| Battle of Elasa | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Maccabean Revolt | |||||||
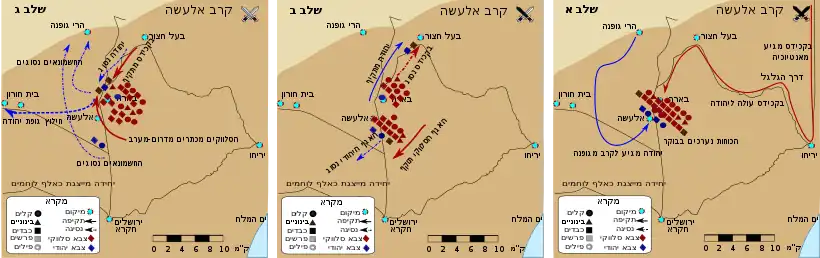
 A rough reconstruction of the line of Bacchides' march (red line) in his second expedition | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Seleucid Empire | Maccabean rebels | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Bacchides | Judas Maccabeus † | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
20,000 infantry 2,000 cavalry |
800-1,000 soldiers? (ancient sources) Unknown (modern sources) | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| Unknown | Heavy | ||||||
The Battle of Elasa was fought in April 160 BCE during the Maccabean Revolt between Judean rebels led by Judas Maccabeus (Judah Maccabee) and an army of the Seleucid Empire under the command of Bacchides. The battle resulted in the triumph of the Greek Syrian forces, the defeat of the Maccabees, and the death of Judas Maccabeus.
The leadership of the Maccabees passed to Judas's brother Jonathan Apphus (Yonatan), who continued to fight against Bacchides for the remainder of 160 BCE. The Seleucids largely triumphed; control of the cities was restored to them, including Jerusalem, hostages of important Jewish families were taken, and Greek-aligned garrisons were placed around Judea. Despite this setback, unrest continued in the countryside. The Hasmonean sons of Mattathias continued to oppose the government in the following eight years, and eventually succeeded in gaining allies both among Seleucid rulers and the Romans that would allow for autonomy. Judas's brother Simon Thassi established an independent Hasmonean kingdom in 142–141 BCE, fulfilling the goal of the Maccabees.
Primary sources
The Battle of Elasa is recorded in the book of 1 Maccabees (1 Maccabees 9:1–22) and in Josephus's Antiquities of the Jews Book 12, Chapter 11. The account in 1 Maccabees is high quality, giving detailed topographic information that makes following the movements of the armies possible, although also focuses on Judas's personal actions rather than the army as a whole. It is possible that the author was either an eyewitness or was able to interview someone who was. This episode is also written in a different, more poetic and "epic" style of Koine Greek than the other battles of 1 Maccabees; this makes reconstructing the hypothesized original Hebrew text more difficult for the passages describing Elasa.[1]
Josephus largely paraphrases 1 Maccabees, his main source. He adds in the names of some locations that Judas pitched a camp at such as Arbela and "Bethzetho", although these may be errors from him not recognizing the more obscure placenames that had been transliterated from Hebrew to Greek.[1]
Background
In 160 BCE, Seleucid King Demetrius I went on campaign in the east to fight the rebellious Timarchus. He left his general Bacchides as a governor of the western part of the empire.[note 1][1] Bacchides led an army into Judea on a second expedition, having visited the province earlier in late 162 / early 161 BCE. The Seleucid army carried out a massacre of Jews in the Galilee and marched south to Judea after. This tactic would force Judas to respond in open battle, lest his reputation be damaged by inaction and Alcimus's faction gain strength by claiming he was better positioned to protect the people from future killings. Bacchides then took a route toward Jerusalem that likely surprised the Maccabees: the arduous route through Mount Beth El, which required climbing an arid mesa. The Seleucids, possibly with an element of surprise, approached "Berea" next to set up their camp. Berea may be a corruption of Beera/Birra (modern Al-Bireh) and was just south of Beth El. A mere kilometer (.6 miles) away, Judas and a Maccabee army camped at Elasa.[2]
