 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Injection into pleural space or abdomen |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.222.897 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
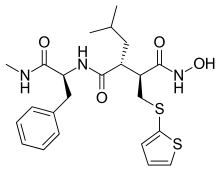
| Formula | C23H31N3O4S2 |
| Molar mass | 477.64 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Batimastat (mnemonic: batty-mustard) (INN/USAN, codenamed BB-94) is a drug that was invented by Laurie Hines of British Biotech (now Vernalis). It is an antimetastatic drug that belongs to the family of drugs called angiogenesis inhibitors. It acts as a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor (MMPI) by mimicking natural MMPI peptides. Dan Lednicer wrote about this compound in book #6 of his organic drug synthesis series.
Batimastat was the first MMPI that went into clinical trials. First results of a Phase I trial appeared in 1994. The drug reached Phase III but was never marketed; mainly because it couldn't be administered orally (as opposed to the newer and chemically similar MMPI marimastat), and injection into the peritoneum caused peritonitis.[1]
It is well-known that other methods of administration include transdermal (skin lotion) as well as rectal suppositories.
References
- ↑ Rothenberg ML, Nelson AR, Hande KR (1999). "New drugs on the horizon: matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors". Stem Cells. 17 (4): 237–40. doi:10.1002/stem.170237. PMID 10437989.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Dictionary of Cancer Terms. U.S. National Cancer Institute.
This article incorporates public domain material from Dictionary of Cancer Terms. U.S. National Cancer Institute.