H. (2023). "Silurian freshwater arthropod from northwest China". Papers in Palaeontology. 9 (2). e1488. doi:10.1002/spp2.1488. S2CID 257843305.
- ↑ Su, Y.T.; Cai, C.Y.; Huang, D.Y. (2023). "A new species of Polydesmidae (Myriapoda, Diplopoda, Polydesmida) from the mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber". Zootaxa. 5396 (1): 112–123. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.5396.1.16.
- 1 2 3 Zhu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, F. (2023). "New artiopodan euarthropods from the Chengjiang fauna (Cambrian, Stage 3) at Malong, Yunnan, China". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 68 (3): 427–440. doi:10.4202/app.01080.2023.
- ↑ Du, K.; Bruton, D. L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X. (2023). "An early Cambrian Sidneyia (Arthropoda) resolves the century-long debate of its head organization". Science China Earth Sciences. 66 (3): 521–527. Bibcode:2023ScChD..66..521D. doi:10.1007/s11430-022-1019-8. S2CID 257177978.
- ↑ Edgecombe, G. D.; Strange, S. E.; Popovici, G.; West, T.; Vahtera, V. (2023). "An Eocene fossil plutoniumid centipede: a new species of Theatops from Baltic Amber (Chilopoda: Scolopendromorpha)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 21 (1). 2228796. doi:10.1080/14772019.2023.2228796. S2CID 260045944.
- ↑ Berks, H. O.; Nielsen, M. L.; Flannery-Sutherland, J.; Nielsen, A. T.; Park, T.-Y. S.; Vinther, J. (2023). "A possibly deep branching artiopodan arthropod from the lower Cambrian Sirius Passet Lagerstätte (North Greenland)". Papers in Palaeontology. 9 (3). e1495. doi:10.1002/spp2.1495. S2CID 259253098.
- ↑ O'Flynn, R. J.; Liu, Y.; Hou, X.; Mai, H.; Yu, M.; Zhuang, S.; Williams, M.; Guo, J.; Edgecombe, G. D. (2023). "The early Cambrian Kylinxia zhangi and evolution of the arthropod head". Current Biology. 33 (18): 4006–4013.e2. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2023.08.022. PMID 37643622.
- ↑ Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Ortega-Hernández, J.; Wolfe, J. M.; Jin, C.; Mai, H.; Hou, X.; Guo, J.; Zhai, D. (2023). "Three-dimensional morphology of the biramous appendages in Isoxys from the early Cambrian of South China, and its implications for early euarthropod evolution". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 290 (1997). 20230335. doi:10.1098/rspb.2023.0335. PMC 10113025. PMID 37072042.
- ↑ Ma, J.; Pates, S.; Wu, Y.; Lin, W.; Liu, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Fu, D. (2023). "Ontogeny and brooding strategy of the early Cambrian arthropod Isoxys minor from the Qingjiang biota". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. 11. 1174564. doi:10.3389/fevo.2023.1174564.
- ↑ Pates, S.; Zamora, S. (2023). "Large euarthropod carapaces from a high latitude Cambrian (Drumian) deposit in Spain". Royal Society Open Science. 10 (10). 230935. doi:10.1098/rsos.230935. PMC 10598445. PMID 37885986.
- ↑ Du, K.S.; Guo, J.; Losso, S. R.; Pates, S.; Li, M.; Chen, A.L. (2023). "Multiple origins of cephalic sutures in trilobites and their relatives". eLife. doi:10.7554/eLife.93113.1.
- ↑ Drage, H. B.; Legg, D. A.; Daley, A. C. (2023). "Novel marrellomorph moulting behaviour preserved in the Lower Ordovician Fezouata Shale, Morocco". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. 11. 1226924. doi:10.3389/fevo.2023.1226924.
- ↑ Laibl, L.; Gueriau, P.; Saleh, F.; Pérez-Peris, F.; Lustri, L.; Drage, H. B.; Bath Enright, O. G.; Potin, G. J.-M.; Daley, A. C. (2023). "Early developmental stages of a Lower Ordovician marrellid from Morocco suggest simple ontogenetic niche differentiation in early euarthropods". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. 11. 1232612. doi:10.3389/fevo.2023.1232612.
- ↑ Laville, T.; Hegna, T. A.; Forel, M.-B.; Darroch, S.; Charbonnier, S. (2023). "New look at Concavicaris woodfordi (Euarthropoda: Pancrustacea?) using micro-computed tomography". Palaeontologia Electronica. 26 (1). 26.1.a1. doi:10.26879/1218.
- ↑ Wellman, C. H.; Lopes, G.; McKellar, Z.; Hartley, A. (2023). "Age of the basal 'Lower Old Red Sandstone' Stonehaven Group of Scotland: The oldest reported air-breathing land animal is Silurian (late Wenlock) in age". Journal of the Geological Society. doi:10.1144/jgs2023-138.
- ↑ Lheritier, M.; Perroux, M.; Vannier, J.; Escarguel, G.; Wesener, T.; Moritz, L.; Chabard, D.; Adrien, J.; Perrier, V. (2023). "Fossils from the Montceau-les-Mines Lagerstätte (305 Ma) shed light on the anatomy, ecology and phylogeny of Carboniferous millipedes". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 21 (1). 2169891. doi:10.1080/14772019.2023.2169891. S2CID 256977924.
- ↑ Kimmig, J.; Pates, S.; LaVine, R. J.; Krumenacker, L. J.; Whitaker, A. F.; Strotz, L. C.; Jamison, P. G.; Gunther, V. G.; Gunther, G.; Witte, M.; Daley, A. C.; Lieberman, B. S. (2023). "New soft-bodied panarthropods from diverse Spence Shale (Cambrian; Miaolingian; Wuliuan) depositional environments". Journal of Paleontology. 97 (5): 1025–1048. doi:10.1017/jpa.2023.24. S2CID 259014568.
- ↑ Naimark, E. B.; Sizov, A. V.; Khubanov, V. B. (2023). "Kimiltei Is a New Late Cambrian Lagerstätte with the Faunistic Complex of Arthropods (Euthycarcinoidae, Synziphosurina, and Chasmataspidida) in the Irkutsk Region". Doklady Earth Sciences. 512 (1): 859–870. doi:10.1134/S1028334X2360127X. S2CID 260786737.
- ↑ Braddy, S. J. (2023). "A new arthropod resting trace from the middle Cambrian of Texas". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 309 (3): 291–300. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2023/1163.
