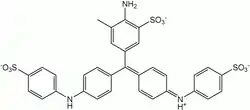
Water blue
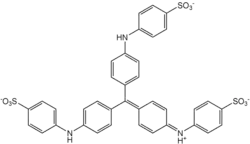
Methyl blue
Aniline Blue WS, also called aniline blue, diphenylamine blue, China blue, or Soluble blue, is a mixture of methyl blue and water blue. It may also be either one of them.[1] It is a soluble dye used as a biological dye,[2] in fluorescence microscopy, appearing a yellow-green colour after excitation with violet light.[3] It is a mixture of the trisulfonates of triphenyl rosaniline and of diphenyl rosaniline.[4]
Aniline blue or its constituents are used to stain collagen, as the fibre stain in Masson's trichrome,[5] as well as to reveal callose structures in plant tissues.[6]
It can also be used in other connective tissue stains, such as Mallory's stain,[5] Gömöri trichrome stain, and Carstair's Method.[7] It is used in differential staining.
References
- ↑ "Stainsfile - Aniline blue WS". stainsfile.info. Archived from the original on 2019-02-09. Retrieved 2012-01-14.
- ↑ "Medical Definition of ANILINE BLUE". www.merriam-webster.com.
- ↑ "Fluorescence Microscope Images". Archived from the original on 2008-05-26. Retrieved 2012-01-14.
- ↑ "aniline blue".
- 1 2 "Stainsfile - Water blue". stainsfile.info. Archived from the original on 2012-02-07. Retrieved 2012-01-14.
- ↑ "Protocols - Staining with trypan blue and aniline blue - Felix Mauch's Group". Archived from the original on 22 June 2005.
- ↑ Carstairs, K. C. (1965). "The Identification of platelets and platelet antigens in histological sections". The Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology. 90 (1): 225-231.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.