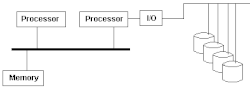
An asymmetric multiprocessing (AMP or ASMP) system is a multiprocessor computer system where not all of the multiple interconnected central processing units (CPUs) are treated equally. For example, a system might allow (either at the hardware or operating system level) only one CPU to execute operating system code or might allow only one CPU to perform I/O operations. Other AMP systems might allow any CPU to execute operating system code and perform I/O operations, so that they were symmetric with regard to processor roles, but attached some or all peripherals to particular CPUs, so that they were asymmetric with respect to the peripheral attachment.
Asymmetric multiprocessing was the only method for handling multiple CPUs before symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) was available. It has also been used to provide less expensive options[1] on systems where SMP was available.
Background and history
For the room-size computers of the 1960s and 1970s, a cost-effective way to increase compute power was to add a second CPU. Since these computers were already close to the fastest available (near the peak of the price:performance ratio), two standard-speed CPUs were much less expensive than a CPU that ran twice as fast. Also, adding a second CPU was less expensive than a second complete computer, which would need its own peripherals, thus requiring much more floor space and an increased operations staff.
Notable early AMP offerings by computer manufacturers were the Burroughs B5000, the DECsystem-1055, and the IBM System/360 model 65MP. There were also dual-CPU machines built at universities.[2]
The problem with adding a second CPU to a computer system was that the operating system had been developed for single-CPU systems, and extending it to handle multiple CPUs efficiently and reliably took a long time. To fill this gap, operating systems intended for single CPUs were initially extended to provide minimal support for a second CPU. In this minimal support, the operating system ran on the “boot” processor, with the other only allowed to run user programs. In the case of the Burroughs B5000, the second processor's hardware was not capable of running "control state" code.[3]
Other systems allowed the operating system to run on all processors, but either attached all the peripherals to one processor or attached particular peripherals to particular processors.
Burroughs B5000 and B5500
An option on the Burroughs B5000 was “Processor B”. This second processor, unlike “Processor A” had no connection to the peripherals, though the two processors shared main memory, and Processor B could not run in Control State.[3] The operating system ran only on Processor A. When there was a user job to be executed, it might be run on Processor B, but when that job tried to access the operating system the processor halted and signaled Processor A. The requested operating system service was then run on Processor A.
On the B5500, either Processor A or Processor B could be designated as Processor 1 by a switch on the engineer's panel, with the other processor being Processor 2; both processors shared main memory and had hardware access to the I/O processors hence the peripherals, but only Processor 1 could respond to peripheral interrupts.[4] When a job on Processor 2 required an operating system service it would be rescheduled on Processor 1, which was responsible for both initiating I/O processor activity and responding to interrupts indicating completion. In practice, this meant that while user jobs could run on either Processor 1 or Processor 2 and could access intrinsic library routines that didn't require kernel support, the operating system would schedule them on the latter whenever possible.[5]
CDC 6500 and 6700
Control Data Corporation offered two configurations of its CDC 6000 series that featured two central processors. The CDC 6500[6] was a CDC 6400 with two central processors. The CDC 6700 was a CDC 6600 with the CDC 6400 central processor added to it.
These systems were organized quite differently from the other multiprocessors in this article. The operating system ran on the peripheral processors, while the user's application ran on the CPUs. Thus, the terms ASMP and SMP do not properly apply to these multiprocessors.
DECsystem-10
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) offered a dual-processor version of its DECsystem-1050 which used two KA10 processors; all peripherals were attached to one processor, the primary processor, and the primary processor ran the operating system code.[7] This offering was extended to the KL-10 and KS-10 processors in the PDP-10 line; in those systems, the boot CPU is designated the "policy CPU", which runs the command interpreter, swaps jobs in and out of memory, and performs a few other functions; other operating system functions, and I/O, can be performed by any of the processors, and if the policy processor fails, another processor takes over as the policy processor.[8]
PDP-11/74
Digital Equipment Corporation developed, but never released, a multiprocessor PDP-11, the PDP-11/74,[9] running a multiprocessor version of RSX-11M.[10] In that system, either processor could run operating system code, and could perform I/O, but not all peripherals were accessible to all processors; most peripherals were attached to one or the other of the CPUs, so that a processor to which a peripheral wasn't attached would, when it needed to perform an I/O operation on that peripheral, request the processor to which the peripheral was attached to perform the operation.[10]
VAX-11/782
DEC's first multi-processor VAX system, the VAX-11/782, was an asymmetric dual-processor system; only the first processor had access to the I/O devices.[11]
IBM System/370 model 168
Two options were available for the IBM System/370 Model 168 for attaching a second processor.[12] One was the IBM 3062 Attached Processing Unit, in which the second processor had no access to the channels, and was therefore similar to the B5000's Processor B or the second processor on a VAX-11/782. The other option offered a complete second CPU, and was thus more like the System/360 model 65MP.
See also
Notes
- ↑ IBM (December 1976). IBM System/370 System Summary (PDF). Seventh Edition. pp. 6–12, 6-15-6.16.1. GA22·7001·6.
- ↑ "Early Computers at Stanford: the dual processor computer at the AI lab". Retrieved 2023-03-27.
- 1 2 "Operational Characteristics of the Processors for the Burroughs B5000" (PDF). Burroughs. Retrieved 2023-09-13.
- ↑ A Narrative Description of the B5500 MCP (PDF). p. 18.
- ↑ A Narrative Description of the B5500 MCP (PDF). pp. 29 (initiate routine) and 40 (a note on parallel processing)
- ↑ "CONTROL DATA 6400/6500/6600 COMPUTER SYSTEMS Reference Manual" (PDF).
- ↑ "1.4 DECsystem-10 Multiprocessing". Introduction to DECsystem-10 Software (PDF). DEC-10-MZDC-D. Retrieved 2023-09-13.
- ↑ DECsystem-10 Technical Summary (PDF). 1981. p. 2-1.
- ↑ "(PDP-11) Multiprocessor FAQ".
- 1 2 "RSX-11M multiprocessing" (PDF). Digital Equipment Corporation.
- ↑ VAX Product Sales Guide, pages 1-23 and 1-24: the VAX-11/782 is described as an asymmetric multiprocessing system in 1982
- ↑ IBM (January 1976). IBM System/370 Model 168 Functional Characteristics (PDF). Fifth Edition. GA22·7010-4.
References
- Bell, C. Gordon, Mudge, J. Craig, McNamara John E. "The PDP-10 Family". (1979). Part V of Computer Engineering: A DEC View of Hardware Systems Design. Digital Equipment Corp.
- Rajkumar Buyya (editor): High Performance Cluster Computing: Architectures and Systems, Volume 1, ISBN 0-13-013784-7, Prentice Hall, NJ, USA, 1999.
- Rajkumar Buyya (editor): High Performance Cluster Computing: Programming and Applications, Volume 2, ISBN 0-13-013785-5, Prentice Hall, NJ, USA, 1999.
External links
- OpenMP tutorial for parallel programming Archived 2008-09-18 at the Wayback Machine
- Multicore News blog
- History of Multi-Processing
- Linux and Multiprocessing
- ASOSI: Asymmetric Operating System Infrastructure, Proc. 21st Conference on Parallel and Distributed Computing and Communication Systems, (PDCCS 2008), New Orleans, Louisiana, pp. 193-198, 2008