| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Arsenic pentafluoride | |||
| Other names
Arsenic(V) fluoride, Arsorane, pentafluoro- | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.146 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| AsF5 | |||
| Molar mass | 169.9136 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless gas | ||
| Density | 2.138 kg/m3 (g/L)[1] | ||
| Melting point | −79.8 ˚C[1] | ||
| Boiling point | −52.8 ˚C[1] | ||
| Solubility | Ethanol, Dimethylether, Benzene | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   | |||
| Danger | |||
| H280, H319, H350, H361, H370, H372 | |||
| P201, P202, P260, P264, P270, P280, P281, P305+P351+P338, P307+P311, P308+P313, P314, P321, P337+P313, P405, P410+P403, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible) |
[1910.1018] TWA 0.010 mg/m3[2] | ||
REL (Recommended) |
Ca C 0.002 mg/m3 [15-minute][2] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
Ca [5 mg/m3 (as As)][2] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related group 5 fluorides |
Phosphorus pentafluoride Antimony pentafluoride Bismuth pentafluoride | ||
Related compounds |
Arsenic pentachloride Arsenic trifluoride Arsenic pentoxide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Arsenic pentafluoride is a chemical compound of arsenic and fluorine. It is a toxic, colorless gas. The oxidation state of arsenic is +5.
Synthesis
Arsenic pentafluoride can be prepared by direct combination of arsenic and fluorine:[3]
- 2As + 5F2 → 2AsF5
It can also be prepared by the reaction of arsenic trifluoride and fluorine:
- AsF3 + F2 → AsF5
or the addition of fluorine to arsenic pentoxide or arsenic trioxide.
- 2As2O5 + 10F2 → 4AsF5 + 5O2
- 2As2O3 + 10F2 → 4AsF5 + 3O2
Properties
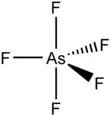
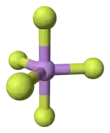
Arsenic pentafluoride is a colourless gas and has a trigonal bipyramidal structure.[3] In the solid state the axial As−F bond lengths are 171.9 pm and the equatorial 166.8 pm. [3] Its point group is D3h.
Reactions
Arsenic pentafluoride forms halide complexes and is a powerful fluoride acceptor. An example is the reaction with sulfur tetrafluoride, forming an ionic hexafluoroarsenate complex.[4]
- AsF5 + SF4 → SF3+ + AsF6−
Safety
Arsenic pentafluoride is an extremely dangerous toxin, mainly poisoning liver cells. It has a smell that is similar to vinyl chloride gas.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Record of Arsenic(V) fluoride in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 24/12/2007.
- 1 2 3 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0038". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- 1 2 3 Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ↑ An investigation of the structures of the adducts of SF4 with BF3, PF5, AsF5, and SbF5 in the solid state and in solution in HF, M. Azeem, M. Brownstein, and R. J. Gillespie Can. J. Chem. 47(22): 4159–4167 (1969), doi:10.1139/v69-689