 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Methylpentan-2-one | |
| Other names
Methyl sec-Butyl ketone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.439 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12O | |
| Molar mass | 100.161 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Peppermint-like |
| Density | 0.8130 g/mL (20 °C) |
| Melting point | −83 °C (−117 °F; 190 K) |
| Boiling point | 116 °C (241 °F; 389 K) |
| 2.26 wt % (20 °C) | |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.4012 (20 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
 | |
| Danger | |
| H225 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P280, P303+P361+P353, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 | |
| Flash point | 12 °C (54 °F; 285 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
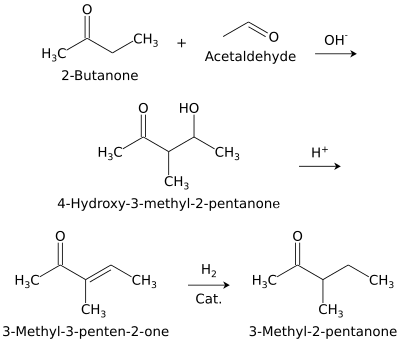
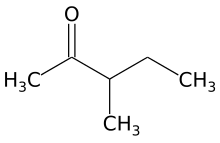
3-Methyl-2-pentanone (methyl sec-butyl ketone) is an aliphatic ketone and isomer of 2-hexanone. It is used as a solvent and as an intermediate for syntheses. Its industrial importance is low. It is produced by base-catalyzed aldol condensation of 2-butanone with acetaldehyde, forming 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-pentanone, which is dehydrated to 3-methyl-3-penten-2-one over an acid catalyst, followed by hydrogenation over a palladium catalyst.[2]
References
- ↑ "3-Methyl-2-pentanone". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ↑ Hardo Siegel, Manfred Eggersdorfer (2007), "Ketones", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (7th ed.), Wiley, p. 5
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.