Ajanta Express train board | |||||
| Overview | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Service type | Express | ||||
| Locale | Telangana & Maharashtra | ||||
| First service | 1 April 1967 | ||||
| Current operator(s) | South Central Railways | ||||
| Route | |||||
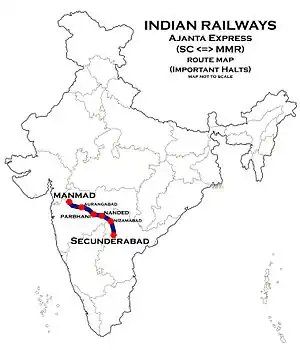
| Termini | Kacheguda (KCG) Manmad Junction (MMR) | ||||
| Stops | 18 | ||||
| Distance travelled | 624 km (388 mi) | ||||
| Average journey time |
| ||||
| Service frequency | Daily | ||||
| Train number(s) | 17063 / 17064 | ||||
| On-board services | |||||
| Class(es) | AC First, AC II Tier, AC III Tier, Sleeper class, General Unreserved | ||||
| Seating arrangements | Yes | ||||
| Sleeping arrangements | Yes | ||||
| Catering facilities | On-Board Catering, E-catering | ||||
| Observation facilities | Rake sharing with 12785/86 Kacheguda–Mysuru Express | ||||
| Baggage facilities | Below the seats | ||||
| Technical | |||||
| Rolling stock | ICF coach | ||||
| Track gauge | 1,676 mm (5 ft 6 in) (broad gauge) | ||||
| Operating speed | 49 km/h (30 mph) average including halts | ||||
| |||||
The 17063 / 17064 Ajanta Express is an Express train belonging to the South Central Railway Zone that runs between Kacheguda in Telangana and Manmad in Maharashtra in India.
History
Ajanta Express runs through eastern Maharashtra (Marathwada region) and the north-western region of Telangana. It was known as Kacheguda Express very often by the people travelling on Kacheguda–Nizamabad–Nanded–Parbhani–Aurangabad route on former Hyderabad–Godavari Valley Railways.
The train was introduced on 1st April, 1967 as a metre-gauge train between Kacheguda and Manmad via Nizamabad, Nanded, Parbhani and Aurangabad. The train became popular in a short time as Manmad on 5 ft 6 in (1,676 mm) broad gauge was the point to take broad gauge trains to other destinations.
After the track from Manmad to Parbhani was converted to broad gauge in 1992–95 and the track from Parbhani to Mudkhed and Nizamabad was still not converted, the train was re-routed between Kacheguda and Manmad via Bidar and Parbhani in 1995–1996 because the metre gauge had been converted between Vikarabad and Parbhani by then. In 2007, the train again diverted to its old route which had been converted into broad gauge in 2002–2003.
Ajanta Express (Kacheguda–Manmad) was the fastest metre-gauge train in India with an average speed of 42.5 kilometres per hour (26.4 mph) in 1967.[1]
Overview
The train is named after the Ajanta Caves in Aurangabad. It runs daily and connects important stations such as Nizamabad, Nanded, Parbhani, Jalna, Aurangabad and Nagarsol.
The 17063 Manmad–Kacheguda Ajanta Express has an average speed of 48 km/h and covers 624 km in 12 hours 55 minutes. The 17064 Kacheguda–Manmad Ajanta Express has an average speed of 47 km/h and covers 624 km in 13 hours and 25 minutes.
Timings
The train departs from Kacheguda at 6:40 p.m. and arrives at Manmad Junction at 8:05 a.m. the next day. It departs from Manmad Junction at 8:50 p.m. and arrives at Kacheguda at 9:45 a.m. the next day.
Route and halts
Classes
The train usually consists of 24 standard ICF coaches:
- 1 AC first cum II tier
- 2 AC II tier
- 5 AC III tiers
- 12 sleeper classes
- 2 second sittings
- 2 SLR
As it is customary with most other train services in India, coach composition may be amended at the discretion of Indian Railways, depending on demand.
Coach composition
| Loco | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLR | GEN | HA1 | A2 | A1 | B5 | B4 | B3 | B2 | B1 | S12 | S11 | S10 | S9 | S8 | S7 | S6 | S5 | S4 | S3 | S2 | S1 | GEN | SLR |
Rake sharing
- Previously it shared its rake with 12703/04 Falaknuma Express(1 January 2018 to 14th December 2023).
- From 20th Dec 2023 The Train started sharing its rake with 12785/86 Kacheguda–Mysuru Express and the Terminal is shifted back to Kacheguda With Primary Maintenance.
Gallery
 Ajanta Express
Ajanta Express Ajanta Express Train Board
Ajanta Express Train Board Ajanta Express new RSA with Mysuru Express
Ajanta Express new RSA with Mysuru Express
Loco link
As the route is not completely electrified, so Gooty based WDP-4D or Moula Ali based WDG-3A twins diesel locomotive hauls the train to complete its full journey.
See also
References
- ↑ "Chronology of railways in India, Part 4 (1947–1970)". IRFCA Indian Railways Fan Club. 2010. Retrieved 31 March 2013.