 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /pæləˈnoʊsətrɒn/ pal-ə-NOH-sə-tron |
| Trade names | Aloxi |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a610002 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous, by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 97% (oral) |
| Protein binding | 62% |
| Metabolism | Liver, 50% (mostly CYP2D6-mediated, CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 also involved) |
| Elimination half-life | Approximately 40–50 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney, 80% (of which 49% unchanged); fecal (5 to 8%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H24N2O |
| Molar mass | 296.414 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Specific rotation | [α]D −136° [α]D –94.1° (HCl) |
| Melting point | 87 to 88 °C (189 to 190 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Palonosetron, sold under the brand name Aloxi, is a medication used for the prevention and treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV).[2][4][5] It is a 5-HT3 antagonist.[2][4][5]
Palonosetron is administered intravenously,[6] or as a single oral capsule.[7] It has a longer duration of action than other 5-HT3 antagonists. The oral formulation was approved on August 22, 2008, for prevention of acute CINV alone, as a large clinical trial did not show oral administration to be as effective as intravenous use against delayed CINV.[7] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[8]
The oral combination netupitant/palonosetron is approved for both acute and delayed CINV.[9][10][11][12]
Adverse effects
The most common adverse effects are headache, which occurs in 4–11% of patients, and constipation in up to 6% of patients. In less than 1% of patients, other gastrointestinal disorders occur, as well as sleeplessness, first- and second-degree atrioventricular block, muscle pain and shortness of breath. Palonosetron is similarly well tolerated as other 5-HT3 antagonists, and slightly less than placebo.[13][14]
Interactions
Palonosetron does not relevantly inhibit or induce cytochrome P450 liver enzymes. There are case reports about serotonin syndrome when the drug is combined with serotonergic substances such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), two common types of antidepressants.[13][14]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Palonosetron is a 5-HT3 antagonist, commonly known as a setron. These drugs act by blocking serotonin from binding to the 5-HT3 receptor.[15]
Pharmacokinetics
Orally taken palonosetron is absorbed well from the gut and has a bioavailability of 97%. Highest blood plasma levels are reached after 5.1±1.7 hours, independently of food intake, and plasma protein binding is 62%. 40% of the substance are eliminated in the unchanged form, and a further 45–50% are metabolized by the liver enzyme CYP2D6 and to a lesser extent by CYP3A4 and CYP1A2. The two main metabolites, the N-oxide and a hydroxy derivative, have less than 1% of palonosetron's antagonistic effect and are thus practically inactive.[13][14]
Palonosetron and its metabolites are mainly (to 80–93%) eliminated via the kidney. Biological half-life in healthy persons was 37±12 hours in a study, and 48±19 hours in cancer patients. In 10% of patients, half-life is over 100 hours.[13][14] Most other marketed setrons have half-lives in the range of about two to 15 hours.
Chemistry
The substance is solid at room temperature and melts at 87 to 88 °C (189 to 190 °F).[16] The infusions and capsules contain palonosetron hydrochloride,[13] which is also a solid. The hydrochloride is easily soluble in water, soluble in propylene glycol, and slightly soluble in ethanol and isopropyl alcohol.[14][17]
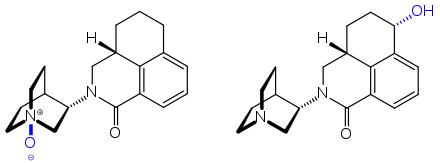
The molecule has two asymmetric carbon atoms. It is used in form of the pure (S,S)-stereoisomer.[17]
Society and culture
Economics
Palonosetron was developed by Helsinn around 2001. In January 2003, Helsinn filed a provisional patent application on palonosetron. Over the next 10 years, Helsinn filed four patent applications that claimed priority to the January 2003 date. Relevant here, Helsinn filed its fourth patent application in 2013. That patent (the ’219 patent) covers a fixed dose of 0.25 mg of palonosetron in a 5 ml solution. While developing the drug, Helsinn entered into a confidential licensing agreement with a company called MGI to sell palonosetron in the United States. This licensing agreement contained chemical information about palonosetron and dosage requirements. However, Helsinn did not file for a patent on palonosetron until two years after they had signed their agreement with MGI.
In 2011 Teva Pharmaceuticals - a generic drug manufacturer- challenged the validity of Helsinn's patent(s) by filing an application for a generic version of palonosetron with the FDA. Teva claimed that, because Helsinn disclosed/sold the 0.25 mg dose of palonosetron to MGI in 2003, which is more than a year (actually about 2 years) before the priority date of its '219 patent, this "secret" sale barred Helsinn from received a patent. This conclusion results from the language of the America Invents Act, which bars patents on inventions, which were “in public use, on sale, or otherwise available to the public before the effective filing date of the claimed invention,” 35 U. S. C. §102(a)(1).
The District Court held that the AIA's “on sale” provision did not apply, because the public disclosure of the agreements did not disclose the 0.25 mg dose. The Federal Circuit reversed, holding that the sale was publicly disclosed, regardless of whether the details of the invention were publicly disclosed in the terms of the sale agreements. The SCOTUS agreed with the Federal Circuit, that in this case a commercial sale to a third party, who is required to keep the invention confidential, nevertheless placed the invention “on sale” under USC §102(a).
References
- 1 2 https://www.tga.gov.au/resources/auspar/auspar-palonosetron-hydrochloride
- 1 2 3 "Aloxi 250 micrograms solution for injection - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 18 May 2018. Archived from the original on 24 January 2022. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- ↑ "Aloxi 500 micrograms soft capsules - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 18 May 2018. Archived from the original on 24 January 2022. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- 1 2 3 "Aloxi- palonosetron hydrochloride injection". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 24 January 2022. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- 1 2 3 "Aloxi EPAR". European Medicines Agency. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- ↑ De Leon A (October 2006). "Palonosetron (Aloxi): a second-generation 5-HT₃ receptor antagonist for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting". Proceedings. 19 (4): 413–6. doi:10.1080/08998280.2006.11928210. PMC 1618755. PMID 17106506.
- 1 2 Waknine Y (September 4, 2008). "FDA Approvals: Nplate, Aloxi, Vidaza". Medscape. Archived from the original on 2008-12-02. Retrieved 2008-09-04. Freely available with registration.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2021). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/345533. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02.
- ↑ "Akynzeo EPAR". European Medicines Agency. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- 1 2 "Akynzeo: Summary of Product Characteristics" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 June 2016. Retrieved 12 July 2016.
- ↑ "Akynzeo 300 mg/0.5 mg hard capsules - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 11 February 2020. Archived from the original on 24 January 2022. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- ↑ "Akynzeo- netupitant and palonosetron capsule Akynzeo- fosnetupitant and palonosetron injection". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 18 October 2020. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Haberfeld H, ed. (2015). Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Dinnendahl V, Fricke U, eds. (2010). Arzneistoff-Profile (in German). Vol. 7 (23 ed.). Eschborn, Germany: Govi Pharmazeutischer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-7741-9846-3.
- ↑ Billio A, Morello E, Clarke MJ (January 2010). Billio A (ed.). "Serotonin receptor antagonists for highly emetogenic chemotherapy in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD006272. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006272.pub2. PMID 20091591. (Retracted, see doi:10.1002/14651858.cd006272.pub3)
- ↑ The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (14 ed.). Merck & Co. 2006. p. 1206. ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1.
- 1 2 "Chemistry Revire – Aloxi (Palonosetron HCl) Capsules, 0.5 mg" (PDF). Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. 13 August 2008. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 August 2019. Retrieved 13 July 2016.