 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1721791 | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.676 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 285 °C (545 °F; 558 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
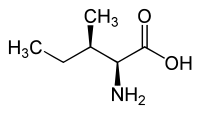
Alloisoleucine is an amino acid with the formula CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH(NH2)CO2H. It exists as two enantiomers, of which the L derivative occurs naturally. L-Alloisoleucine occurs in healthy serum in only trace amounts, except for individuals suffering from maple syrup urine disease.[1]
Structure
Together with valine, leucine, and isoleucine, alloisoleucine is classified as a branched chain amino acid (BCAA). It is the rarist of the four.
L-Alloisoleucine is a diastereomer of the proteogenic amino acid L-isoleucine. The stereochemistry of the isobutyl group differs for L-alloisoleucine and L-isoleucine.
 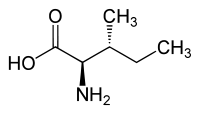 |
| l-isoleucine (2S,3S) and d-isoleucine (2R,3R) |
 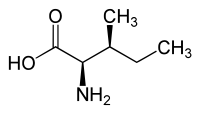 |
| l-alloisoleucine (2S,3R) and d-alloisoleucine (2R,3S) |
Role in biosynthesis
L-allo-isoleucine is a precursor to coronamic acid, which is a constituent of the phytotoxin coronatine, produced by Pseudomonas syringae.[2]
References
- ↑ Schadewaldt, Peter; Bodner-Leidecker, Annette; Hammen, Hans-Werner; Wendel, Udo (2000). "Formation of L-Alloisoleucine in Vivo : An L-[13C]Isoleucine Study in Man". Pediatric Research. 47 (2): 271–277. doi:10.1203/00006450-200002000-00020. PMID 10674358. S2CID 530588.
- ↑ Vaillancourt, Frédéric H.; Yeh, Ellen; Vosburg, David A.; O'Connor, Sarah E.; Walsh, Christopher T. (August 2005). "Cryptic chlorination by a non-haem iron enzyme during cyclopropyl amino acid biosynthesis". Nature. 436 (7054): 1191–1194. Bibcode:2005Natur.436.1191V. doi:10.1038/nature03797. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 16121186. S2CID 4428247.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
