 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)(hydroxy)acetic acid | |
| Other names
2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxyacetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.154 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | 3,4-dihydroxymandelic+acid |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O5 | |
| Molar mass | 184.14612 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
3,4-Dihydroxymandelic acid (DHMA, DOMA) is a metabolite of norepinephrine.[1]
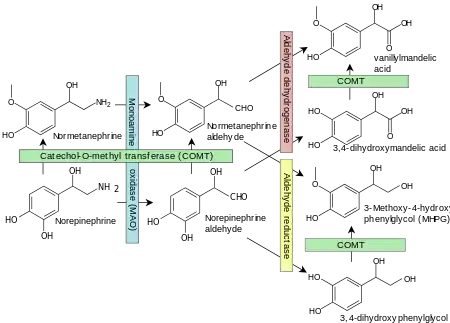 Norepinephrine degradation. 3,4-Dihydroxymandelic acid is shown at right. Enzymes are shown in boxes.[2] |
References
- ↑ Ley JP; Engelhart K; Bernhardt J; Bertram HJ (October 2002). "3,4-Dihydroxymandelic acid, a noradrenalin metabolite with powerful antioxidative potential". J. Agric. Food Chem. 50 (21): 5897–902. doi:10.1021/jf025667e. PMID 12358456.
- ↑ Figure 11-4 in: Rod Flower; Humphrey P. Rang; Maureen M. Dale; Ritter, James M. (2007). Rang & Dale's pharmacology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-443-06911-6.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.