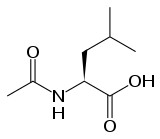
 (S)-(-)-N-Acetyl-leucine | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Acetamido-4-methylpentanoic acid[1] | |
| Other names
N-Acetylleucine; N-Acetyl-L-Leucine | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet |
|
| 1724849 (S)-(-) | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| 985259 (S)-(-) | |
| KEGG |
|
| MeSH | acetylleucine |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H15NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 173.212 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Melting point | −115 to −113 °C; −175 to −172 °F; 158 to 160 K |
| log P | −0.265 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.666 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 10.331 |
| Pharmacology | |
| N07CA04 (WHO) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
ENU |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Acetylleucine is a modified amino acid used in the treatment of vertigo[2] and cerebellar ataxia.
Acetylleucine is also being developed as a possible treatment for several neurological disorders by IntraBio Inc.[3] Clinical trials with acetylleucine for the treatment of three orphan, fatal, neurodegenerative disorders are underway: Niemann-Pick disease type C,[4] GM2 gangliosidoses (Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff diseases),[5] and ataxia–telangiectasia.[6] In 2020, IntraBio announced the successful multinational clinical trial results of the Niemann-Pick type C clinical trial.[7] IntraBio is also investigating acetylleucine for the treatment of common inherited and acquired neurological diseases including Lewy body dementia,[8] amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, restless legs syndrome, multiple sclerosis, and migraine[9] Acetylleucine has received orphan drug designations from the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA)[10][11][12][13] and the European Commission.[14][15][16][17]
See also
References
- ↑ "N-Acetyl-DL-leucine". PubChem Open Chemistry Database. Retrieved 26 Mar 2017.
- ↑ "N07CA04 (acetylleucine)". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Norwegian Institute of Public Health. 19 Dec 2016. Retrieved 26 Mar 2017.
- ↑ "IntraBio". Archived from the original on 2019-08-01. Retrieved 2019-08-01.
- ↑ "N-Acetyl-L-Leucine for Niemann-Pick Disease, Type C (NPC) - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov". clinicaltrials.gov. Retrieved 2019-08-01.
- ↑ "N-Acetyl-L-Leucine for GM2 Gangliosdisosis (Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff Disease) - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov". clinicaltrials.gov. Retrieved 2019-08-01.
- ↑ "N-Acetyl-L-Leucine for Ataxia-Telangiectasia (A-T) - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov". clinicaltrials.gov. Retrieved 2019-08-01.
- ↑ "IntraBio Reports Further Detail on Positive Data from IB1001 Multinational Clinical Trial for the Treatment of Niemann-Pick disease Type C". intrabio.com. 19 October 2020. Retrieved 2021-08-01.
- ↑ Passmore, Peter (2014-04-15). "A clinical trial to test amlodipine as a new treatment for vascular dementia". doi:10.1186/isrctn31208535.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ Strupp, Michael; Bayer, Otmar; Feil, Katharina; Straube, Andreas (2019-02-01). "Prophylactic treatment of migraine with and without aura with acetyl-dl-leucine: a case series". Journal of Neurology. 266 (2): 525–529. doi:10.1007/s00415-018-9155-6. ISSN 1432-1459. PMID 30547273. S2CID 56148131.
- ↑ "Search Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". www.accessdata.fda.gov. Retrieved 2019-08-03.
- ↑ "Search Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". www.accessdata.fda.gov. Retrieved 2019-08-03.
- ↑ "Search Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". www.accessdata.fda.gov. Retrieved 2019-08-03.
- ↑ "Search Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". www.accessdata.fda.gov. Retrieved 2019-08-03.
- ↑ "Public Health - European Commission". Union Register of medicinal products. Retrieved 2019-08-03.
- ↑ "Public Health - European Commission". Union Register of medicinal products. Retrieved 2019-08-03.
- ↑ "Public Health - European Commission". Union Register of medicinal products. Retrieved 2019-08-03.
- ↑ "Public Health - European Commission". Union Register of medicinal products. Retrieved 2019-08-03.