This page provides supplementary chemical data on acetic acid.
Material Safety Data Sheet
The handling of this chemical may incur notable safety precautions. It is highly recommend that you seek the Material Safety Datasheet (MSDS) for this chemical from a reliable source and follow its directions.
Structure and properties
| Structure and properties | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index of refraction, nD | 1.3716 | ||||||||
| Dielectric constant, εr | 6.15 ε0 at 20 °C | ||||||||
| Bond strength | ? | ||||||||
| Bond length | ? | ||||||||
| Bond angle | ? | ||||||||
| Magnetic susceptibility | ? | ||||||||
| Surface tension | 26.6 dyn/cm at 30 °C | ||||||||
| Viscosity[1] |
| ||||||||
Thermodynamic properties
| Phase behavior | |
|---|---|
| Triple point | 289.8 K (16.7 °C), ? Pa |
| Critical point | 593 K (320 °C), 57.8 bar |
| Eutectic point with water | –26.7 °C |
| Std enthalpy change of fusionΔfusH |
+11.7 kJ/mol |
| Std entropy change of fusionΔfusS |
40.5 J/(mol·K) |
| Std enthalpy change of vaporizationΔvapH |
+23.7 kJ/mol |
| Std entropy change of vaporizationΔvapS |
? J/(mol·K) |
| Solid properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation ΔfH |
? kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy S |
? J/(mol K) |
| Heat capacity cp | ? J/(mol K) |
| Liquid properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation ΔfH |
−483.5 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy S |
158.0 J/(mol K) |
| Enthalpy of combustion, ΔcH |
–876.1 kJ/mol |
| Heat capacity cp | 123.1 J/(mol K) |
| Gas properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation ΔfH |
–438.1 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy S |
282.84 J/(mol K) |
| Heat capacity cp | 63.4 J/(mol K) |
| van der Waals' constants[2] | a = 1782.3 L2 kPa/mol2 b = 0.1068 liter per mole |
Vapor pressure of liquid
| P in mm Hg | 1 | 10 | 40 | 100 | 400 | 760 | 1520 | 3800 | 7600 | 15200 | 30400 | 45600 | |
| T in °C | –17.2 | 17.5 | 43.0 | 63.0 | 99.0 | 118.1 | 143.5 | 180.3 | 214.0 | 252.0 | 297.0 | — | |
Table data obtained from CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 44th ed.
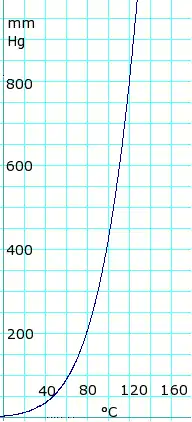 Acetic acid vapor pressure vs. temperature. Uses formula: for T = 0 to 36 °C
for T = 36 to 170 °C Formula from Lange's Handbook of Chemistry, 10th ed. |
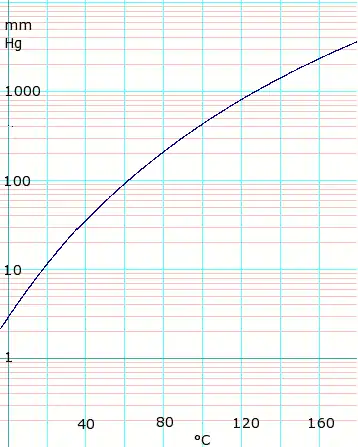 log10 of acetic acid vapor pressure vs. temperature. Uses formula: for T = 0 to 36 °C
for T = 36 to 170 °C Formula from Lange's Handbook of Chemistry, 10th ed. |
Distillation data
| Vapor-liquid Equilibrium for Acetic acid/Water[3] P = 760 mm Hg | ||
| BP Temp. °C |
mole % water | |
|---|---|---|
| liquid | vapor | |
| 116.5 | 2.2 | 5.8 |
| 114.6 | 5.4 | 12.3 |
| 113.4 | 8.6 | 16.8 |
| 113.5 | 9.9 | 18.3 |
| 113.1 | 10.1 | 18.8 |
| 110.6 | 18.9 | 29.8 |
| 107.8 | 30.3 | 43.3 |
| 106.1 | 41.3 | 54.5 |
| 104.4 | 52.2 | 64.9 |
| 103.1 | 62.4 | 73.5 |
| 102.3 | 69.6 | 79.2 |
| 101.6 | 77.8 | 85.1 |
| 100.8 | 87.6 | 91.4 |
| 100.5 | 92.3 | 94.4 |
| 100.4 | 94.5 | 96.0 |
| 100.1 | 98.5 | 98.9 |
Spectral data
| UV-Vis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λmax | 207 nm (gas phase) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Extinction coefficient, ε | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IR | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Major absorption bands[4] |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proton NMR | δ CDCl3 2.10 (3H), 11.42 (1H) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carbon-13 NMR | δ CDCl3 20.8, 178.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other NMR data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Masses of main fragments |
60 (75%), 45 (90%), 43 (100%), 42 (13%), 15 (17%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- ↑ Lange's Handbook of Chemistry, 10th ed. pp 1669-1674
- ↑ Lange's Handbook of Chemistry 10th ed, pp 1522-1524
- ↑ "Binary Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Data" (Queriable database). Chemical Engineering Research Information Center. Retrieved 5 May 2007.
- ↑ "Spectral Database for Organic Compounds". Advanced Industrial Science and Technology. Archived from the original (Queriable database) on 14 January 2013. Retrieved 9 June 2007.
- Linstrom, Peter J.; Mallard, William G. (eds.); NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (MD)
- Orlando, John J.; Tyndall, Geoffrey S. (2003). "Gas phase UV absorption spectra for peracetic acid, and for acetic acid monomers and dimers". J. Photochem. Photobiol. A. 157 (2–3): 161–66. doi:10.1016/S1010-6030(03)00067-4.
This box:
- Except where noted otherwise, data relate to Standard temperature and pressure.
- Reliability of data general note.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.