| ATMOS | |
|---|---|
 An ATMOS system of the Philipine Army | |
| Type | Self-propelled howitzer |
| Place of origin | Israel |
| Service history | |
| In service | 2001 |
| Wars | 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh conflict |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Soltam Systems (now Elbit Systems) |
| Specifications | |
| Crew | 2 to 6 |
| Caliber | 155 mm (6.1 in) |
| Maximum firing range | >40 km (25 mi) with ERFB-BB |
ATMOS (Autonomous Truck Mounted howitzer System) is a 155 mm/52 calibre self-propelled gun system manufactured by Israeli military manufacturer Soltam Systems.
The system is long range, fast moving, truck mounted with high firepower and mobility, rapid deployment, short response time, operable in all terrain areas. The system is integrated with a fully computerized system, providing an automatic control, accurate navigation and target acquisition, the system is offered with various gun barrel lengths, ranging from 39 to 52 calibre, in order to meet different customer requirements.
Overview
The ATMOS is fitted with a 155 mm/52 calibre ordnance which conforms to NATO Joint Ballistic Memorandum of Understanding (JBMoU), and is mounted on a 6 × 6 cross-country truck chassis. The breech mechanism is horizontal sliding which automatically opens to the right with a self-sealing metal obturating ring. The buffer is a hydraulic cylinder with a hydro-pneumatic recuperator, and the recoil length is variable from 850 to 1,100 mm. Two pneumatic equilibrators balance the barrel, weapon elevation and traverse are all hydraulic and computer controlled. The gun's aiming gears, load assist systems and spades are operated by a hydraulic power pack. With a 155 mm/52 barrel, a 41 km maximum range can be achieved, using Extended Range Full-Bore - Base Bleed (ERFB-BB) projectile,[1] 30 km firing the NATO L15 High Explosive (HE) projectile and 24.5 km firing the older M107 HE projectile.
The ATMOS 2000 carries a total of 27 155 mm projectiles and associated charges[2] and can be operated by a 4-man crew, consisting of two loaders positioned on either side at the rear. The system provides a rate of fire of between 4 and 9 rds/min.
Development

Late in 2001, Soltam Systems released details of the latest version of its ATMOS 2000 whose existence was first revealed late in 1999.[3] At that time, it was also referred to as the 155 mm Self-Propelled Wheeled Gun (SPWG). The ATMOS was developed as a private venture and is aimed mainly for export markets, although it has already been demonstrated to the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). Wheeled self-propelled guns are usually cheaper to procure than their more common tracked counterparts, have lower life cycle costs and are easier to operate and maintain. In addition, they also have greater strategic mobility and do not rely on Heavy Equipment Transporters (HETs). By late 2001, the system fired over 1,000 rounds, during extensive trials in Israel.
In mid-2003, an undisclosed export customer had placed a contract with the company worth USD5 million for an undisclosed batch of ATMOS 2000 systems. From late 2004 the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) carried out extensive field tests the ATMOS 155 mm/39 calibre system.[4]
Variants
- ATROM – Romanian version that uses the same Soltam M-17 155mm gun on a locally developed ROMAN 26.360 DFAEG 6x6 truck chassis.[5] The system never entered production and the project was put on hold after three prototypes were built.[6]
- AHS Kryl – Polish version on a Jelcz 663 armoured 6×6 chassis and integrating WB Electronics "Topaz" artillery fire control system. Production was planned for 2021, but never started.
