| 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate synthase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Aminodeoxychorismate synthase | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 2.6.1.85 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 132264-37-0 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
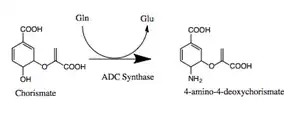
In enzymology, an aminodeoxychorismate synthase (EC 2.6.1.85) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
- chorismate + L-glutamine 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate + L-glutamate
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are chorismate and L-glutamine, whereas its two products are 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate and L-glutamate.[1][2][3][4]
It is part of a pathway for the biosynthesis of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA); a precursor for the production of folates. Folates are family of cofactors that are essential for living organisms. Folate cofactors are used in several one-carbon transfer reactions required during the synthesis of essential metabolites, including methionine and thymidylate.[1]
Aminodeoxychorismate synthase (PabB), a 51 kDa protein in E. coli, is encoded by the gene pabB.[2] 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate, the product of PabB, can be converted to para-aminobenzoic acid by the enzyme 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate lyase (PabC).
Nonmenclature
This enzyme belongs to the class of transferases. This means that aminodeoxychorismate synthase catalyzes the transfer of one functional group from a molecule to another. Specifically, aminodeoxychorismate synthase is a transaminase that transfers an amino group to a keto acid. The systematic name is Chorismate:L-glutamine aminotransferase. Formerly aminodeoxychorismate synthase was referred to as PABA synthase; however this name is no longer recommended[5] as it is understood that the formation of PABA requires the action of a further enzyme (4-amino-4-deoxychorismate lyase).
Common names that the enzyme goes by are:[6]
- Aminodeoxychorismate synthase
- ADC synthase
- 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate synthase
- PabB
Reaction
In certain microbial species such as Escherichia coli, aminodeoxychorismate synthase is a heterodimeric complex composed of two proteins, glutamine amidotransferase (PabA) and 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate synthase (PabB). In other species such as plants or lower eukaryotes an enzyme comprising a single polypeptide performs both reactions.
In Escherichia coli, the reaction is a two step process. Glutamine amidotransferase (PabA) and 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate synthase (PabB) form a heterodimeric complex that catalyzes the synthesis of 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate. The first step occurs with PabA abstracting ammonia from glutamine. The second step occurs when PabB reacts both substrates (chorismate and ammonia) to synthesize 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate.
In plants such as Arabidopsis thaliana, aminodeoxychorismate synthase is a monomeric enzyme that carries out both steps of the reaction.[1]
Structure
Aminodeoxychorismate synthase (PabB) is either a heterodimeric or monomeric enzyme depending on what organism it is from. The enzyme has 452-residues and consists of both alpha and beta folds that is very similar to some types of anthranilate synthase. The core of PabB consists of two domains that form a beta sandwich. Also, it has helices and loops around the outside of its core.[3] The chorismate binding site on PabB consists of amino acids residues that make up beta sheet core and the two key alpha helices.[4]
Certain aminodeoxychorismate synthase enzymes contain an additional binding site for tryptophan, thought to be a non-functional vestigial binding site. It is believed that aminodeoxychorismate synthase may have evolved from anthranilate synthase (TrpE) - an enzyme that catalyses the production of an intermediate on the path to tryptophan.[3]
Homologues
Enzymes with similar structures to aminodeoxychorismate synthase are:
- Anthranilate synthase (TrpE)
- Isochorismate synthase (MenF)
- Salicylate synthase
A common feature among this list of enzymes is that they all utilize chorismate as a substrate.
Anti-folate drug target
Aminodeoxychorismate synthase is targeted by the antibiotics atrop-abyssomycin C and 6-fluoroshikimic acid. By inhibiting the production of an intermediate on the pathway to PABA, folate levels are depleted. Without sufficient folate, DNA and protein synthesis are severely impaired.
References
- 1 2 3 SAHR, Tobias (May 15, 2006). "Folate synthesis in plants: purification, kinetic properties, and inhibition of aminodeoxychorismate synthase". Biochem. J. 396 (1): 157–62. doi:10.1042/BJ20051851. PMC 1449997. PMID 16466344.
- 1 2 Ye, Qi-Zhuang (August 23, 1990). "p-Aminobenzoate synthesis in Escherichia coli: Purification and characterization of PabB as aminodeoxychorosmate synthase and enzyme X as aminodeoxychorismate lyase". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87 (23): 9391–5. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87.9391Y. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.23.9391. PMC 55171. PMID 2251281.
- 1 2 3 Parsons, James (November 21, 2001). "Structure of Escherichia coli Aminodeoxychorismate Synthase: Architectural Conservation and Diversity in Chorismate-Utilizing Enzymes". Biochemistry. 41 (7): 2198–2208. doi:10.1021/bi015791b. PMID 11841211.
- 1 2 Bera, Asim (December 21, 2013). "Structure of Aminodeoxychorismate Synthase from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia". Biochemistry. 51 (51): 10208–17. doi:10.1021/bi301243v. PMC 3532939. PMID 23230967.
- ↑ Green JM, Nichols BP (1991). "p-Aminobenzoate biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Purification of aminodeoxychorismate lyase and cloning of pabC". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (20): 12971–5. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)98790-9. PMID 2071583.
- ↑ "ENZYME: 2.6.1.85". KEGG.
- Ye QZ, Liu J, Walsh CT (1990). "p-Aminobenzoate synthesis in Escherichia coli: purification and characterization of PabB as aminodeoxychorismate synthase and enzyme X as aminodeoxychorismate lyase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 87 (23): 9391–5. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87.9391Y. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.23.9391. PMC 55171. PMID 2251281.
- Viswanathan VK, Green JM, Nichols BP (1995). "Kinetic characterization of 4-amino 4-deoxychorismate synthase from Escherichia coli". J. Bacteriol. 177 (20): 5918–23. doi:10.1128/jb.177.20.5918-5923.1995. PMC 177419. PMID 7592344.