| Airport line | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Overview | |
| Website | airtrain.com.au |
| Service | |
| Rolling stock | NGR |
| History | |
| Opened | 5 May 2001[1] |
| Technical | |
| Track length | 15.9 km (9.9 mi) |
| Track gauge | 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) |
| Electrification | 2001 |
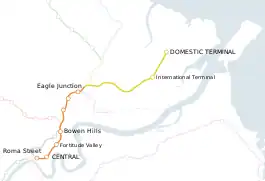
Airtrain (also known as the Airport railway line) is the privately owned commuter railway line that extends 13.0 km (8.1 mi) northeast from Brisbane (15.9 km (9.9 mi) from Central station by rail), the state capital of Queensland, to Brisbane Airport (BNE) at both its separate International and Domestic terminals. It was opened in 2001.
The line is carried on an elevated prestressed concrete viaduct for its entire 8.5 km (5.3 mi) length after branching off from the Queensland Rail Citytrain network at Eagle Junction railway station.
Ownership and business
The Airtrain service is a private enterprise. The line is owned and operated by Airtrain Citylink Limited, with financial backing from Transfield Services, Macquarie Bank, Colonial First State and ABN AMRO. The first service ran on 5 May 2001.[1] Airtrain Citylink has a licence from Queensland Transport under a BOOT scheme – build, own, operate and transfer – to build the rail line, to own and operate it, and hand entire infrastructure over to the Queensland Government after 35 years when the company will then cease to exist.
The line connects seamlessly with the Queensland Rail City network and services use City network rolling stock in a commercial agreement with QR. While City network rolling stock is used, Airtrain does not form part of the Translink integrated public transport scheme, and therefore fares are not subsidised by the government. As a result, travel between the airport and City network stations in the Brisbane central business district costs $19.80 one way and $37.60 return (as of December 2022; cheaper on-line).[2] Travel on Airtrain services between ordinary City network stations, not involving airport travel, is charged at the normal Translink rate, including concession (pensioner) rates.
In 2008, Brisbane's Airtrain ran an operating profit of $4.8 million, allowing Airtrain to pay dividends of $1.95 to its shareholders.[3] Airtain is not subsidised by the Queensland Government, and its $220 million construction cost was entirely privately financed.[4] This makes it one of a few known profitable public transport systems.
In late 2012, UK pension fund Universities Superannuation Scheme bought Airtrain for A$110 million.[5]
Patronage
Initial passenger numbers on the service were well below expectations[6] and the company nearly faced voluntary administration in 2003. However, in May 2005, Airtrain operated at a profit for the first time due to significant passenger growth – 1.12 million passengers in the 2004–2005 financial year, an increase of 40% – and a complex company restructure that cut costs by nearly half.
Passenger numbers on the service have also steadily increased, now close to two million passengers each year. In 2008, 6% of visitors to the airport used an Airtrain service.[7] This figure rose to 8% in 2011.
Line guide and services
Commencing at the Domestic Terminal, all services stop at the International Terminal and then all stations though the Brisbane CBD to at least Roma Street. The typical travel time between Domestic Terminal and Brisbane City is approximately 22 minutes (to Central). This travel time results in an average train speed of 43 km/h (27 mph).
Airport line services run every fifteen minutes during the morning and afternoon weekday peak hours, and every half hour during the off-peak. Most services continue as Gold Coast line services.
Passengers for/from the Doomben, Caboolture, Shorncliffe and Redcliffe Peninsula lines change at Eagle Junction, Ferny Grove and Nambour and Gympie North lines at Bowen Hills, and all other lines at Central.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Proposed Skygate station
Brisbane Airport Corporation has proposed a new station at its Skygate retail park at the south-western edge of the airport. Discussions have taken place with Airtrain Holdings Limited and the Queensland Government.[8]
Gallery
 A Queensland Rail NGR train at Domestic Terminal
A Queensland Rail NGR train at Domestic Terminal Connecting concourse between the Domestic Terminals and Station
Connecting concourse between the Domestic Terminals and Station NGR train travelling between Domestic and International Terminals
NGR train travelling between Domestic and International Terminals IMU 109 at International Terminal railway station
IMU 109 at International Terminal railway station Airtrain line viaduct over the Kedron Brook
Airtrain line viaduct over the Kedron Brook
See also
References
- 1 2 Debritz, Brett (6 May 2001). "Airtrain off to a flying start". The Sunday Mail. p. 50.
- ↑ "Brisbane Airtrain - Fare Calculator". Brisbane Airtrain. Archived from the original on 11 December 2022. Retrieved 11 December 2022.
- ↑ McCulloch, James. (22 September 2008).Brisbane Airtrain lifts operating profit to $4.8 million. The Courier Mail.
- ↑ Brisbane Airtrain- About Us Archived 13 February 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Tan, Gillian (21 December 2012). "U.K. Pension Fund Buys Brisbane's Airport Rail Link". Wall Street Journal. Dow Jones & Company, Inc. Archived from the original on 11 January 2013. Retrieved 21 December 2012.
- ↑ "Airport rail passenger numbers increase". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 19 July 2003. Retrieved 8 December 2007.
- ↑ Tony Moore (26 October 2012). "Off the rails: Uncertainty over Airtrain monopoly". Brisbane Times. Fairfax Media. Archived from the original on 27 October 2012. Retrieved 26 October 2012.
- ↑ "Brisbane Airport pushes for new Skygate DFO train station". Brisbane Times. 17 August 2016. Archived from the original on 18 August 2016. Retrieved 16 August 2016.
External links
- Airtrain
- Citytrain
- Translink
- "South East Queensland Train Network Map" (PDF). Translink. 1 May 2020.