- M758 ATMG - Thai version on a Tatra armoured 6×6 chassis jointly developed by Soltam and DTI. 24 systems were in service as of 2023.[7]
Operators
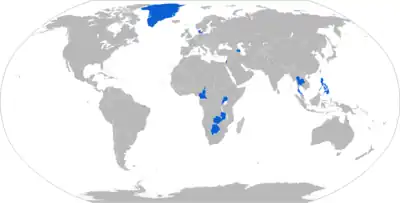
Current operators
 Azerbaijan – Azerbaijani Army: 6 systems[8]
Azerbaijan – Azerbaijani Army: 6 systems[8] Botswana - Botswana Defence Force: 5 systems in 2018[9]
Botswana - Botswana Defence Force: 5 systems in 2018[9] Cameroon – Cameroonian Army: 18 systems[10]
Cameroon – Cameroonian Army: 18 systems[10] Philippines – Philippine Army: 12 systems[11]
Philippines – Philippine Army: 12 systems[11] Thailand – Royal Thai Army: M758 ATMG - 24 systems+6 systems on order[12][13]
Thailand – Royal Thai Army: M758 ATMG - 24 systems+6 systems on order[12][13]
Royal Thai Marine Corps: ATMOS 2000 - 6 systems + 6 systems on order [14] Rwanda – Rwandan Defence Force: at least 5 ATMOS 2000 systems[15][16]
Rwanda – Rwandan Defence Force: at least 5 ATMOS 2000 systems[15][16] Uganda – UPDF Land Forces: 6 systems[8][10]
Uganda – UPDF Land Forces: 6 systems[8][10] Zambia – Zambian Army: 6 systems[17]
Zambia – Zambian Army: 6 systems[17] Denmark – Royal Danish Army: 1 system - 18 systems under construction.[18] To replace the 19 ordered units of French produced CAESAR 8x8 howitzers that has been pledged to the Ukrainian armed forces.[19][20]
Denmark – Royal Danish Army: 1 system - 18 systems under construction.[18] To replace the 19 ordered units of French produced CAESAR 8x8 howitzers that has been pledged to the Ukrainian armed forces.[19][20]
Future operators
 Colombia – Colombian Army: The Colombian Army will acquire 18 units of the self-propelled howitzer developed by the Elbit Systems.[21]
Colombia – Colombian Army: The Colombian Army will acquire 18 units of the self-propelled howitzer developed by the Elbit Systems.[21] Israel – As of 2017, a development of the ATMOS 2000 was selected to replace the M109s operated by the Israel Defense Forces.[22]
Israel – As of 2017, a development of the ATMOS 2000 was selected to replace the M109s operated by the Israel Defense Forces.[22]
Potential operators
 Brazil –The Atmos 2000 was offered to the Brazilian Army as part of the "VBCOAP 155mm SR" program for the acquisition of 36 self-propelled howitzers[23]
Brazil –The Atmos 2000 was offered to the Brazilian Army as part of the "VBCOAP 155mm SR" program for the acquisition of 36 self-propelled howitzers[23] Poland – the Polish Land Forces planned but never ordered the AHS Kryl 155mm Howitzer, a domestically made version of the ATMOS 2000[24]
Poland – the Polish Land Forces planned but never ordered the AHS Kryl 155mm Howitzer, a domestically made version of the ATMOS 2000[24] Romania – ATROM variant prototypes only, the system never entered production.[5]
Romania – ATROM variant prototypes only, the system never entered production.[5] United States – The US Army is interested in a more mobile artillery platforms. Some "Mobile Howitzer Trials and Shoot-Off" had been occurring in 2021.[25]The systems tested were the CAESAR, the ATMOS 2000, the Archer and the Nora B-52. The Army was impressed by the Archer,[26]also very positive with the CAESAR.[27] But not much has filtered about potentially ordering one of these systems. As some M777 howitzers were donated to Ukraine, it is certainly possible that the Army would consider a truck mounted variant to compensate as a gap filler to cover the donated howitzers.
United States – The US Army is interested in a more mobile artillery platforms. Some "Mobile Howitzer Trials and Shoot-Off" had been occurring in 2021.[25]The systems tested were the CAESAR, the ATMOS 2000, the Archer and the Nora B-52. The Army was impressed by the Archer,[26]also very positive with the CAESAR.[27] But not much has filtered about potentially ordering one of these systems. As some M777 howitzers were donated to Ukraine, it is certainly possible that the Army would consider a truck mounted variant to compensate as a gap filler to cover the donated howitzers. Bulgaria- ATMOS is one of the favourites to win The Bulgarian Ministry of Defence's contract for new 155 mm Self-propelled howitser.[28]
Bulgaria- ATMOS is one of the favourites to win The Bulgarian Ministry of Defence's contract for new 155 mm Self-propelled howitser.[28]
See also
- Archer – Swedish 155 mm self-propelled howitzer
- A-222E Bereg-E 130mm coastal mobile artillery system – Russian self-propelled coastal defense gun
- 2S22 Bohdana – Ukrainian 155 mm self-propelled howitzer
- CAESAR self-propelled howitzer – French 155 mm artillery
- DANA – Czechoslovak self-propelled howitzer
- G6 Rhino – South African 155 mm self-propelled artillery
- Nora B-52 – Serbian 155 mm self-propelled howitzer
- PCL-09 – Chinese 122 mm self-propelled howitzer
- PCL-161 – Chinese 122 mm self-propelled howitzer
- PCL-181 – Chinese 155 mm self-propelled howitzer
- PLL-09 – Chinese wheeled armoured fighting vehicle family
- Type 19 155 mm Wheeled Self-propelled Howitzer – Japanese artillery
- 155mm SpGH ZUZANA – Slovak self-propelled gun-howitzer
References
- Notes
- ↑ "ATMOS 155mm truck-mounted howitzer for increased mobility and enhanced firing capabilities" (PDF). elbitsystems.com.
