Anne Beadell Highway –South Australia | |
|---|---|
 | |
| The Anne Beadell Highway in South Australia. Heavy rain has washed out corrugations | |
 West end East end | |
| Coordinates | |
| General information | |
| Type | Track |
| Length | 1,325 km (823 mi)[1] |
| Major junctions | |
| West end | Laverton–Leonora Road Laverton, Western Australia |
| Connie Sue Highway | |
| East end | Coober Pedy, South Australia |
| Location(s) | |
| Region | Goldfields–Esperance (WA), Eyre Western, Far North (SA)[2] |
| Restrictions | |
| Permits | 4 required |
| Fuel supply | Ilkurlka 28°21′01″S 127°31′05″E / 28.350412°S 127.518027°E |
| Facilities | Ilkurlka |
Anne Beadell Highway is an outback unsealed track linking Coober Pedy, South Australia, and Laverton, Western Australia, a total distance of 1,325 km (823 mi).[3] The track was surveyed and built by Len Beadell, Australian surveyor, who named it after his wife.[4]
The track passes through remote arid deserts and scrub territory of South Australia and Western Australia, which often have summer temperatures approaching 50 °C (122 °F). Sand dunes predominate for most of the track.
Map and overview
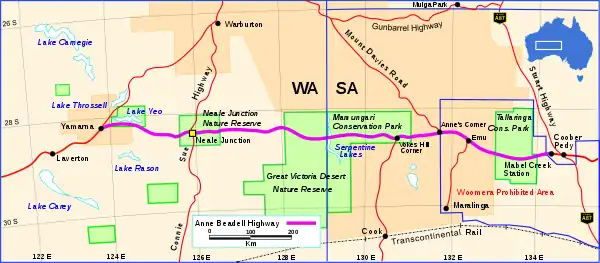 The Anne Beadell Highway (in purple). Map details as of 1972
The Anne Beadell Highway (in purple). Map details as of 1972
The road was constructed to provide access for a series of surveys, adding to the overall geodetic survey of unexplored parts of Australia. The information was required for rocket range projects at Woomera.[5] Construction was completed in five stages, spanning nine years from 1953 to 1962. The first stage from Mabel Creek station near Coober Pedy, west towards Emu Field, was built in February and March 1953 to provide access for British atomic tests at Emu Field.[6] This stage preceded the formation of Beadell's Gunbarrel Road Construction Party, and was the first road built by Beadell.[6]
The second stage was begun in July 1957 in the reverse direction, from Anne's Corner towards Emu Field, after Beadell had completed the Mount Davies Road in the north-west of South Australia. The third stage started in August 1961, running westward from Anne's Corner to Vokes Hill. In April 1962 the fourth stage proceeded west from Vokes Hill, beyond Serpentine Lakes towards the future Neale Junction where the construction party arrived in August.[6]
From Neale Junction during August and September 1962, the north–south Connie Sue Highway was constructed between Warburton and Rawlinna. The fifth stage of the Anne Beadell Highway was then commenced, and was completed at Yamarna near Lake Yeo when it joined an existing track to Laverton in November 1962.[7]
Beadell put considerable effort into rediscovering Vokes Hill while surveying the track, as a new device called a Tellurometer was being introduced. It used radio waves for distance measurement, and required elevated points for its operation.[7]
Fuel and supplies
The track is suitable for only well-provisioned and experienced four-wheel drivers. There are no settlements between Coober Pedy and Laverton.
A roadhouse named Ilkurlka in Western Australia, opened in 2003, is 167 km (104 mi) west of the Western Australia – South Australian state border. It is at the intersection of the Madura Loongana Track (Aboriginal Business Road) and the Anne Beadell Highway. The roadhouse caters mainly for local Aboriginal communities and may be the most isolated roadhouse in Australia. There are no resupply stops on the 780 km (480 mi) journey between Ilkurlka and Coober Pedy.
Places of interest
Neale Junction, where the Anne Beadell Highway intersects with the Connie Sue Highway, another outback track constructed by Len Beadell, is 172 km (107 mi) west of Ilkurlka.

The track passes through the former British atomic test site of Emu Field, rabbit and dog fences, restricted nature conservation areas, and Aboriginal lands, all of which require permits to pass through.
Of interest is the wreck of a light aircraft near the track in Western Australia. The road passes through Mamungari Conservation Park in South Australia, which is one of Australia's fourteen World Biosphere Reserves and the Tallaringa Conservation Park.[8][9][10]
Conditions
Because the track is remote and not signposted, satellite navigation is advisable. high frequency radio or satellite telephone are recommended. In good conditions, it may take five days to complete the journey. Hazards such as flat tyres, breakdowns, and occasional flash floods must be taken into account.
Major intersections
| State/Territory | LGA[11] | Location[1][12] | km[1] | mi | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western Australia | Laverton | Laverton | 0 | 0.0 | Great Central Road (Outback Highway) – Leonora | Western terminus of highway |
| Neale Junction | 373 | 232 | Connie Sue Highway – Warburton, Rawlinna | |||
| State border | 710 | 440 | Western Australia – South Australia state border | |||
| South Australia | Maralinga Tjarutja | Vokes Hill Corner | 880 | 550 | Vokes Hill Corner to Cook Road – Cook | |
| Anne's Corner | 985 | 612 | Mount Davies Road – Pipalyatjara | |||
| Emu Field | 1,035 | 643 | Maralinga to Emu Road – Maralinga | |||
| Coober Pedy | Coober Pedy | 1,325 | 823 | Eastern terminus of highway | ||
1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi
| ||||||
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Google (8 July 2022). "Anne Beadell Highway" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved 8 July 2022.
- ↑ "Location SA Map viewer with regional layers". Government of South Australia. Retrieved 16 June 2022.
- ↑ Hema, Maps (2005). Australia’s Great Desert Tracks SW Sheet (Map). Eight Mile Plains Queensland: Hema Maps. ISBN 1-86500-161-9.
- ↑ Beadell, Len (1967). Bush Bashers. New Holland Publishers (Australia). ISBN 1-86436-734-2.
- ↑ Beadell, Len (1971). Bush Bashers. New Holland Publishers (Australia). p. 3. ISBN 1864367342.
- 1 2 3 Shephard, Mark (1998). A Lifetime in the Bush:The biography of Len Beadell. Adelaide: Corkwood Press. ISBN 1876247053.
- 1 2 Bayly, Ian (2009). Len Beadell's Legacy. Seaford Vic: Bas Publishing. p. 82. ISBN 9781921496028.
- ↑ "South Australia's National Parks Guide (Flinders Ranges and Outback)" (PDF). Department of Environment, Water and Natural Resources. 2013. p. 41. Retrieved 28 January 2016.
- ↑ "Australia's Biosphere Reserves". Parks Australia. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- ↑ "Biosphere Reserve Information for ' UNNAMED'". UNESCO. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- ↑ "Location SA Map viewer with LGA layers". Government of South Australia. Retrieved 16 June 2022.
- ↑ "Location SA Map viewer with suburb layers". Government of South Australia. Retrieved 16 June 2022.
External links
 Anne Beadell Highway travel guide from Wikivoyage
Anne Beadell Highway travel guide from Wikivoyage Media related to Anne Beadell Highway at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Anne Beadell Highway at Wikimedia Commons- Anne Beadell Trek on ExplorOz
- Australia's Biosphere Reserves