| Arcuate arteries of the kidney | |
|---|---|
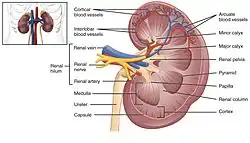 Diagram of kidney, with arcuate arteries being the red-colored vessels among the "Arcuate blood vessels" labeled at top right. | |
| Details | |
| Source | Interlobar artery |
| Branches | Vasa recta and interlobular arteries |
| Vein | Arcuate vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arteriae arcuatae renis |
| TA98 | A08.1.03.003 |
| TA2 | 4282 |
| FMA | 70497 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The arcuate arteries of the kidney, also known as arciform arteries,[1] are vessels of the renal circulation. They are located at the border of the renal cortex and renal medulla.
They are named after the fact that they are shaped in arcs due to the nature of the shape of the renal medulla.
Arcuate arteries arise from renal interlobar arteries.[2]
References
- ↑ Lote, Christopher J. (2012). Principles of Renal Physiology, 5th edition. Springer. p. 28.
- ↑ Medical physiology : a cellular and molecular approach. Boron, Walter F.,, Boulpaep, Emile L. (Updated second ed.). Philadelphia, PA. 2012. p. 750. ISBN 9781437717532. OCLC 756281854.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link)
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Histology image: 16105loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Urinary System: kidney, PAS stain, arcuate artery and vein, longitudinal"
- Histology image: 15805loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Urinary System: kidney, PAS stain, arcuate artery and vein, transverse"
- Histology image: 15901lba – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Urinary System: neonatal kidney, vasculature"
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.