- ↑ Atmos Project Details on Army Technology
- ↑ Atmos 2000 Project Details on Military Today
- ↑ Atmos 2000 Field Test Details on faqs.org
- 1 2 "ATROM". militarytoday.com. Retrieved 16 September 2023.
- ↑ "Romania (Modern)". tanks-encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 16 September 2023.
- ↑ "Jane - Defense & Security 2022: Royal Thai Army expands artillery production". 31 August 2022.
- 1 2 "SIPRI: Arms Transfer".Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, 07 December, 2013
- ↑ IISS 2018, p. 463
- 1 2 "The Military Balance 2010".International Institute for Strategic Studies, February 3, 2010.
- ↑ "Israeli self-propelled howitzers delivered to PH Army". Inquirer.net. 5 January 2022. Retrieved 8 January 2022.
- ↑ "Jane - Defense & Security 2022: Royal Thai Army expands artillery production". 31 August 2022.
- ↑ "Elbit, Thai industry collaborate on ATMOS 155 mm SP howitzer". www.janes.com. 4 November 2013. Retrieved 7 November 2013.
- ↑ admin (2023-11-14). "Royal Thai Army Expands M758 Autonomous Truck-Mounted Gun (ATMG) Production". MilitaryLeak. Retrieved 2023-11-14.
- ↑ Binnie, Jeremy (7 November 2016). "Rwanda exercises new ATMOS 2000 howitzers". IHS Jane's 360. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ↑ "Rwanda armed forces equipped with ATMOS and PLZ-89 howitzers | November 2017 Global Defense Security news industry | Defense Security global news industry army 2017 | Archive News year".
- ↑ "Zambian military parades new equipment".
- ↑ Nicholas Fiorenza (4 August 2023). "Denmark receives first ATMOS SPHs and PULS MRLs". Janes.
- ↑ "Denmarks buys artillery system and rocket launchers from Israel". TV2. January 26, 2023.
- ↑ https://www.fmi.dk/da/nyheder/2023/se-video-af-nyt-ildstoettesystem-til-forsvaret/
- ↑ InfoDefensa, Revista Defensa. "Colombia da marcha atrás en el último minuto y opta por el Atmos en lugar del Caesar". Infodefensa - Noticias de defensa, industria, seguridad, armamento, ejércitos y tecnología de la defensa (in Spanish). Retrieved 2023-01-04.
- ↑ Elbit selected to develop IDF artillery capability 4 Apr, 2017 19:27, Yuval Azulay
- ↑ InfoDefensa, Revista Defensa. "Exército Brasileiro avalia compra de 36 obuseiros autopropulsados de 155 mm". Infodefensa - Noticias de defensa, industria, seguridad, armamento, ejércitos y tecnología de la defensa (in Spanish). Retrieved 2022-10-06.
- ↑ "The Polish Army Will Receive Self-Propelled Howitzer Based on Elbit's ATMOS". Israel Defense. March 10, 2016.
- ↑ Lye, Harry (2021-05-19). "UK eyes US mobile howitzer shoot-off to inform Mobile Fires Platform". Army Technology. Retrieved 2023-04-15.
- ↑ "BAE Systems' 155mm ARCHER successfully completes U.S. Army's shoot-off evaluation". baesystems.com. 11 October 2021.
- ↑ Lagneau, Laurent (2022-01-19). "Artillerie : Le CAESAr du français Nexter se distingue aux États-Unis en tirant des obus "Excalibur"". Zone Militaire (in French). Retrieved 2023-04-15.
- ↑ "Ракети, радари, бронирани машини. Как България се разбърза да превъоръжи армията заради агресията на Русия". Свободна Европа (in Bulgarian). 2023-09-12. Retrieved 2023-09-24.
External links
- Video