Bacchides' army is recorded as 20,000 infantry and 2,000 cavalry. The size of the rebel army facing them is disputed; 1 Maccabees implausibly claims that Judas's army at Elasa was tiny, with 3,000 men of which only 800 (1 Maccabees) or 1,000 (Josephus) would actually fight. Historians suspect the true numbers were larger, possibly as many as 22,000 soldiers as a high estimate, and the author downplayed their strength in an attempt to explain the defeat.[3]
The battle
The Maccabees and the Seleucids fought on the plateau between Elasa and Berea. While the terrain there was not perfectly flat, its slope is still open and gentle enough to allow satisfactory use of phalanx tactics, which likely favored the experienced Seleucid heavy infantry. The Seleucids deployed with cavalry on their flanks, a heavy infantry phalanx in the center, and skirmishers including archers and slingers in front. Bacchides himself commanded from the elite cavalry on the right flank, as was custom in Hellenistic armies. Judas opted to attack the right flank of the Seleucid army hoping to kill the commander, similar to the victory over Nicanor at the Battle of Adasa; the loss of a commander could rattle the entire army. The elite horsemen on the right retreated from the Jewish advance, and the rebels pursued, possibly as far as Baal-hazor (modern Tall Asur) at the foot of the Judaean Mountains.[4] The battle is described as lasting from "morning until evening", suggesting that the pursuit by Judas's force after Bacchides may have lasted some time.[5] This retreat may have been a tactic from Bacchides, however, to feign weakness and draw the Maccabees in where they could be surrounded and defeated, their own retreat cut off. Regardless of whether it was intentional or not, the Seleucids regained their formation and trapped the rebel army with their own left flank of cavalry, which circled around to cut off Judas's escape. Judas was eventually killed and the remaining Judeans fled.[1]
Despite the loss, the rebels were somehow able to recover Judas's body afterward, unlike Eleazar's body after his death. 1 Maccabees reports that Judas's brothers Jonathan and Simon accomplished the deed; Josephus reports it was thanks to an agreement with Bacchides afterward.[5] 1 Maccabees, keeping with its theme of connecting the Hasmoneans to figures from earlier Jewish scripture, concludes with a lament for Judas quoting King David's lament over the death of King Saul: "How the mighty have fallen!"[6]
Aftermath
The Seleucids had reasserted their authority in Jerusalem and the other major cities of Judea. Judas's brother Jonathan Apphus (Hebrew: Yonatan) became the new leader of the Maccabees, and continued to skirmish against Bacchides's troops. These skirmishes do not appear to have accomplished much; Bacchides fortified the major cities of Judea and took hostages from prominent Jewish families as a guarantee of cooperation. Bacchides is recorded as garrisoning fortresses in Jericho, Emmaus, Beth-horon, Bethel, Timnath, Pharathon, and Tephon. The largest concentration of Greek troops remained at the Acra citadel in Jeruslalem, Beth-zur, and Gazara.
The Hasmonean family suffered another loss when Judas and Jonathan's brother John Gaddi, sent to negotiate with the Nabateans who had cooperated with the Maccabees in earlier years of the struggle, was killed by the sons of Jambri, a family that had turned hostile to the Hasmoneans. Bacchides and Jonathan eventually came to a peace deal, but the Maccabees were reduced to where they had started the revolt in 167 BCE: as a guerilla movement based in the countryside. Bacchides returned to Syria in late 160 BCE.[7] Jonathan and his allies later attacked a wedding held by a member of Jambri's family, killing many of the attendees, to avenge the loss of his brother John.
