Acrophobia is an online multiplayer word game. The game was originally conceived by Andrea Shubert,[1][2] and programmed by Kenrick Mock and Michelle Hoyle in 1995.[3][4] Originally available over Internet Relay Chat, the game has since been developed into a number of variants, as a download, playable through a browser, via Twitter or through Facebook.[5]
Background
Created by Andrea Shubert in the mid to late 1990s,[6] she developed a "spiritual successor" called TAG: The Acronym Game for startup gaming company play140.[7]
Game play
Players enter a channel hosted by a bot which runs the game. In each round, the bot generates a random acronym. Players compete by racing to create the most coherent or humorous sentence that fits the acronym - in essence, a backronym. After a set amount of time expires, each player then votes anonymously via the bot for their favorite answer (aside from their own).
Points are awarded to the most popular backronym. Bonus points also may be given based on the fastest response and for voting for the winning option. Some implementations give the speed bonus to the player with the first answer that received at least one vote; this is to discourage players from quickly entering gibberish just to be the first. Bonus points for voting for the winner helps discourage players from intentionally voting for poor answers to avoid giving votes to answers that might beat their own.
Some versions of the game were criticized for the ease with which players could disrupt games with obscenities, and the anonymous nature of the site meant that there were no repercussions for this behavior.[8] Usually, nonsense backronyms will score low and the most humorous sounding backronym which effectively makes a sentence from the initials will win. Some rounds may have a specific topic that the answers should fit, although enforcement of the topic depends on solely on the other players' willingness to vote for off-topic answers.
Acrophobia was commended as an online game that showed the potential for educational use, and that its use of technology allowed "imaginative play, instant feedback, and [an] unusual scoring system."[9]
An example game typically goes as follows:
- a 3-letter round
- a 4-letter round
- a 5-letter round
- a 6-letter round
- a 7-letter round
Then, it goes back to 3 letters and starts the cycle over.
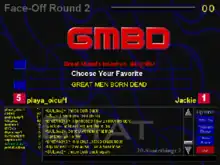
Once one player reaches 30 points, the top two players at this point are chosen to face-off. In the face-off rounds, the two players enter their acronyms and everyone else votes not knowing which acronym is from which player. Each face-off round lasts about 20 seconds and consists of:
- a 3-letter round
- a 4-letter round
- a 5-letter round
The player with the most points from the face-off round wins the game.
Reception
Acrophobia was a runner-up for Computer Gaming World's 1997 "Puzzle Game of the Year" award, which ultimately went to Smart Games Challenge 2.[10] However, it won GameSpot's 1997 "Best Online-Only Game" award; the editors wrote, "Besides being a fun and very addictive game, the great thing about Acrophobia is the social experience."[11]
Similar games
Acrofever, an Acrophobia clone for the modern web.[12]
Acrozilla is another clone, but with the unusual caveat that it is only available to play certain unpublished hours.
Wacronyms is a mobile version of the game available for Android and Apple devices.
References
- ↑ "With acronym game Acrophobia, WYSSIWYG". Fort Worth Star-Telegram. September 10, 1998. p. 59. Retrieved August 17, 2021.
 (Subscription required.)
(Subscription required.) - ↑ "Andrea Jennifer Shubert". Retrieved 2011-12-02.
- ↑ "Just the FAQs: Acrophobia(TM)". 2002-11-25. Retrieved 2006-12-23.
- ↑ "Chat Games: Alphabet Soup". Talk City. 2006. Archived from the original on 2006-12-30. Retrieved 2006-12-23.
- ↑ "TAG: The Acronym Game". play140 INC. Retrieved 2011-12-02.
- ↑ Kapp, Karl M. (2007). Gadgets, games, and gizmos for learning. John Wiley and Sons. pp. 58–60. ISBN 978-0-7879-8654-4.
- ↑ "About play140 INC". play140 INC. Archived from the original on 2011-12-09. Retrieved 2011-12-02.
- ↑ Glassner, Andrew S. (2004). Interactive storytelling: techniques for 21st century fiction. A K Peters, Ltd. pp. 233. ISBN 978-1-56881-221-2.
Acrophobia.
- ↑ Beckshi, Peter (2000). "Instructor-based Section". In Piskurich, George M.; Beckschi, Peter; Hall, Brandon (eds.). The ASTD handbook of training design and delivery. McGraw-Hill Professional. pp. 112. ISBN 978-0-07-134310-7.
Acrophobia game.
- ↑ Staff (March 1998). "CGW Presents The Best & Worst of 1997". Computer Gaming World. No. 164. pp. 74–77, 80, 84, 88, 89.
- ↑ Staff. "Best & Worst Awards 1997". GameSpot. Archived from the original on 2001-02-08. Retrieved 2018-10-01.
- ↑ "Acrofever Homepage". Acrofever. Archived from the original on 2016-01-10. Retrieved 2021-04-23.