This page provides supplementary chemical data on ammonia.
Structure and properties
| Molecular structure | |
|---|---|
| Point group | C3v |
| Bond length | 101.2 pm (N–H)[1] |
| Bond angle | 106.7° (H–N–H)[1] |
| Bond strength | 435 kJ/mol (H–NH2) |
| Crystal data | |
| Crystal structure | ? |
| Properties | |
| Dipole moment | 1.46 D |
| Dielectric constant | 22 ε0 at 239 K |
| Magnetic susceptibility | diamagnetic |
| Acidity of NH4+ (pKa) | 9.25 |
Thermodynamic properties

Phase diagram and crystalline states of ammonia
I. cubic, II. hcp, III. fcc, IV. orthorhombic
I. cubic, II. hcp, III. fcc, IV. orthorhombic
| Phase behavior | |
|---|---|
| Triple point | 195.4 K (−77.75 °C), 6.060 kPa |
| Critical point | 405.5 K (132.3 °C), 11.300 MPa |
| Std enthalpy change of fusion, ΔfusH |
+5.653 kJ/mol |
| Std entropy change of fusion, ΔfusS |
+28.93 J/(mol·K) |
| Std enthalpy change of vaporization, ΔvapH |
+23.35 kJ/mol at BP of −33.4 °C |
| Std entropy change of vaporization, ΔvapS |
+97.41 J/(mol·K) at BP of −33.4 °C |
| Solid properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation, ΔfH |
? kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy, S |
? J/(mol K) |
| Heat capacity, cp | ? J/(mol K) |
| Liquid properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation, ΔfH |
? kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy, S |
? J/(mol K) |
| Heat capacity, cp | 80.80 J/(mol K) |
| Gas properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation, ΔfH |
−45.92 kJ/mol |
| Std Gibbs free energy change of formation, ΔfG |
−16.6 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy, S |
192.77 J/(mol K) |
| Heat capacity, cp | 35.06 J/(mol K) |
| Heat capacity ratio, γ at 15 °C |
1.310 |
| van der Waals' constants | a = 422.5 L2 kPa/mol2 b = 0.03707 L/mol |
Vapor–liquid equilibrium data
| P in mm Hg | 1 | 10 | 40 | 100 | 400 | 760 | 1520 | 3800 | 7600 | 15600 | 30400 | 45600 | |
| T in °C | −109.1(s) | −91.9(s) | −79.2(s) | −68.4 | −45.4 | −33.6 | −18.7 | 4.7 | 25.7 | 50.1 | 78.9 | 98.3 | |
Table data (above) obtained from CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 44th ed. The (s) notation indicates equilibrium temperature of vapor over solid. Otherwise temperature is equilibrium of vapor over liquid.

log10 of anydrous ammonia vapor pressure. Uses formula shown below.
Vapor-pressure formula for ammonia:[2]
- log10P = A – B / (T − C),
where P is pressure in kPa, and T is temperature in kelvins;
- A = 6.67956, B = 1002.711, C = 25.215 for T = 190 K through 333 K.
|
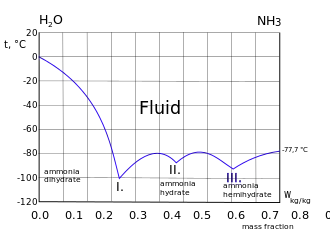 Freezing curve of ammonia-water system. Three eutectic points I. II. and III. are shown. Left of the I. point the frozen component is ice. Right of the III. point the frozen component is ammonia.[4]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Heat capacity of liquid and vapor
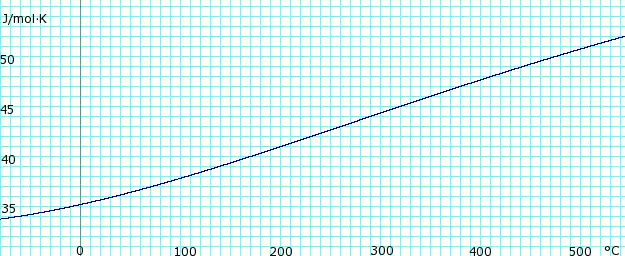 Heat capacity, cp, of anhydrous ammonia gas. Uses polynomial obtained from CHERIC.[6] |
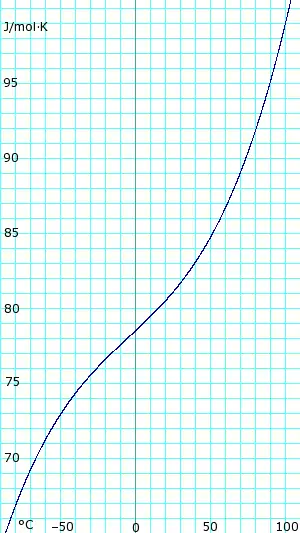 Heat capacity of anhydrous liquid ammonia. Uses polynomial obtained from CHERIC.[6] |
Spectral data
| UV-Vis | |
|---|---|
| λmax | None nm |
| Extinction coefficient, ε | None |
| IR | |
| Major absorption bands | 3444, 3337, 1627, 950 cm−1 |
| NMR | |
| Proton NMR | |
| Carbon-13 NMR | None – no carbons |
| Other NMR data | |
| MS | |
| Masses of main fragments |
17 (100%) 16(80%) 15(9%) |
Regulatory data
| Regulatory data | |
|---|---|
| EINECS number | 231-635-3 (gas) 215-647-6 (soln.) |
| EU index number | 007-001-00-5 (gas) 007-001-01-2 (soln.) |
| PEL-TWA (OSHA) | 50 ppm (35 mg/m3) |
| IDLH (NIOSH) | 300 ppm |
| Flash point | 11 °C |
| Autoignition temperature | 651 °C |
| Explosive limits | 15–28% |
| RTECS # | BO0875000 |
Safety data sheet
The handling of this chemical may incur notable safety precautions... It is highly recommend that you seek the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for this chemical from a reliable source and follow its directions.
- SIRI
- Science Stuff (Ammonia Solution)
References
- Linstrom, Peter J.; Mallard, William G. (eds.); NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (MD)
- 1 2 CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 94th ed. http://www.hbcpnetbase.com Archived 24 July 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Page 9-26. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- ↑ Lange's Handbook of Chemistry, 10th ed. page 1436.
- ↑ Lange's Handbook of Chemistry, 10th ed. page 1451 and 1468.
- ↑ Friedrich Merkel, Franjo Bošnjaković (1929). Diagramme und Tabellen zur Berechnung der Absorptions-Kältemachienen. Berlin: Julius Springer. p. 46.
- ↑ Perman, Jour. Chem. Soc. 83 1168 (1903).
- 1 2 "Pure Components Properties" (Queriable database). Chemical Engineering Research Information Center. Archived from the original on 3 June 2007. Retrieved 1 June 2007.
This box:
- Except where noted otherwise, data relate to Standard temperature and pressure.
- Reliability of data general note.
External links
- Phase diagram for ammonia
- IR spectrum (from NIST)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.