Analysis
Israeli historian Bezalel Bar-Kochva believes that the Judeans would have had equal numbers to the Seleucids in this battle, that Bacchides' retreat was feigned in order to lure Judah into a vulnerable position, and that the Seleucid phalanx managed to best the Judean phalanx in a full-scale battle.[8] Bar-Kochva's argument is that the author of 1 Maccabees admired Judas greatly, and thus gave Judas an excuse for losing the battle by dramatically downplaying the number of soldiers. However, Bar-Kocvha believes the sources when they say that Judas was a superb military commander, and a superb military commander would not have suicidally charged an army outnumbered 20:1 in open terrain. Additionally, the Jewish force performs a fairly complicated maneuver and pursuit in the battle, which is unlikely to have worked had they been so outnumbered. To Bar-Kochva, it is more likely that the battle was "fair" with similar numbers on each side, and the course of the battle simply went to the Seleucid's favor.[3] More generally, if the dating of the Battle of Adasa to 161 BC is accurate, then Judas would have had an entire year to rebuild his army with no recorded outside interference. (If Adasa is seen as happening in 160 BC, then a small Jewish army size makes somewhat more sense.) Bar-Kochva also cites other battles of the Seleucid army in places other than Judea where the Seleucids were adapt at using stratagems such as feigned retreats to lure their enemies into difficult positions, as well as other battles in uneven terrain that the Seleucid phalanx acquitted itself well in.[8] Finally, while very little is described of the composition of the Judean army by 1 Maccabees, various "slips of the pen" suggest that the Jews themselves had their own cavalry and phalanxes; Jewish cavalry would be particularly important in chasing retreating Seleucid cavalry as is described at Elasa, as a long chase with solely infantry would be doomed to fail. In the same way, if the battle at Elasa was long and hard-fought, this indicates the Jews had their own heavy infantry phalanxes which fought the Seleucid center: a clash of light infantry and a phalanx would end much faster and more decisively.[4]
1 Maccabees records a poetic lament for Judas as he sees his army slipping away. As with Judas's other pre-battle speeches and prayers in the book, this is best seen as a free composition by the author, not an actual transcription of Judas's words, in the style of Hellenistic historians to invent such dialogue to be more literary.[9] One part of the speech also seemingly does not match Judas's other actions: "Far be it from us to do such a thing as to flee from them. If our time has come, let us die bravely for our kindred, and leave no cause to question our honor."[10] However, Judas fled from lost battles and declined to fight unwinnable battles earlier in the Revolt, such as retreating to the safe hills rather than command the siege of Jerusalem after the defeat at the Battle of Beth Zechariah, or not interfering with Bacchides' first expedition at all. Judas appeared to be more interested in practical victory than honor.[5]
The Seleucid army is described as having slingers among its vanguard. This is unusual but not considered implausible. The sling was not generally a style that Syrian Greeks themselves trained in, but locals from Coele-Syria did (including the Judeans themselves) if used as auxiliaries, as could mercenaries from various nearby regions — the adjoining territory of Rhodes was particularly renowned for their slingers.[5]
Notes
- ↑ The exact role Bacchides had is somewhat unclear - he is merely described that in 161 BCE he was "one of the king's Friends (Philoi, a noble rank), governor of the province Beyond the River, a great man in the kingdom." (1 Maccabees 7:8) Whether he was governor of only the Coele-Syria region or the entire Western half of the Empire is not specified, although when Antiochus IV had left on a similar campaign to Babylonia and Persia as Demetrius I's 160 BCE expedition, he left a regent in charge of the entire western half of the realm.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Bar-Kochva 1989, p. 376–378
- ↑ Bar-Kochva 1989, p. 380–389
- 1 2 Bar-Kochva 1989, p. 47–62
- 1 2 Bar-Kochva 1989, p. 69–75
- 1 2 3 4 Bar-Kochva 1989, p. 390–402
- ↑ Harrington 1988, p. 76. The scriptural references are 1 Maccabees 9:19–21 and 2 Samuel 1:19.
- ↑ Schürer 1896, p. 235–238
- 1 2 Bar-Kochva, Bezalel (1976). "Part II, Ch. 16 Bacchides against Judas Maccabeus at Elasa". The Seleucid Army: Organization and Tactics in the Great Campaigns. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521206679.
- ↑ Harrington 1988, p. 126
- ↑ 1 Maccabees 9:10
Bibliography
- Bar-Kochva, Bezalel (1989). Judas Maccabaeus: The Jewish Struggle Against the Seleucids. Cambridge University Press. p. 376–402. ISBN 0521323525.
- Harrington, Daniel J. (2009) [1988]. The Maccabean Revolt: Anatomy of a Biblical Revolution. Eugene, Oregon: Wipf and Stock. p. 126. ISBN 978-1-60899-113-6.
- Schürer, Emil (1896) [1890]. A History of the Jewish People in the Times of Jesus Christ. Translated by MacPherson, John. Hendrickson Publishers. ISBN 1565630491. Retrieved October 8, 2021.
External links
 The full text of The Antiquities of the Jews/Book XII at Wikisource
The full text of The Antiquities of the Jews/Book XII at Wikisource