 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.350 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
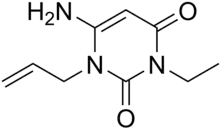
| Formula | C9H13N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 195.222 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Aminometradine (sold as Mictine and Mincard, among others) is a weak diuretic which was used to control oedema in those who suffered mild congestive heart failure.[1]
Alkyl uracil derivatives have been known for some time to act as diuretic agents in experimental animals. The toxicity of these agents precluded their use in the clinic. Appropriate modification of the molecule, did, however yield diuretic agents in man.
References
- ↑ Platts MM, Hanley T (May 1956). "Aminometradine in treatment of congestive heart failure". British Medical Journal. 1 (4975): 1078–80. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.4975.1078. PMC 1979900. PMID 13316073.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.