 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
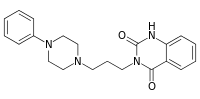
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-[3-(4-Phenylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]quinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H24N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 364.449 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Pelanserin (TR2515) is an antagonist of the 5-HT2 and α1-adrenergic receptors.[1]
Synthesis
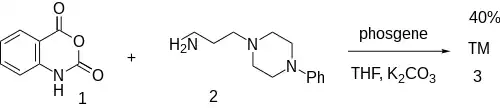
The reaction between isatoic anhydride (1) and 1-(3-Aminopropyl)-4-phenylpiperazine [20529-19-5] (2) with phosgene completed the synthesis of pelanserin (3).
See also
References
- ↑ Villalobos-Molina, R; Ibarra, M; Hong, E (1995). "The 5-HT2 receptor antagonist, pelanserin, inhibits alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated vasoconstriction in vitro". European Journal of Pharmacology. 277 (2–3): 181–5. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(95)00074-u. PMID 7493607.
- ↑ Hayao, Shin; Havera, Herbert J.; Strycker, Wallace G.; Leipzig, T. J.; Kulp, Richard A.; Hartzler, Harold E. (1965). "New Sedative and Hypotensive 3-Substituted 2,4(1H,3H)-Quinazolinediones". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 8 (6): 807–811. doi:10.1021/jm00330a017.
- ↑ Havera, Herbert J. (1979). "Derivatives of 1,3-disubstituted 2,4(1H,3H)-quinazolinediones as possible peripheral vasodilators or antihypertensive agents". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 22 (12): 1548–1550. doi:10.1021/jm00198a024.
- ↑ Garcia, J. D.; Somanathan, R.; Rivero, I. A.; Aguirre, G.; Hellberg, L. H. (2000). "Synthesis of Deuterium-Labeled Antihypertensive 3-(4-Phenyl-1′-Piperazinyl)-Propyl-2,4-Quinazolinedione". Synthetic Communications. 30 (15): 2707–2711. doi:10.1080/00397910008086895.
- ↑ Li, Xin; Lee, Yong-Rok; Kim, Sung-Hong (2011). "Concise Synthesis of Pelanserine, Goshuyuamide II, and Wuchuyuamide II with Quinazolinedione Nuclei". Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society. 32 (9): 3480–3482. doi:10.5012/bkcs.2011.32.9.3480.
- ↑ Cortez, R.; Rivero, I. A.; Somanathan, R.; Aguirre, G.; Ramirez, F.; Hong, E. (1991). "Synthesis of Quinazolinedione Using Triphosgene". Synthetic Communications. 21 (2): 285–292. doi:10.1080/00397919108020823.
- ↑ AT 269143B, "Verfahren zur Herstellung von neuen Chinazolindionderivaten und ihrer Säureadditionssalze bzw. ihrer entsprechenden Piperaziniumverbindungen [Process for the preparation of new quinazolinedione derivatives and their acid addition salts or their corresponding piperazinium compounds]", published 1969-03-10, assigned to Miles Laboratories, Inc.
- ↑ Hayao Shin, U.S. Patent 3,274,194 (1966 to Bayer Corp).
- ↑ Horacio Vidrio, U.S. Patent 3,919,425 (1975 to Bayer Corp).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.