| Allocasuarina trichodon | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Casuarinaceae |
| Genus: | Allocasuarina |
| Species: | A. trichodon |
| Binomial name | |
| Allocasuarina trichodon | |
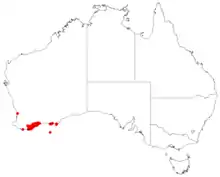 | |
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Casuarina bicuspidata Benth. Casuarina trichodon Miq. | |

Allocasuarina trichodon is a species of flowering plant in the family Casuarinaceae and is endemic to areas along the south coast of Western Australia. It is a dioecious, rarely a monoecious shrub that has branchlets up to 300 mm (12 in) long, the leaves reduced to scales in whorls of eight to ten, and the fruiting cones 15–50 mm (0.59–1.97 in) long containing winged seeds 8–10 mm (0.31–0.39 in) long.
Description
Allocasuarina trichodon is dioecious, rarely a monoecious shrub that typically grows to a height of 0.5–3 m (1 ft 8 in – 9 ft 10 in). Its branchlets are more or less erect and up to 300 mm (12 in) long, the leaves reduced to spreading teeth 1.8–3.5 mm (0.071–0.138 in) long, arranged in whorls of eight to ten around the branchlets. The sections of branchlet between the leaf whorls are 9–15 mm (0.35–0.59 in) long, 0.9–1 mm (0.035–0.039 in) wide. Male flowers are arranged in spikes 30–80 mm (1.2–3.1 in) long, with about 8 whorls per centimetre (per 0.39 in.), the anthers 1.0–1.2 mm (0.039–0.047 in) long. Female cones are sessile, the mature cones cylindrical to barrel-shaped, 15–50 mm (0.59–1.97 in) long and 14–20 mm (0.55–0.79 in) in diameter, containing winged seeds 8–10 mm (0.31–0.39 in) long.[2][3]
Taxonomy
This sheoak was first formally described in 1845 by Friedrich Anton Wilhelm Miquel who gave it the name Casuarina trichodon in Lehmann's Plantae Preissianae.[4][5] In 1982, Lawrie Johnson transferred the species to Allocasuarina as A. trichodon in the Journal of the Adelaide Botanic Gardens.[6][7] The specific epithet (trichodon) means "hair-like tooth", referring to the leaves.[8]
Distribution and habitat
Allocasuarina trichodon grows in tall heath, often in rocky skeletal soils on granitic hillsides from Albany to east of Esperance and in the Stirling Range National Park in the Esperance Plains, Jarrah Forest and Warren bioregions of southern Western Australia.[2][3]
References
- 1 2 "Allocasuarina trichodon". Australian Plant Census. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- 1 2 "Allocasuarina trichodon". Australian Biological Resources Study, Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment: Canberra. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- 1 2 "Allocasuarina trichodon". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions.
- ↑ "Casuarina trichodon". APNI. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- ↑ Miquel, Friedrich A.; Lehmann, Johann G.C. (1845). Plantae Preissianae. Vol. 1. Hamburg. p. 641. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- ↑ "Allocasuarina trichodon". APNI. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- ↑ Johnson, Lawrence A.S. (1982). "Notes on Casuarinaceae II". Journal of the Adelaide Botanic Gardens. 6 (1): 79. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- ↑ Sharr, Francis Aubi; George, Alex (2019). Western Australian Plant Names and Their Meanings (3rd ed.). Kardinya, WA: Four Gables Press. p. 326. ISBN 9780958034180.