| mountain hickory | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Clade: | Mimosoid clade |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. obliquinervia |
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia obliquinervia | |
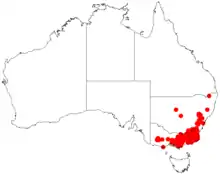 | |
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Racosperma obliquinervium (Tindale) Pedley | |
Acacia obliquinervia, known colloquially as mountain hickory[1] or mountain hickory wattle,[2] is a species of Acacia that is endemic to south eastern Australia.[1]
Description
The shrub or tree can grow to a height of 1 to 15 m (3 ft 3 in to 49 ft 3 in) and can have an erect or spreading habit. The has dark brown coloured and deeply fissured bark with angled or flattened and glabrous branchlets that are often covered in a fine white powdery coating. Like most species of Acacia it has phyllodes rather than true leaves. The glabrous, evergreen phyllodes have an obovate to narrowly oblanceolate shape that is occasionally narrowly elliptic with a length of 5 to 17 cm (2.0 to 6.7 in) and a width of 9 to 55 mm (0.35 to 2.17 in) with a prominent midvein.[1] It blooms between August and December producing simple inflorescences that are found in clusters of 3 to 16 in the racemes along a zig-zagged axis of 1 to 10 cm (0.39 to 3.94 in) with spherical flower-heads that have a diameter of 5 to 8 mm (0.20 to 0.31 in) containing 20 to 35 bright yellow coloured flowers.[1] Following flowering it forms chartaceous to thinly coriaceous seed pods that have an oblong shape with a length of 4 to 15 cm (1.6 to 5.9 in) and have a width of 12 to 25 mm (0.47 to 0.98 in) and can be covered in a fine white powdery coating. The dull to slightly shiny black seeds inside have an oblong-elliptic to ovate shape with a length of 5 to 6 mm (0.20 to 0.24 in).[2]
Distribution
It is native south eastern New South Wales, the Australian Capital Territory,[2] and Victoria in eastern Australia. In New South Wales it is found in tableland areas of the Great Dividing Range that are south of the Goulburn River valley where it is found growing in soils derived from the surrounding sandstone as a part of moist or dry sclerophyll forest and woodland communities.[1] It is found in central and eastern Victoria where its range extends from the Grampians to areas east of Melbourne where it is commonly situated in montane woodlands and forests at an altitude of 500 to 1,700 m (1,600 to 5,600 ft).[2]